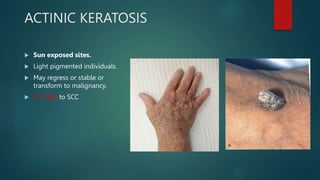
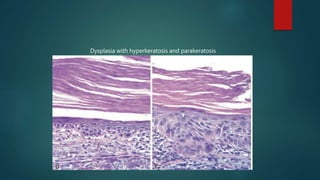
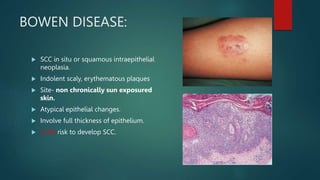
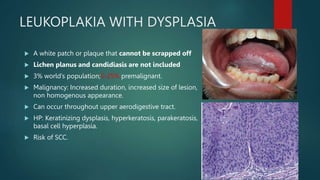
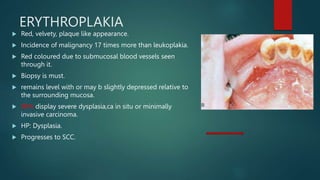
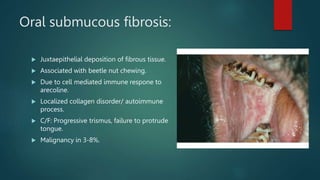
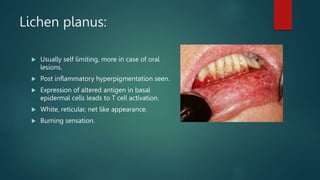
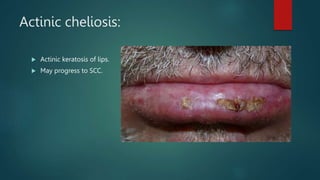
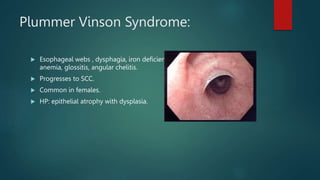
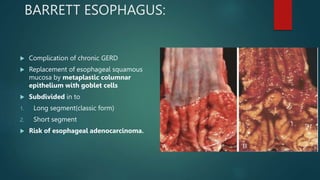
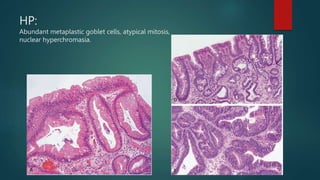
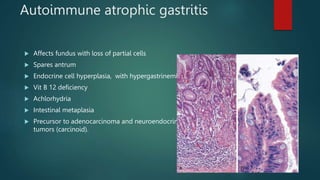
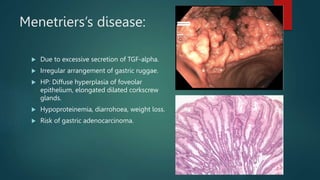
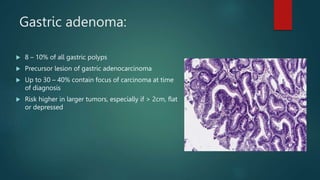
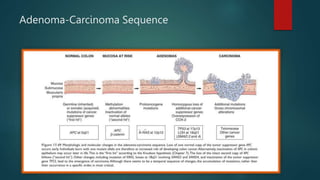
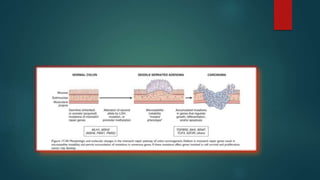
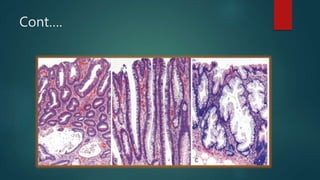
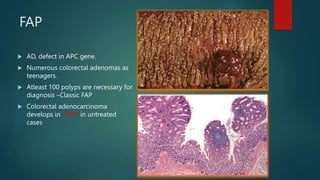
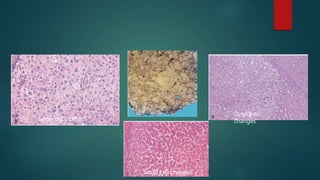
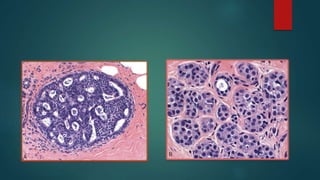
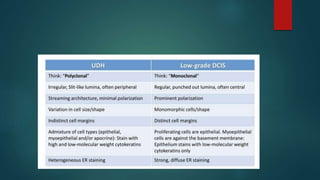
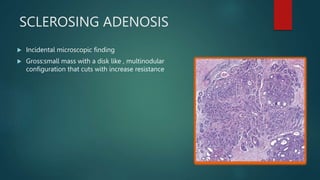
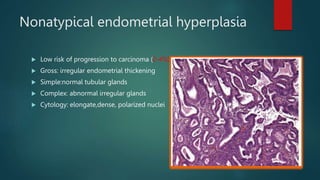
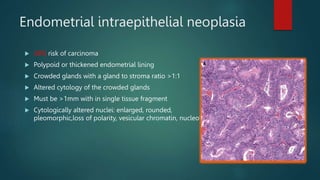
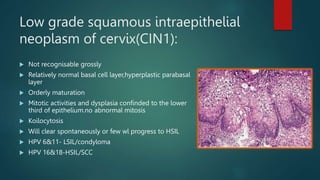
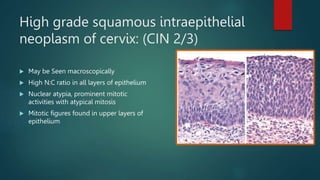
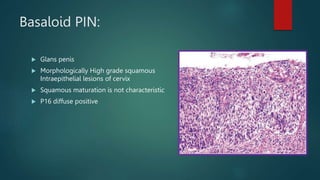
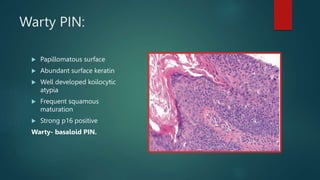
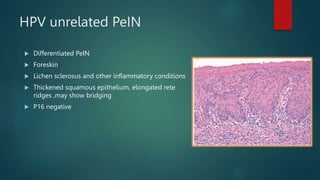
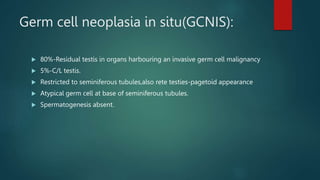
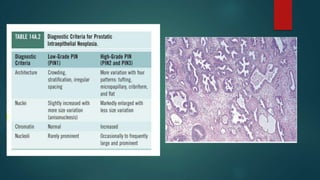
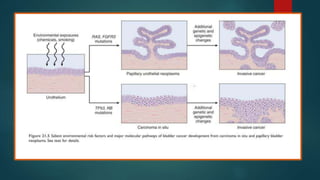
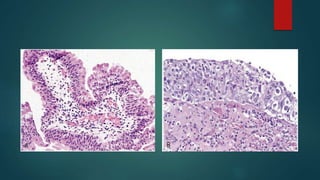
This document discusses numerous preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions across multiple organ systems. Preneoplastic lesions involve abnormal cells with an increased cancer risk, while neoplastic lesions are cancerous or precancerous. Examples mentioned include actinic keratosis and Bowen's disease of the skin; oral leukoplakia; Barrett's esophagus; colonic adenomas; cirrhosis-associated liver cell changes; asbestos-related lung changes; various breast lesions; cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; penile intraepithelial neoplasia; prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia; and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, which can progress to myeloma.