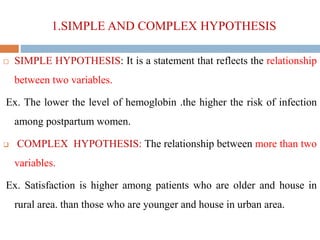
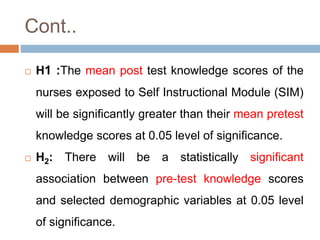
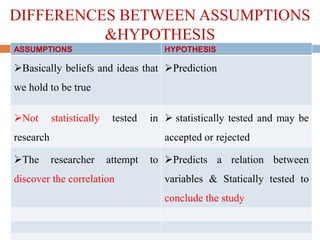
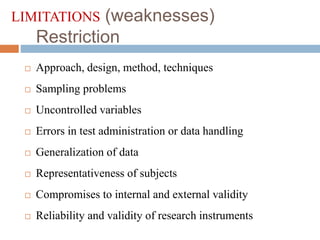
This document discusses hypotheses, including their definition, nature, types, and formulation. A hypothesis is a formal, testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables. Hypotheses can be associative or causal, directional or non-directional, simple or complex. They must be clearly stated using empirical, measurable variables. Formulating a good hypothesis involves identifying dependent and independent variables and specifying the expected relationship at a given level of significance. The testing of hypotheses is a four-step process of stating hypotheses, collecting data, setting decision criteria, and evaluating results. Assumptions are beliefs taken as true but not scientifically tested, while limitations and delimitations define the boundaries and weaknesses of a study.