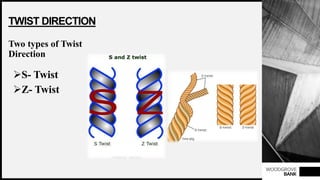
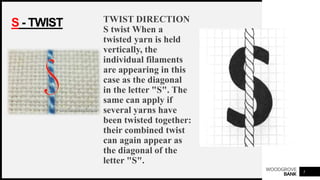
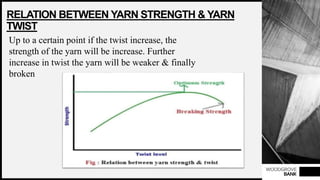
This document discusses yarn twist, which is the spiral arrangement of fibers around a yarn's axis that binds the fibers together and contributes to the yarn's strength. There are two types of twist direction: S-twist and Z-twist. The amount and direction of twist impacts a yarn's appearance, strength, and other properties. Twisting fibers increases yarn strength by holding them together tightly. Both higher and lower twist levels can affect a yarn's absorbency, aesthetic effects, and tensile properties. The objectives and importance of twisting fibers into yarn include binding fibers, increasing strength and evenness, and shaping the yarn into a round form.