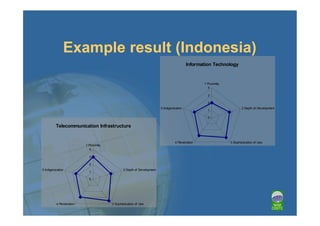
This document provides an overview of e-readiness self-assessment and manuals for improving countries' e-readiness. It discusses conducting self-assessments to determine a country's level of e-readiness as basic, developing, or advanced. Factors to evaluate include e-leadership, infrastructure, IT, policies, and regulations. The document outlines strategies, prerequisites, and funding systems for each e-readiness level and establishing an ICT program within NAM countries.