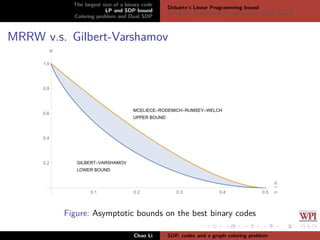
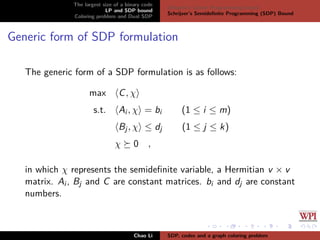
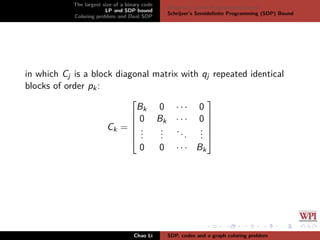
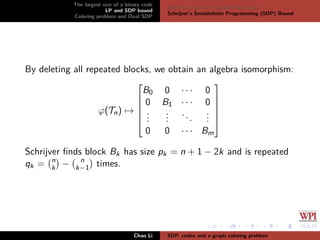
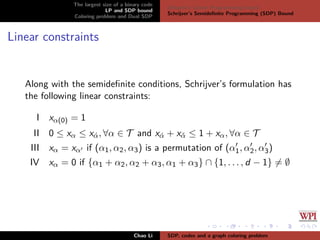
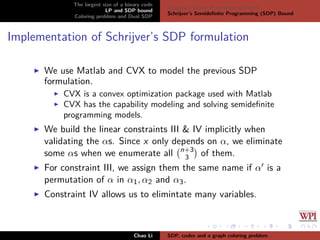
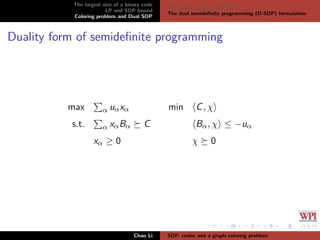
The document discusses the largest size of a binary error-correcting code and related problems, focusing on linear programming (LP) and semidefinite programming (SDP) bounds. It defines key concepts such as Hamming distance, binary codes, and provides an overview of established upper bounds and recent advancements in determining the maximum size of binary codes with specific lengths and distances. The work highlights the significance of these codes in maintaining high information rates while resisting noise during transmission.


















![The largest size of a binary code
LP and SDP bound
Coloring problem and Dual SDP
Delsarte’s Linear Programming bound
Schrijver’s Semidefinite Programming (SDP) Bound
Characteristic vector
The characteristic vector x of a code C has one entry for each
c ∈ Fn, xc = 1 if c ∈ C; xc = 0 otherwise.
For example, for F2 = {00, 01, 10, 11}, a code C = {00, 01}
will have the characteristic vector [1, 1, 0, 0].
Chao Li SDP, codes and a graph coloring problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d93368ee-dea9-4105-93af-3edfe6a035b5-150615221416-lva1-app6892/85/Semidefinite-programming-binary-codes-and-a-graph-coloring-problem-21-320.jpg)
![The largest size of a binary code
LP and SDP bound
Coloring problem and Dual SDP
Delsarte’s Linear Programming bound
Schrijver’s Semidefinite Programming (SDP) Bound
Characteristic vector
The characteristic vector x of a code C has one entry for each
c ∈ Fn, xc = 1 if c ∈ C; xc = 0 otherwise.
For example, for F2 = {00, 01, 10, 11}, a code C = {00, 01}
will have the characteristic vector [1, 1, 0, 0].
Define
ai =
1
|C|
x Ai x
Later we call this xC instead of x.
Chao Li SDP, codes and a graph coloring problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d93368ee-dea9-4105-93af-3edfe6a035b5-150615221416-lva1-app6892/85/Semidefinite-programming-binary-codes-and-a-graph-coloring-problem-22-320.jpg)