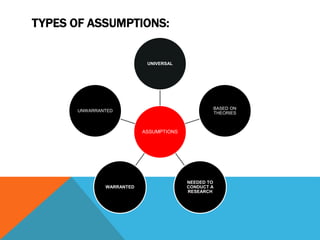
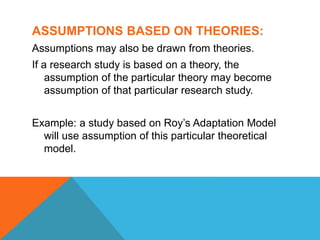
The document discusses the concept of assumptions in research, defining them as beliefs taken for granted without empirical evidence. It categorizes assumptions into universal, theory-based, warranted, and unwarranted assumptions, and highlights their essential role in forming the basis for research and theory development. Additionally, it distinguishes between assumptions and hypotheses, and addresses the limitations that can affect the credibility of research findings.