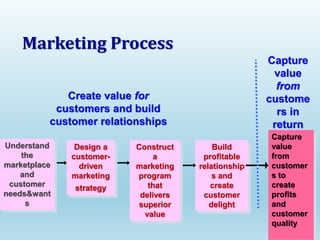
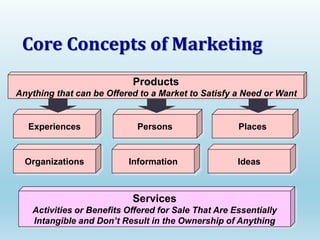
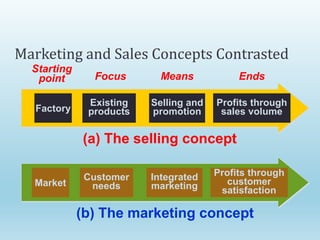
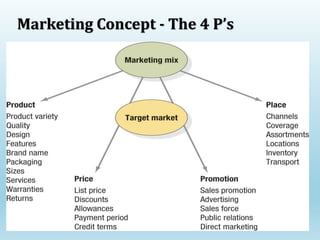
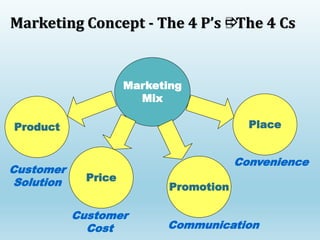
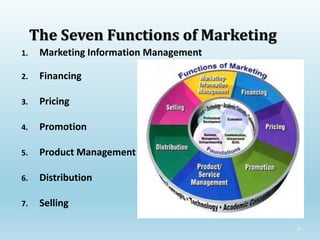
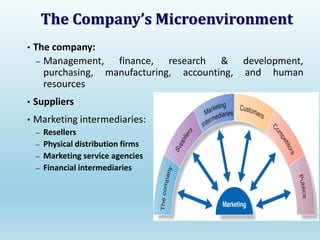
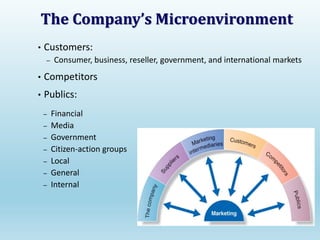
The document provides a comprehensive overview of marketing principles, emphasizing the importance of satisfying customer needs and building profitable relationships through superior value delivery. It discusses core concepts such as needs, wants, demands, and the marketing mix, while also detailing the evolution of marketing from production-focused strategies to relationship-based approaches. Additionally, it highlights the marketing environment, including micro and macro factors that impact marketing practices.