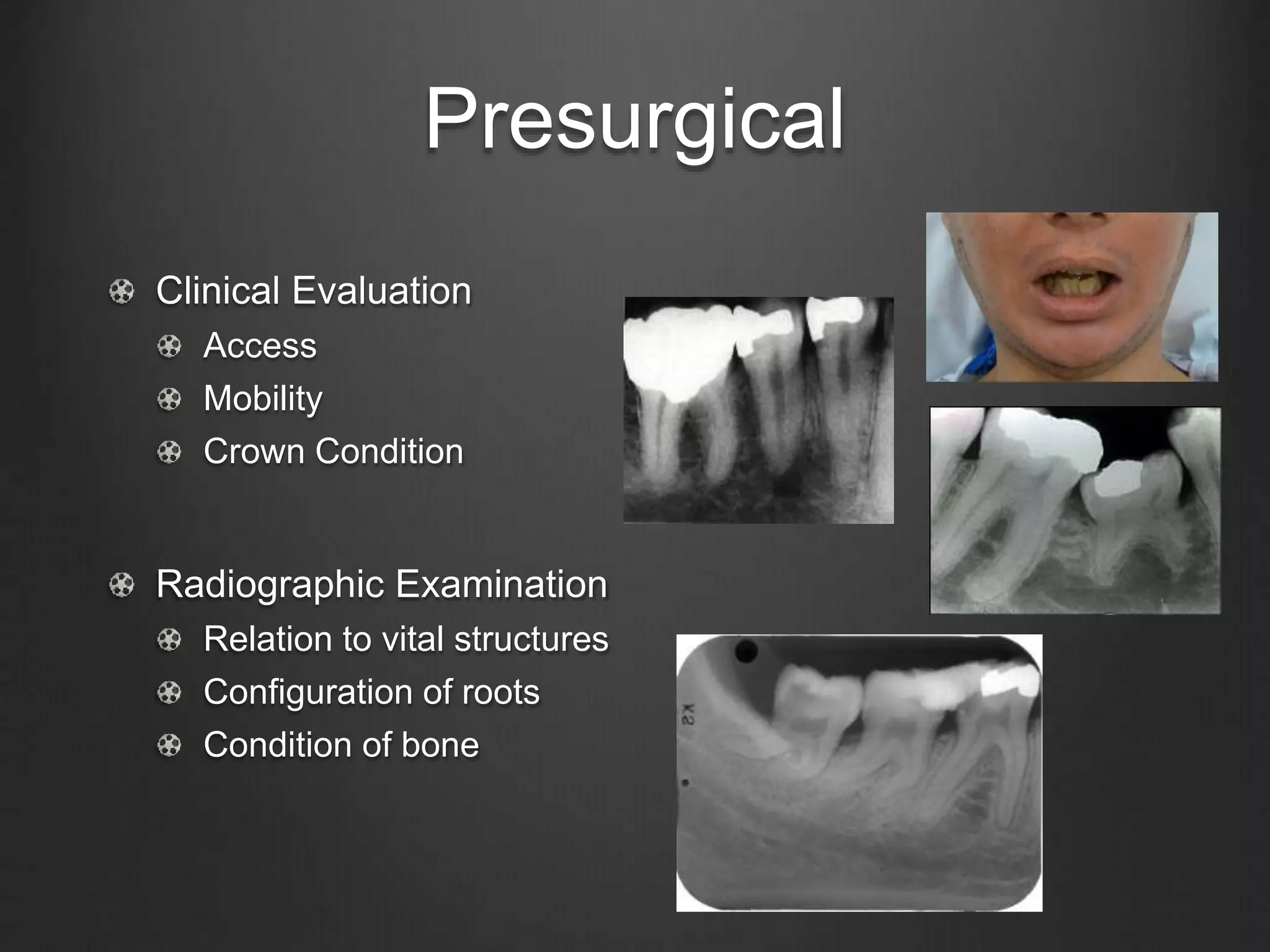
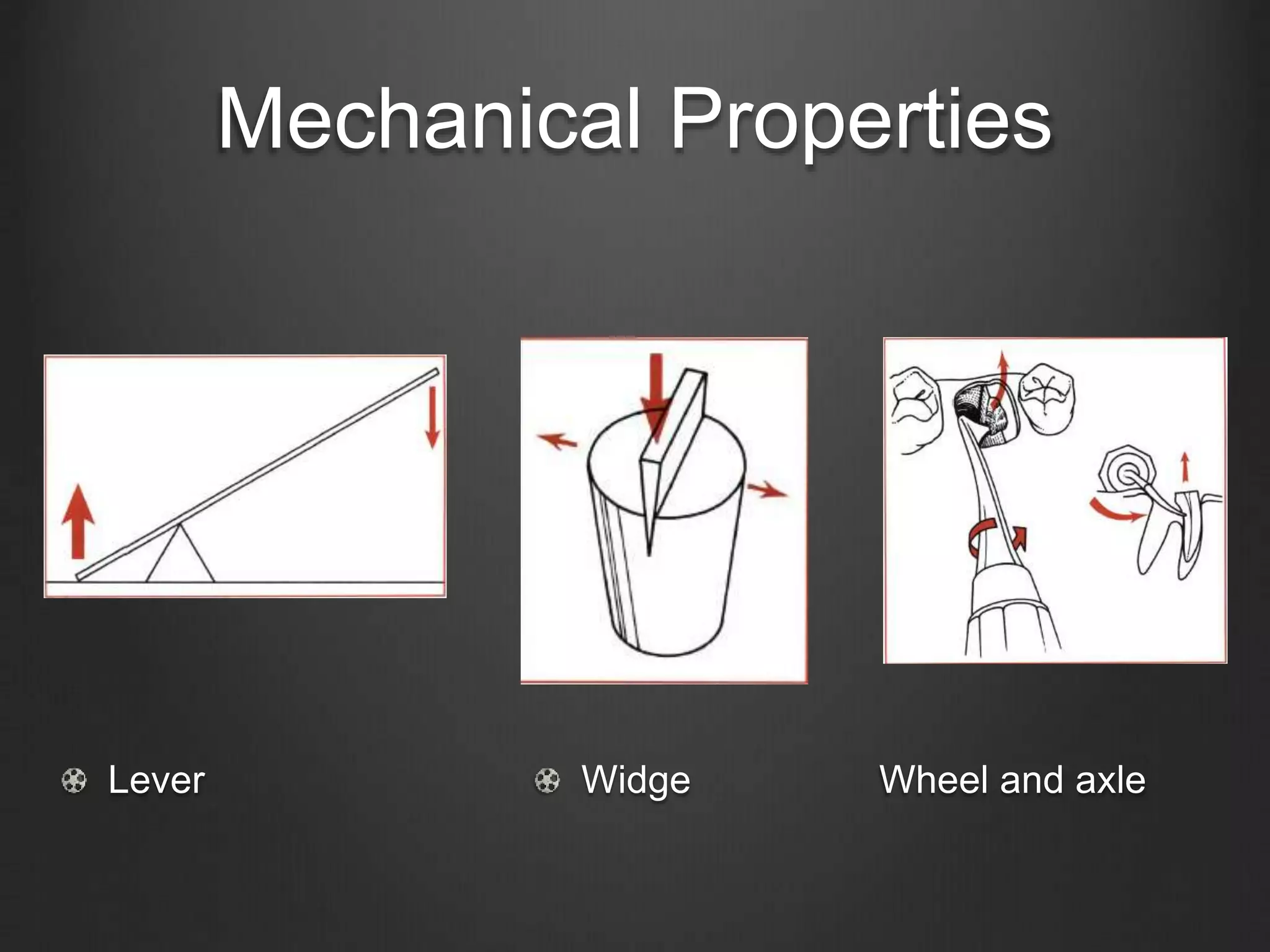
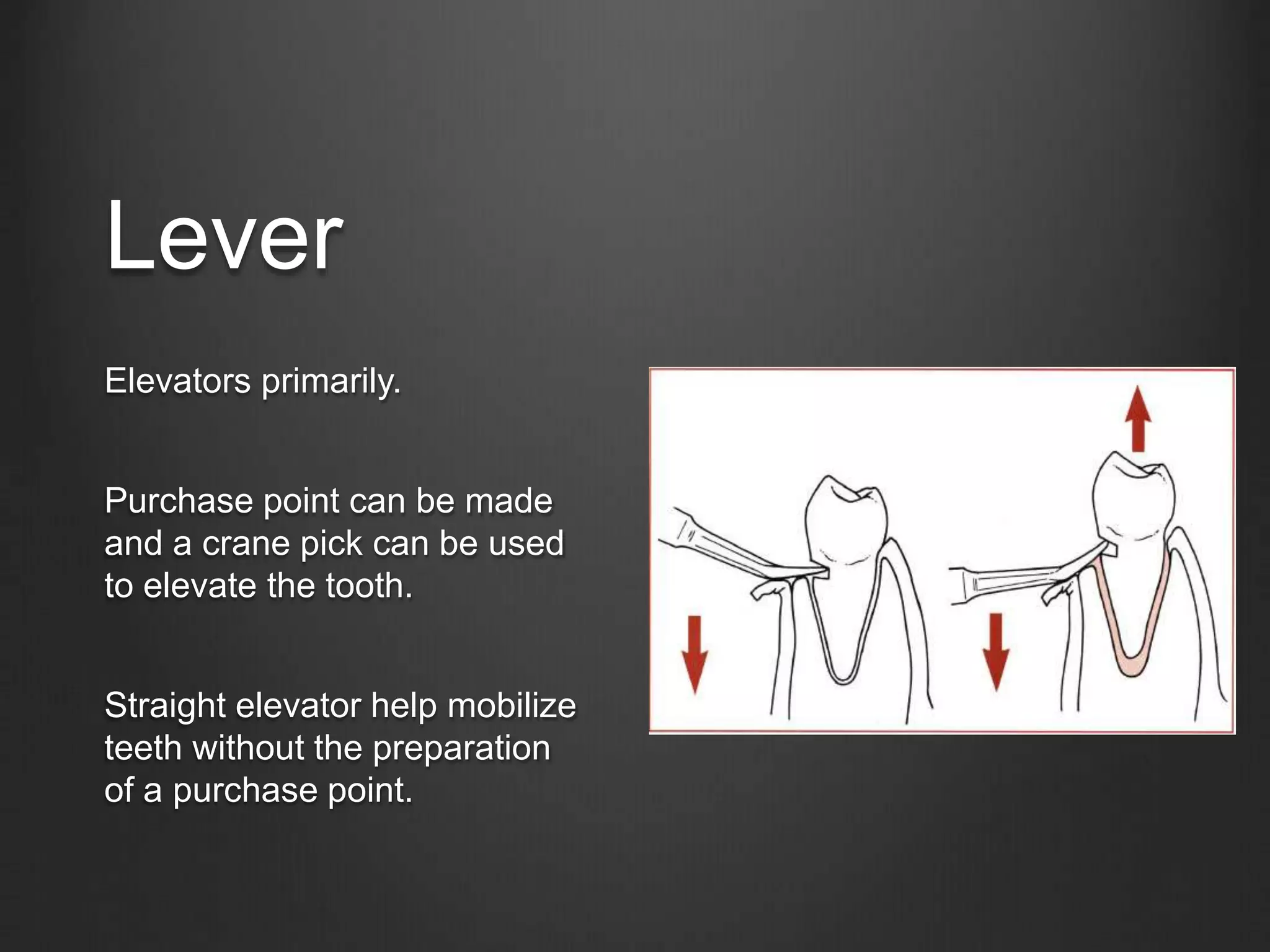
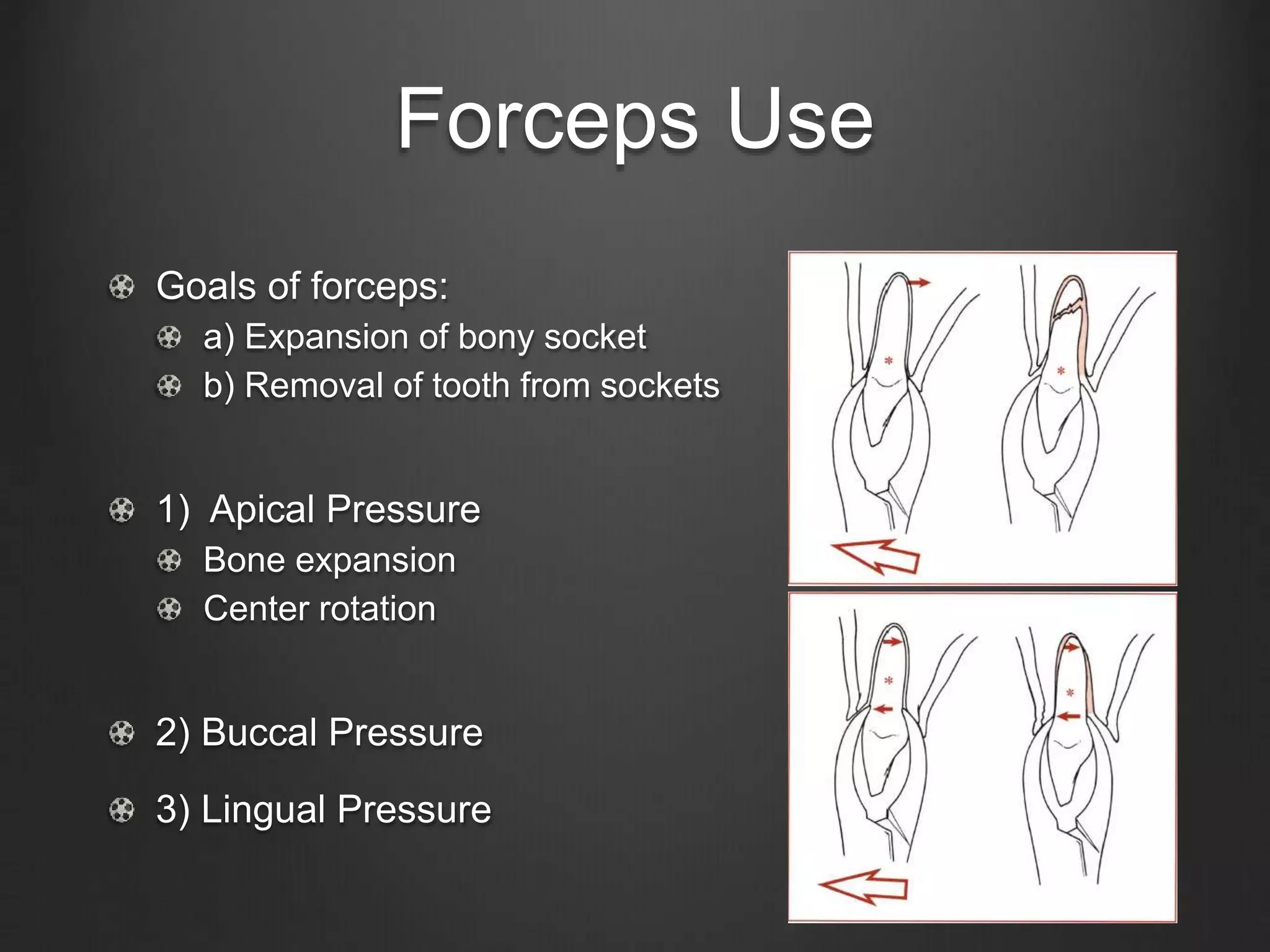
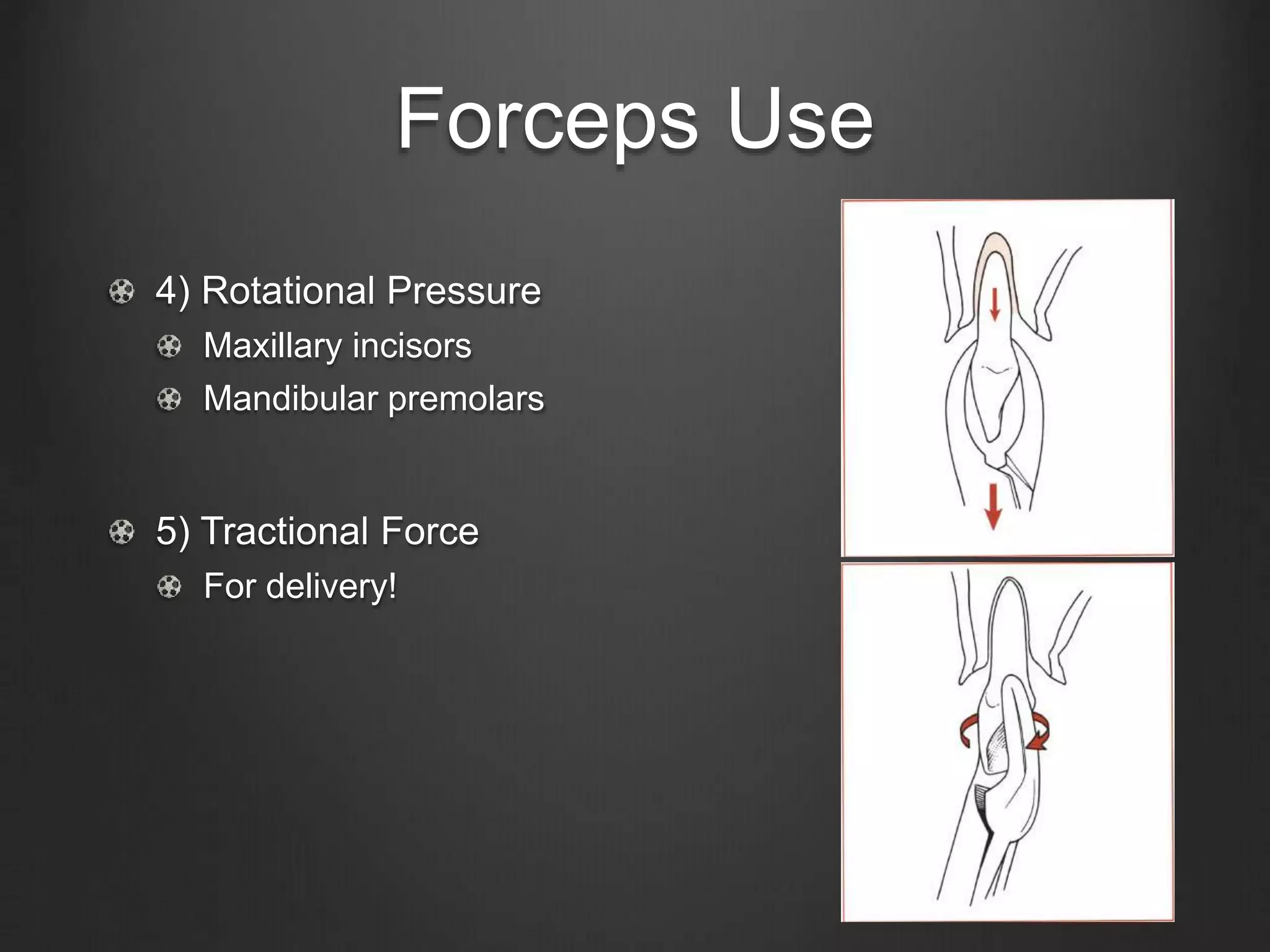
This document outlines the principles of uncomplicated tooth extraction. It discusses presurgical assessment including medical status, indications and contraindications for removal. Clinical evaluation involves assessing access, mobility, crown condition and radiographs. Mechanical principles that aid extraction include levers, elevators and forceps. Forceps are used to expand the bony socket, remove the tooth and apply different forces like apical, buccal, lingual and rotational pressure depending on the tooth. The goals are to mobilize and deliver the tooth from the socket in a safe manner.