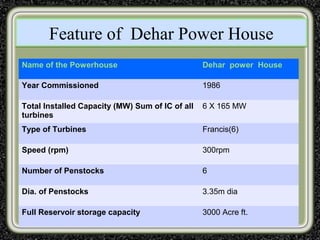
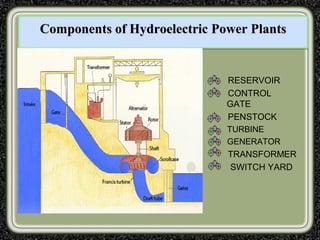
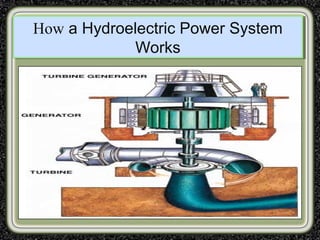
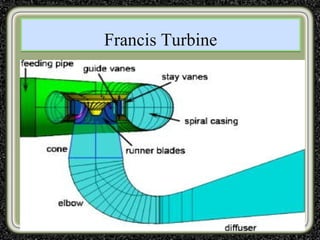
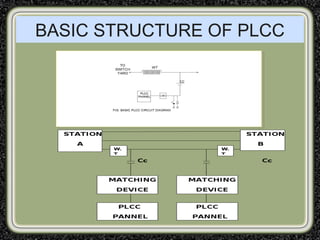
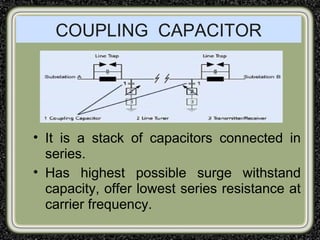
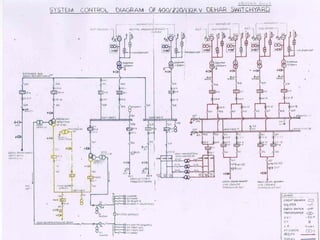
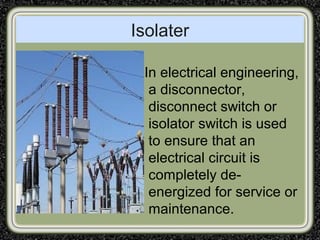
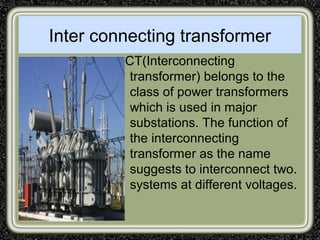
The training was conducted at the Dehar Power House hydroelectric plant. The objectives of the training were to understand the basic principles of power line communication, excitation systems, protection schemes, transformers, and the switchyard. Key components of the hydroelectric plant discussed included the reservoir, penstocks, Francis turbines capable of 165MW each, generators, transformers, and the switchyard. The switchyard uses components like circuit breakers, current transformers, potential transformers, and isolators to transmit and distribute power from the generating station.