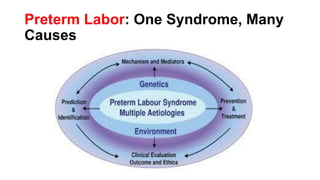
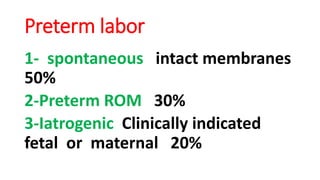
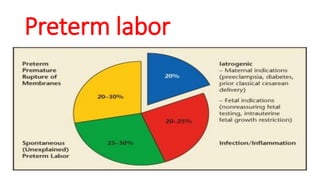
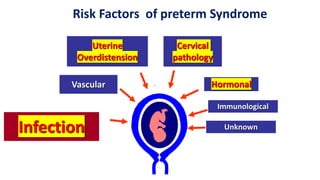
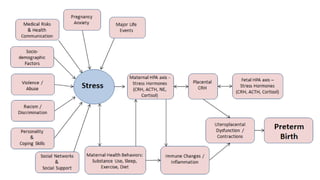
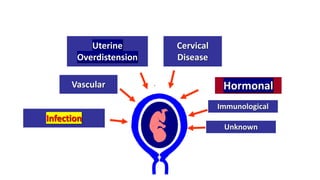
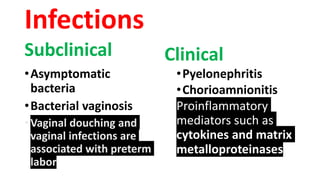
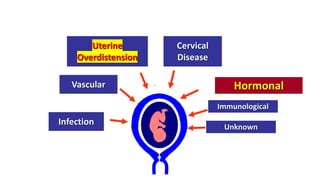
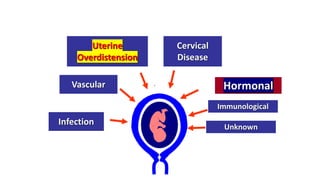
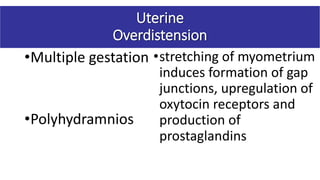
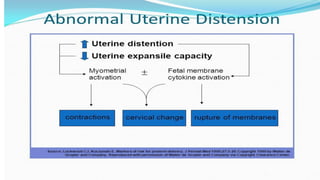
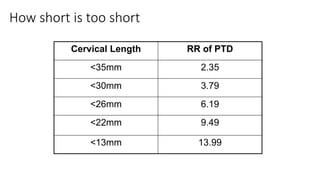
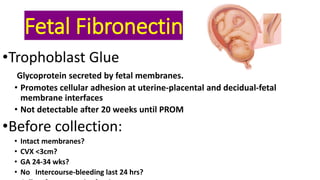
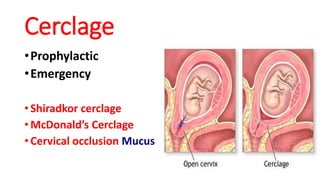
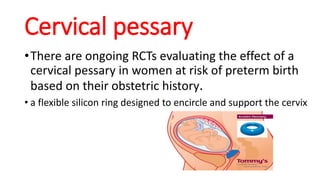
Preterm labor is defined as contractions and cervical changes before 37 weeks of gestation and is the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. It has many potential causes including infection, cervical issues, hormonal factors, uterine overdistension, and unknown etiologies. Risk factors include previous preterm births, infections, short cervical length, and medical conditions. Prevention strategies encompass progesterone supplementation, cervical cerclage, infection treatment, and bedrest. Diagnosis involves examining for contractions and cervical changes while monitoring is used to assess risk of imminent preterm delivery. Treatment focuses on stopping contractions with tocolytics if not yet at delivery while improving neonatal outcomes with corticosteroids if delivery is imminent.