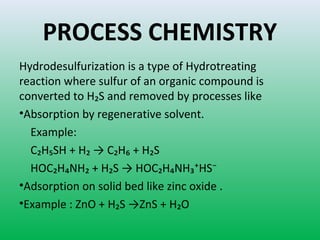
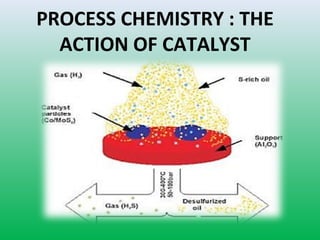
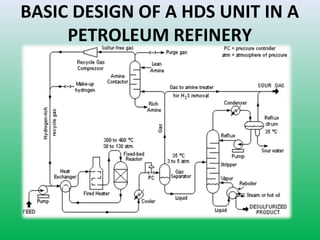
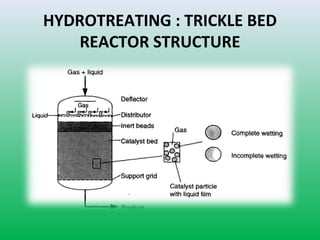
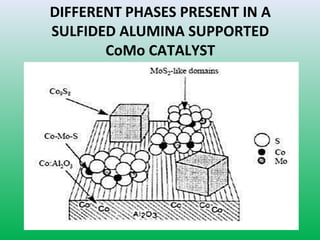
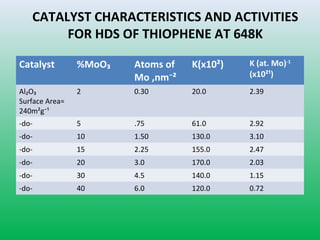
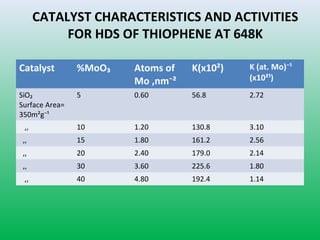
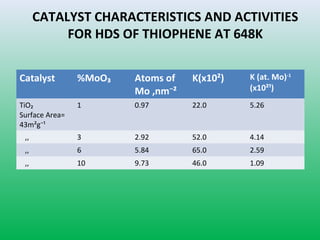
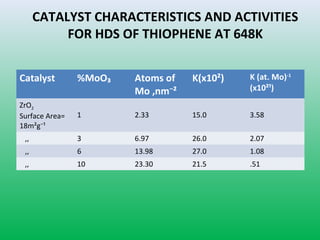
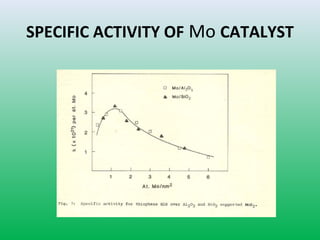
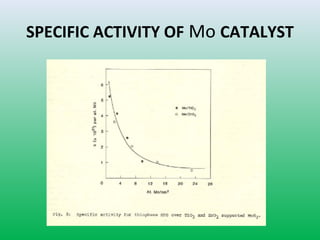
This document summarizes a student project on the design of hydrodesulfurization reactors. The objectives are to study the construction of trickle bed HDS reactors, experimentally test molybdenum catalysts on different material beds, and compare efficiencies of different catalyst systems. Hydrodesulfurization is introduced as a process to remove sulfur from fuels by converting it to hydrogen sulfide. Trickle bed reactors are commonly used, with catalyst particles in a three-phase bed. Experimental results on thiophene hydrodesulfurization show that molybdenum catalyst activity depends on the support material used. New composite and multi-component catalyst supports are being developed to improve catalyst mechanical strength, activity, and life.