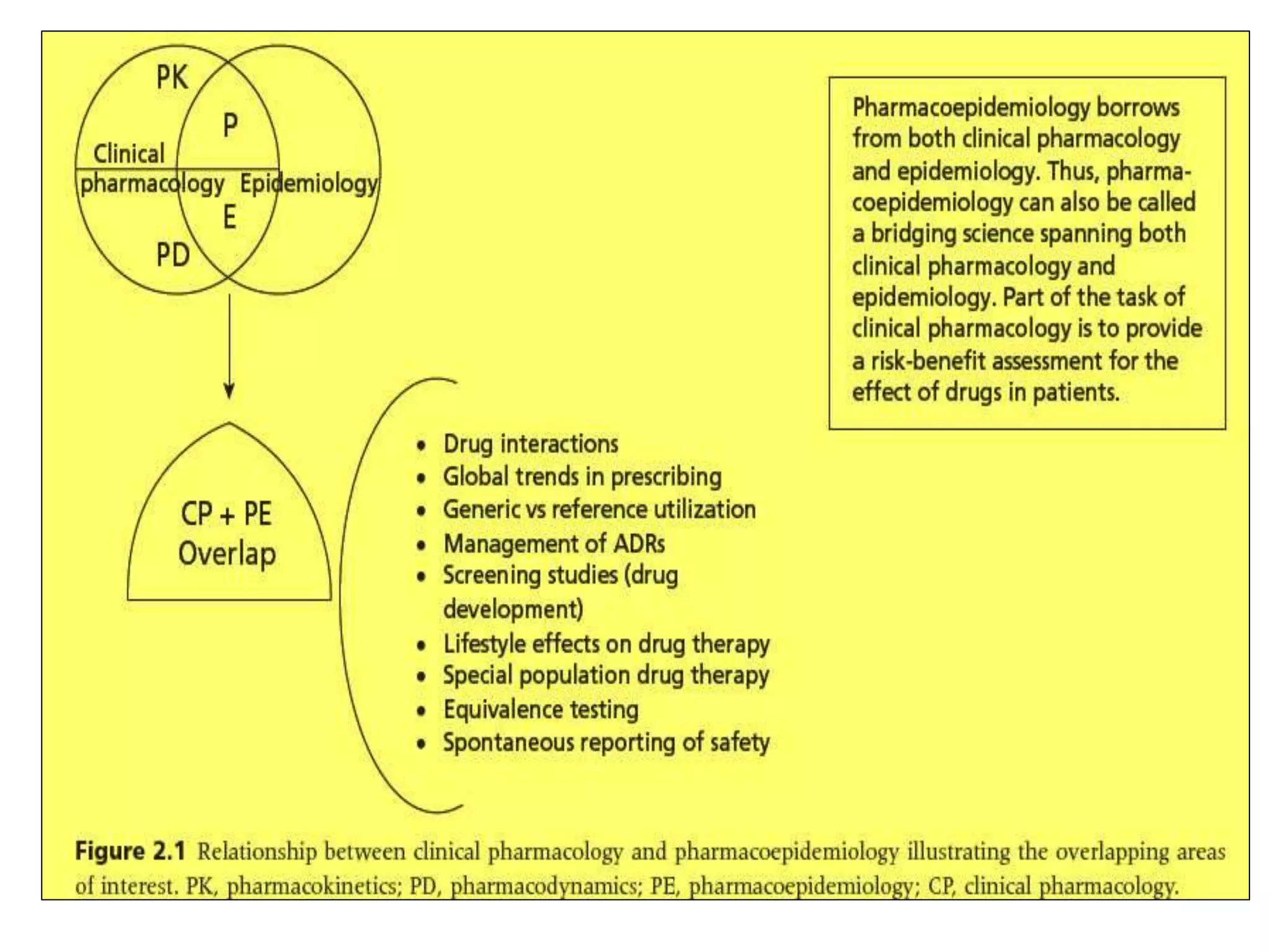
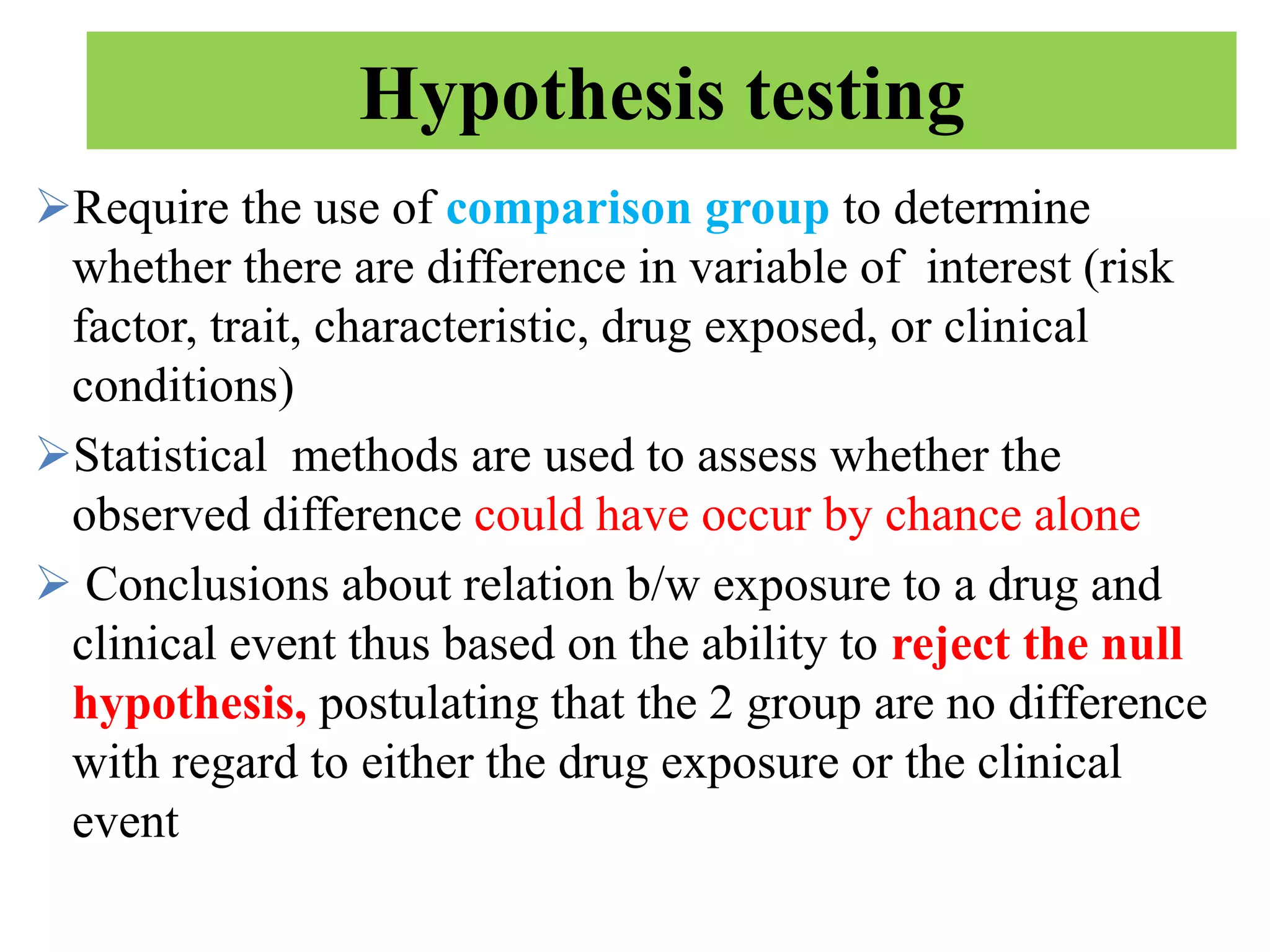
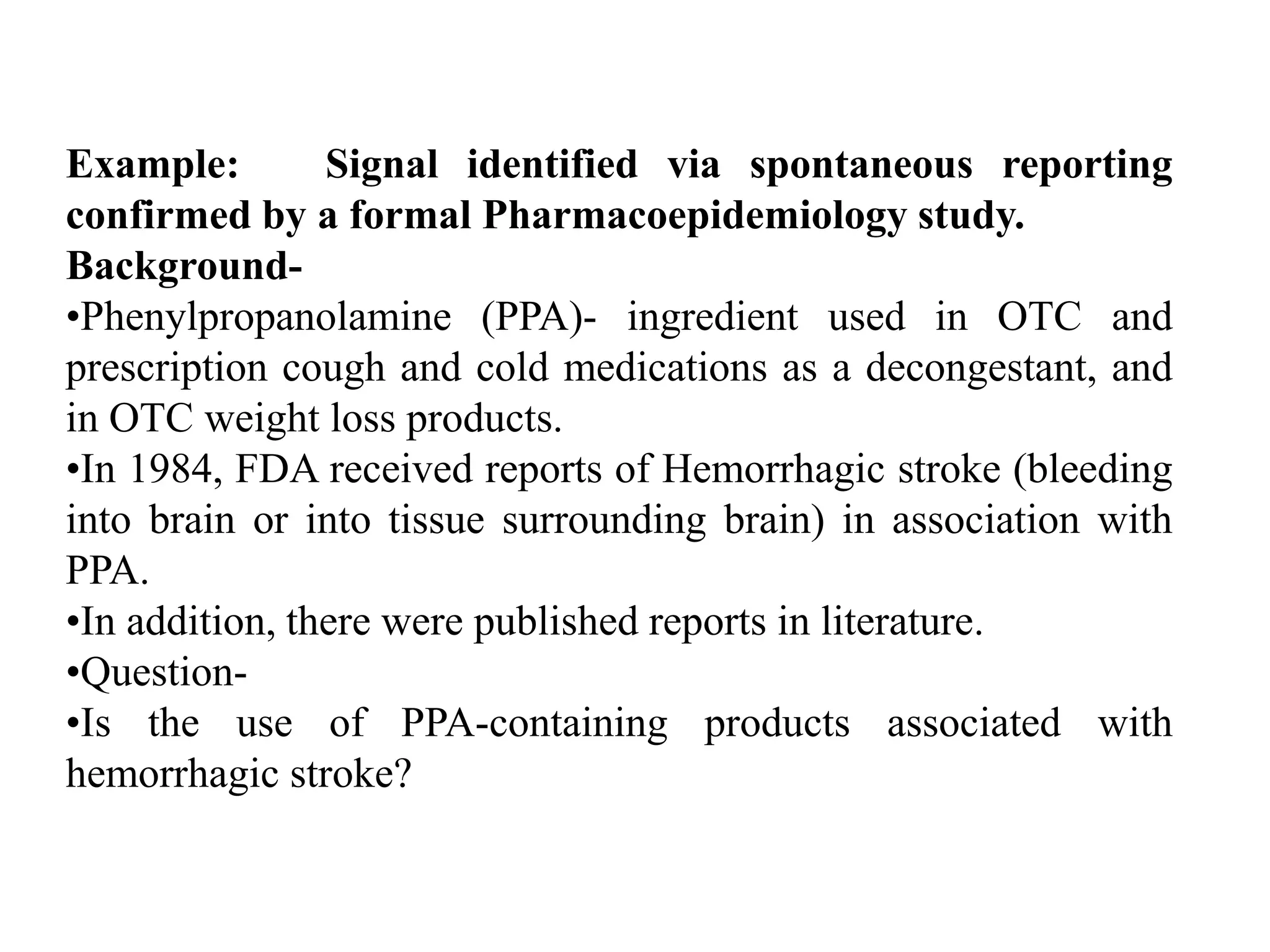
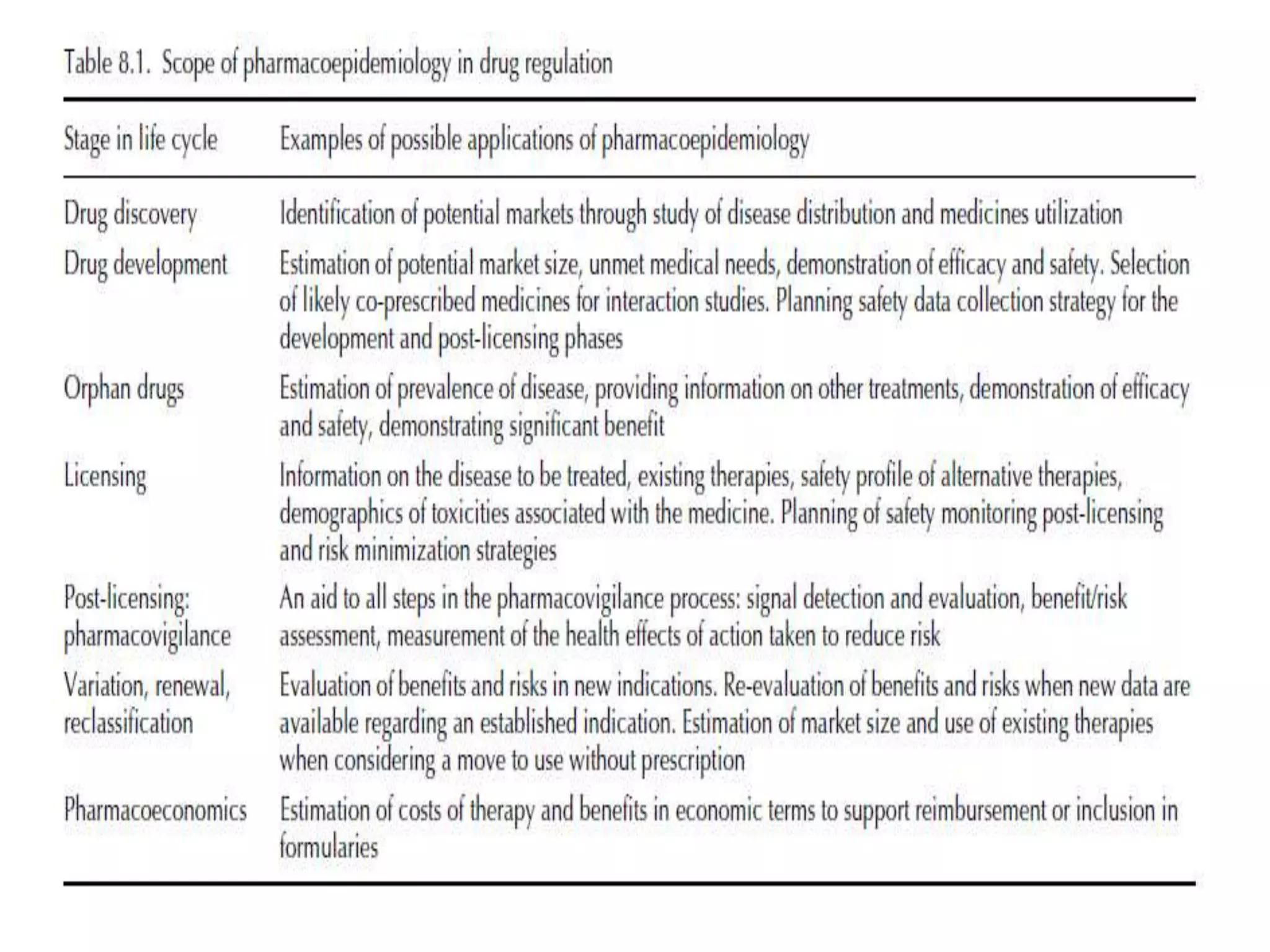
Pharmacoepidemiology involves applying epidemiological methods to study drug use and effects in large populations. It is primarily concerned with post-marketing drug safety surveillance but also analyzes patterns of drug use and assesses effectiveness. Pharmacoepidemiological studies use large healthcare databases and are important for identifying adverse drug reactions, determining risk factors, and improving appropriate medication use. Common study designs include cohort studies, case-control studies, and randomized controlled trials. Pharmacoepidemiology plays a key role in drug regulation, marketing, clinical practice, and public health policy.