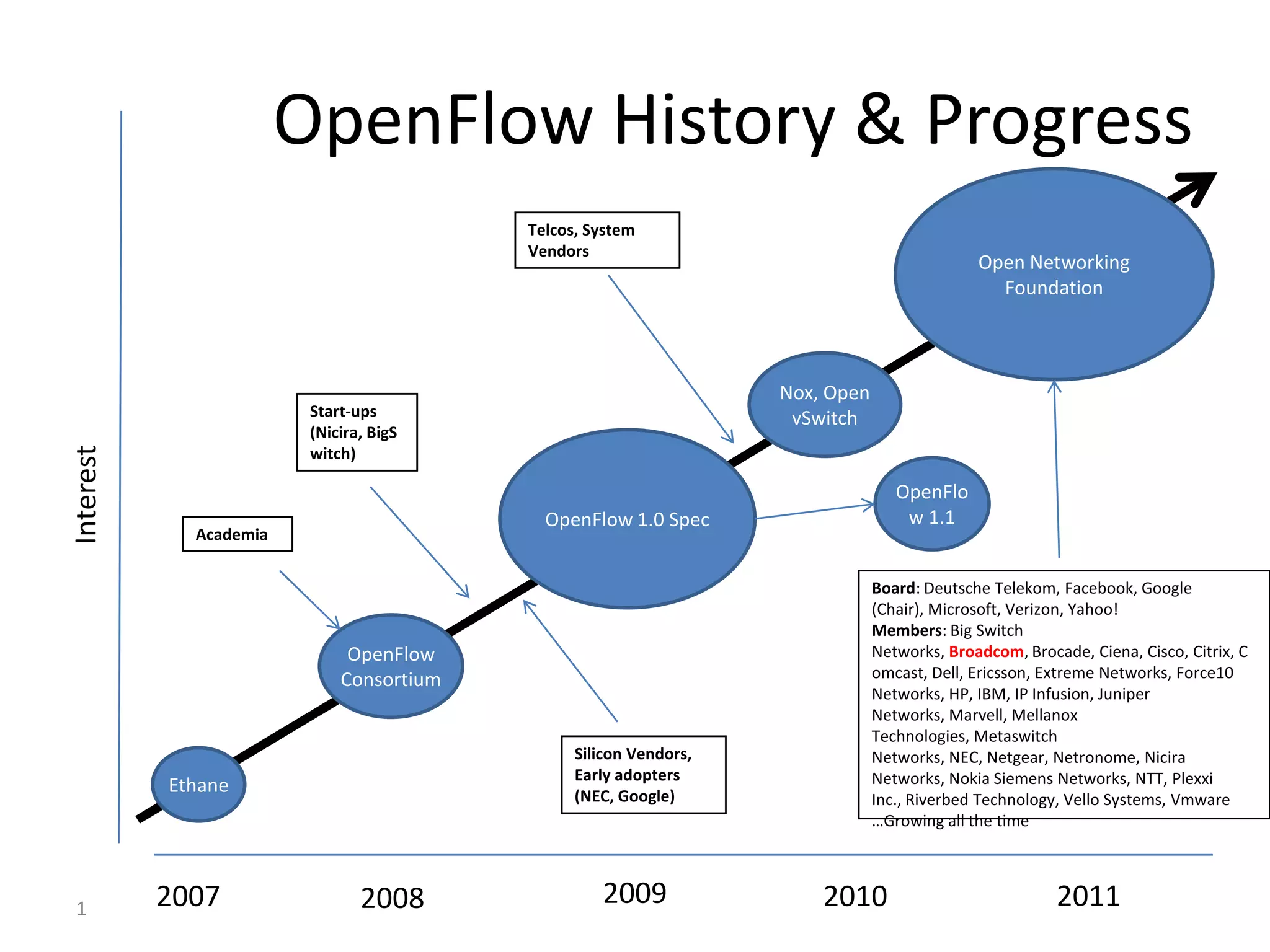
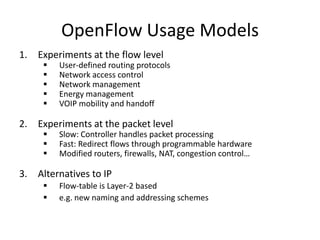
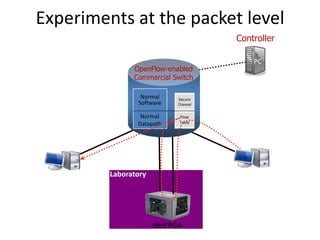
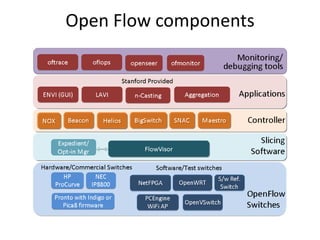
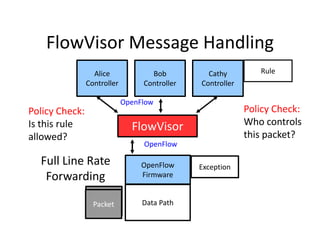
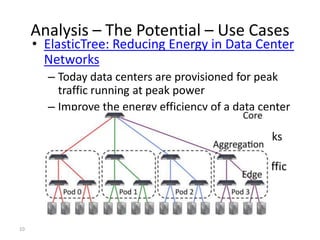
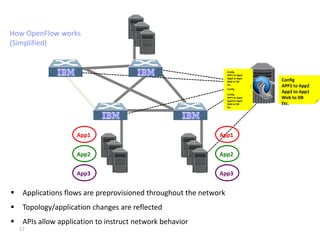
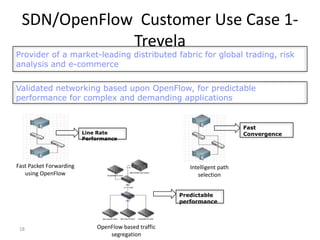
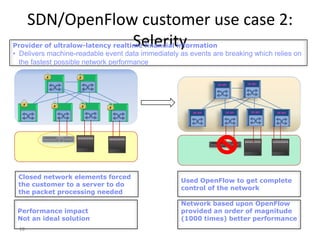
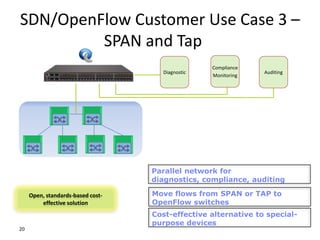
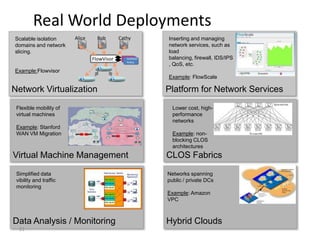
The document discusses the history and progress of OpenFlow and SDN. It traces OpenFlow from its origins in academia in 2007 to its growing adoption by major tech companies and standardization through the Open Networking Foundation by 2011. It outlines how OpenFlow allows centralized control of network traffic through software-defined controllers that programmatically configure flow-based forwarding using the OpenFlow protocol in switches.