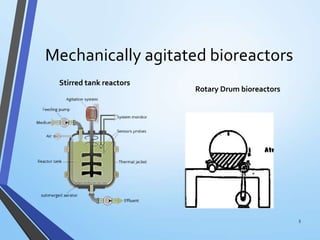
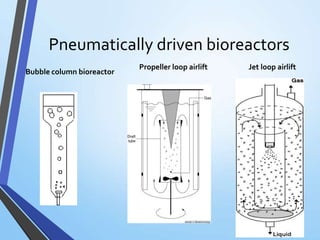
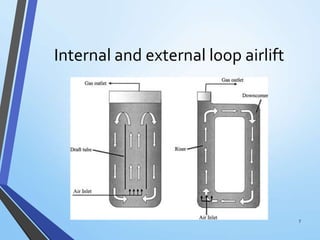
Mechanically agitated bioreactors, pneumatically driven bioreactors, and hydrodynamically driven disposable bioreactors are the main types used in plant cell cultures. Disposable bioreactors are becoming more common as they are low cost, simple to operate, and ensure high process security by eliminating cleaning and sterilization needs. These bioreactors are primarily used for large scale production of secondary metabolites and biotransformation of compounds in the pharmaceutical industry.