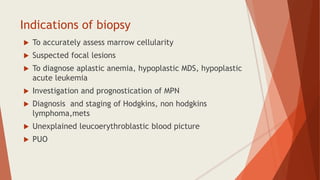
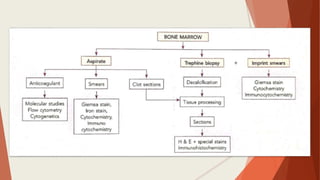
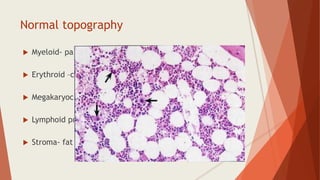
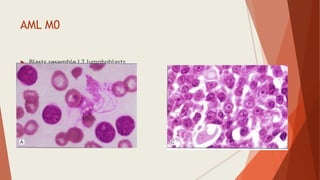
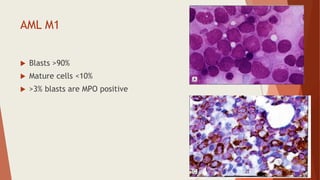
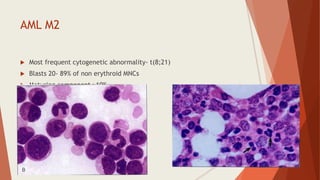
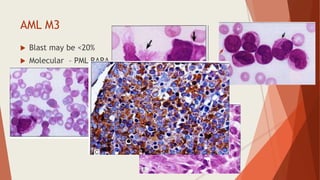
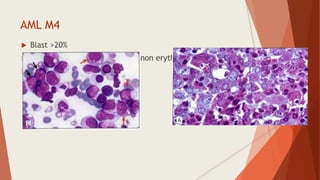
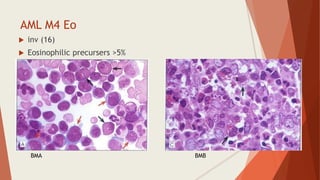
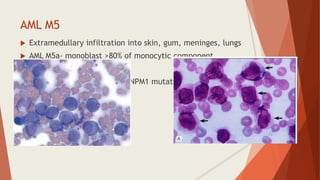
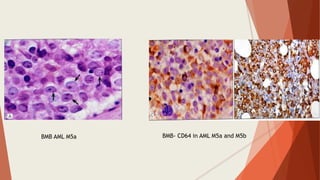
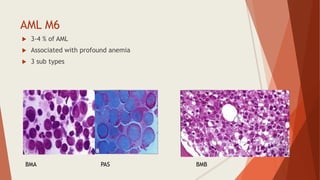
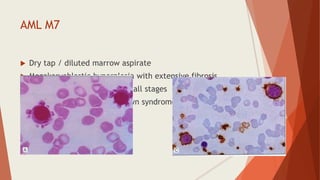
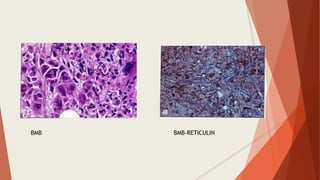
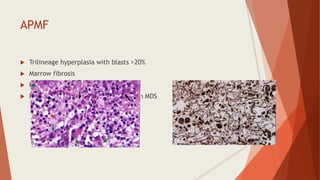
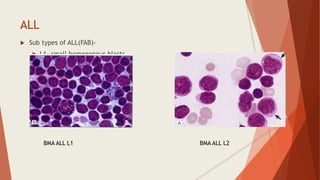
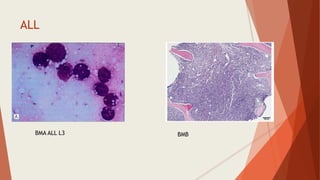
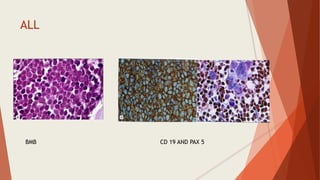
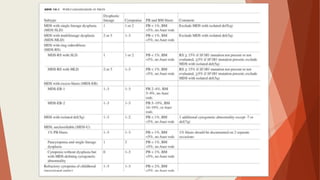
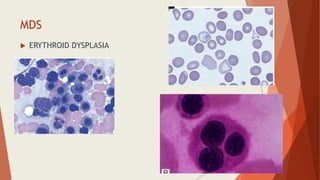
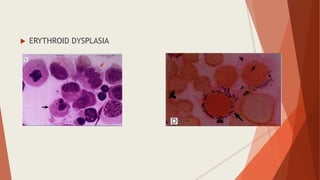
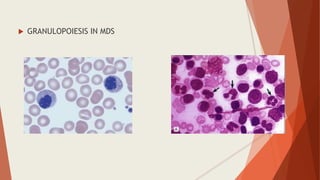
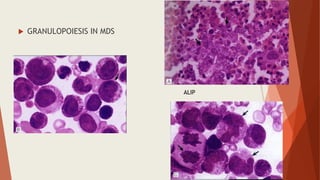
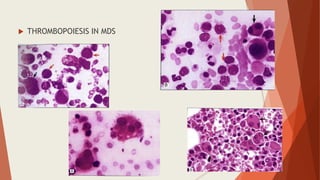
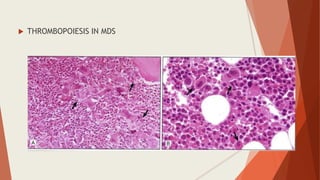
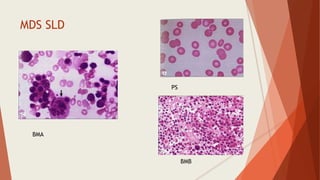
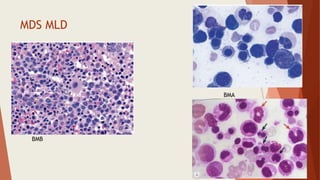
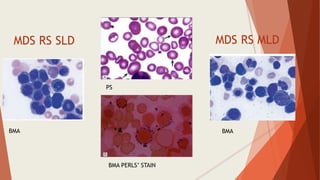
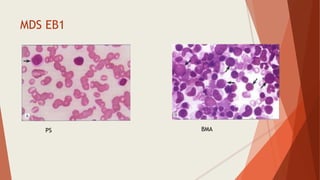
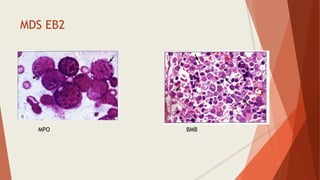
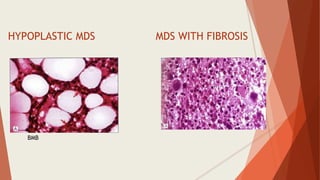
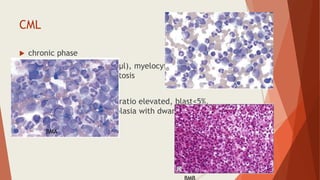
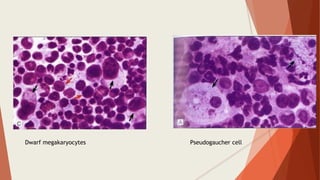
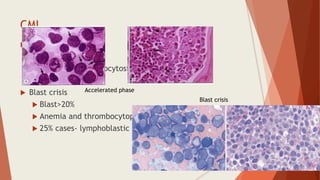
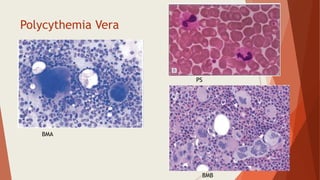
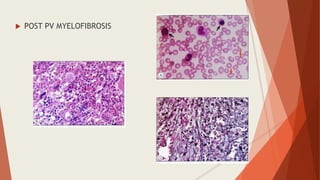
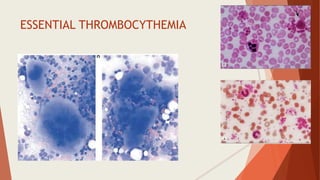
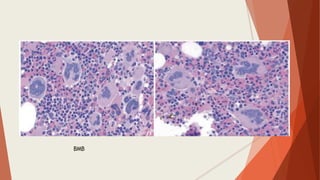
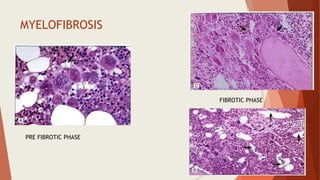
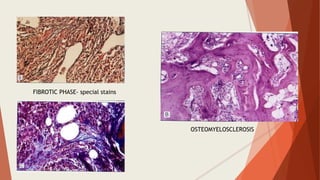
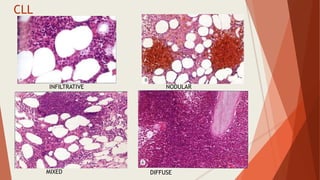
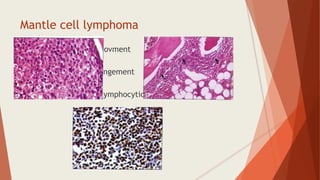
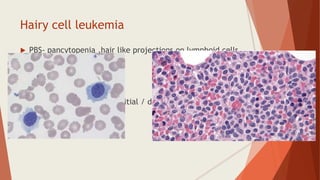
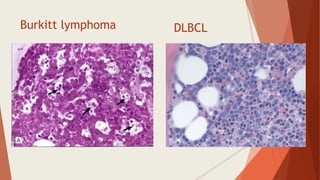
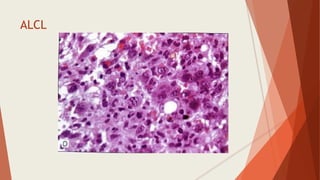
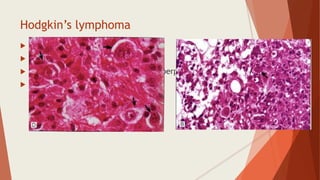
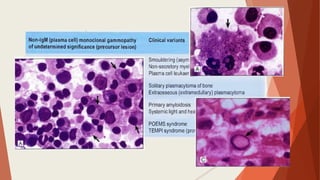
Bone marrow biopsy is useful for diagnosing and managing hematological diseases. It evaluates cellularity, fibrosis, and infiltrative disease. Indications include assessing marrow cellularity, suspected focal lesions, aplastic anemia, myeloproliferative neoplasms, lymphomas, multiple myeloma, and amyloidosis. Adequate biopsies are 1.5-2 cm in length with 5-6 trabecular spaces and 4 micron sections. Bone marrow biopsy along with aspiration helps diagnose conditions like acute leukemias, myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative neoplasms, lymphomas, and plasma cell neoplasms through assessing cellularity, infiltrates, and special stains.