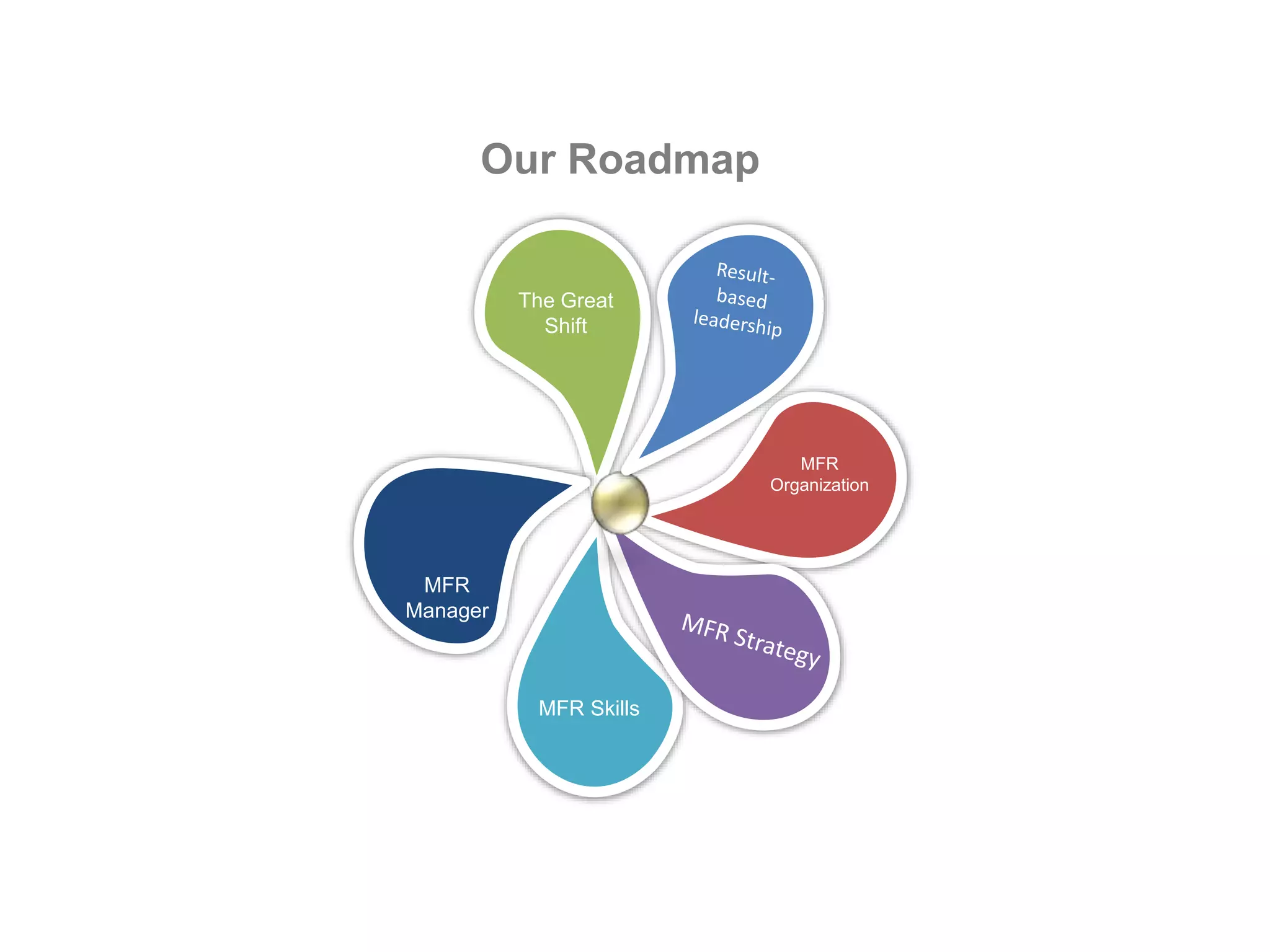
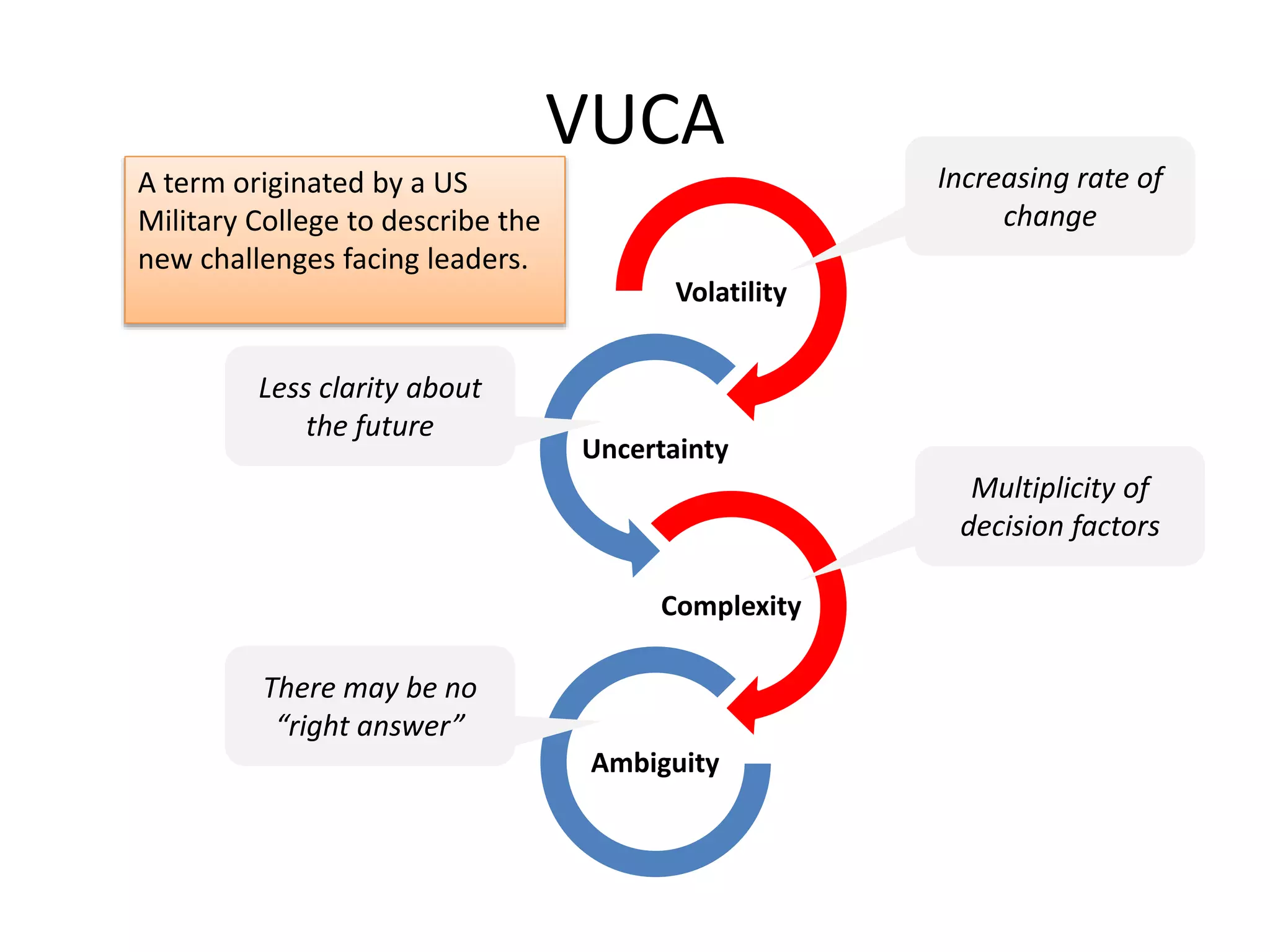
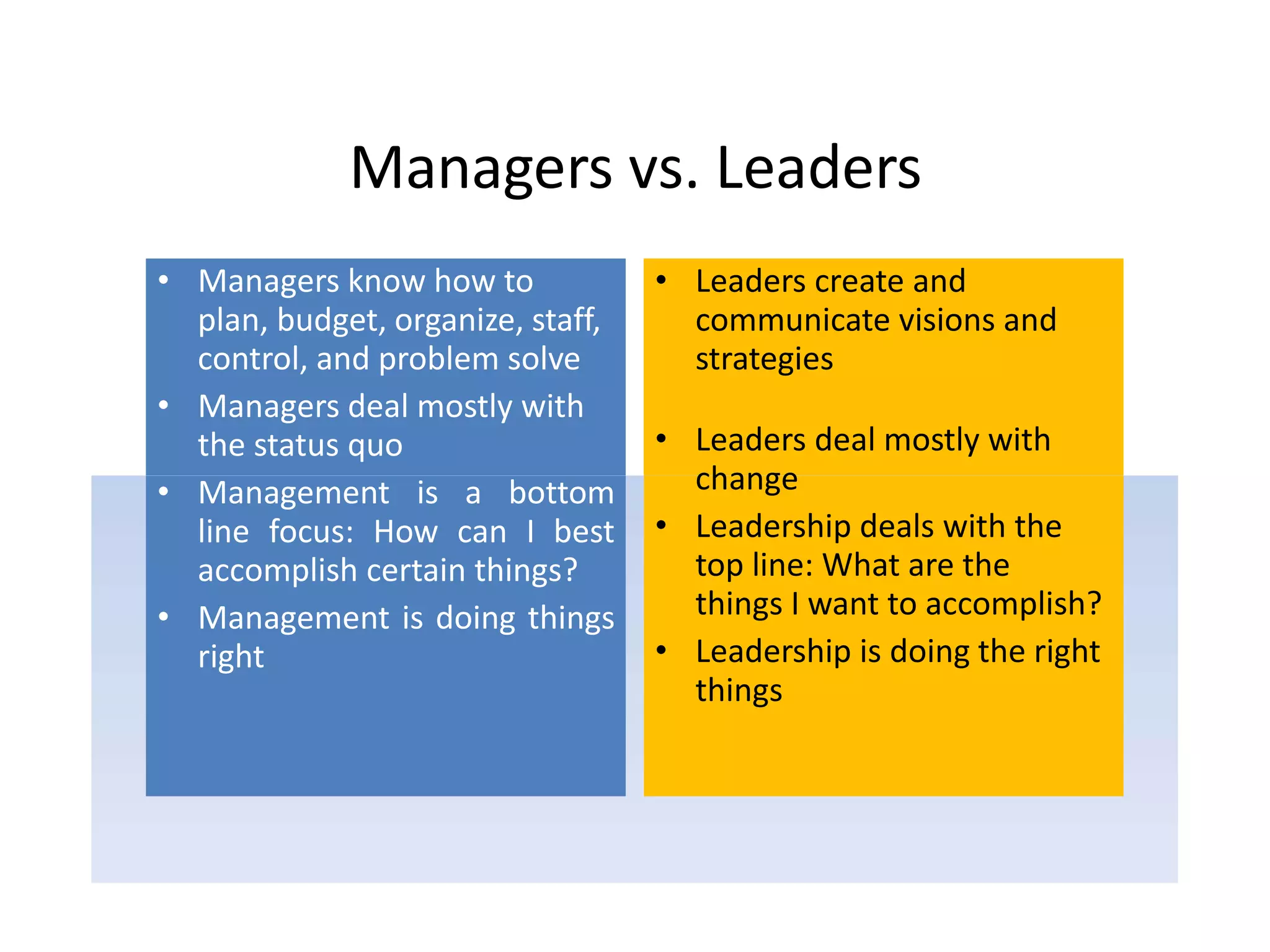
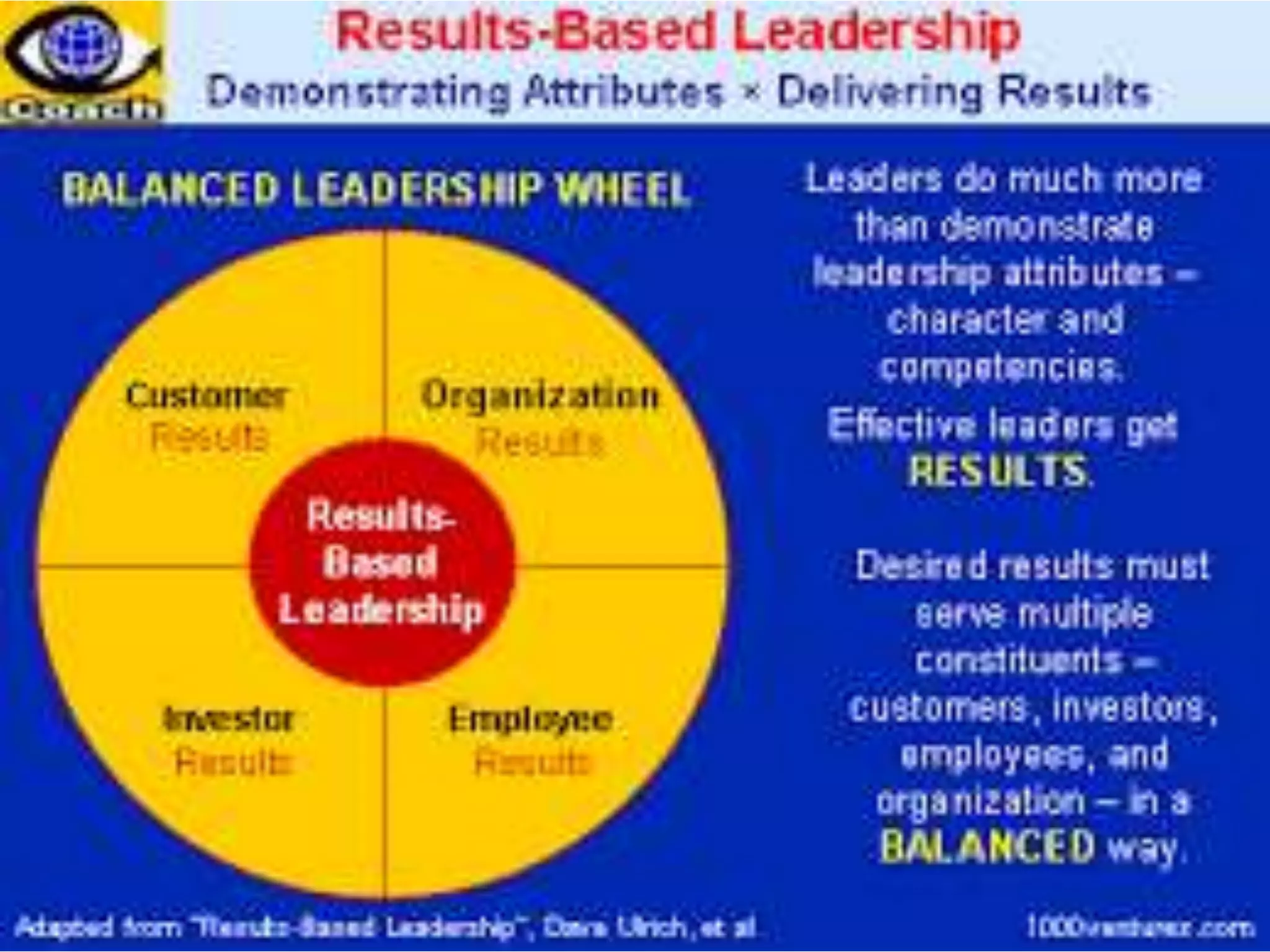
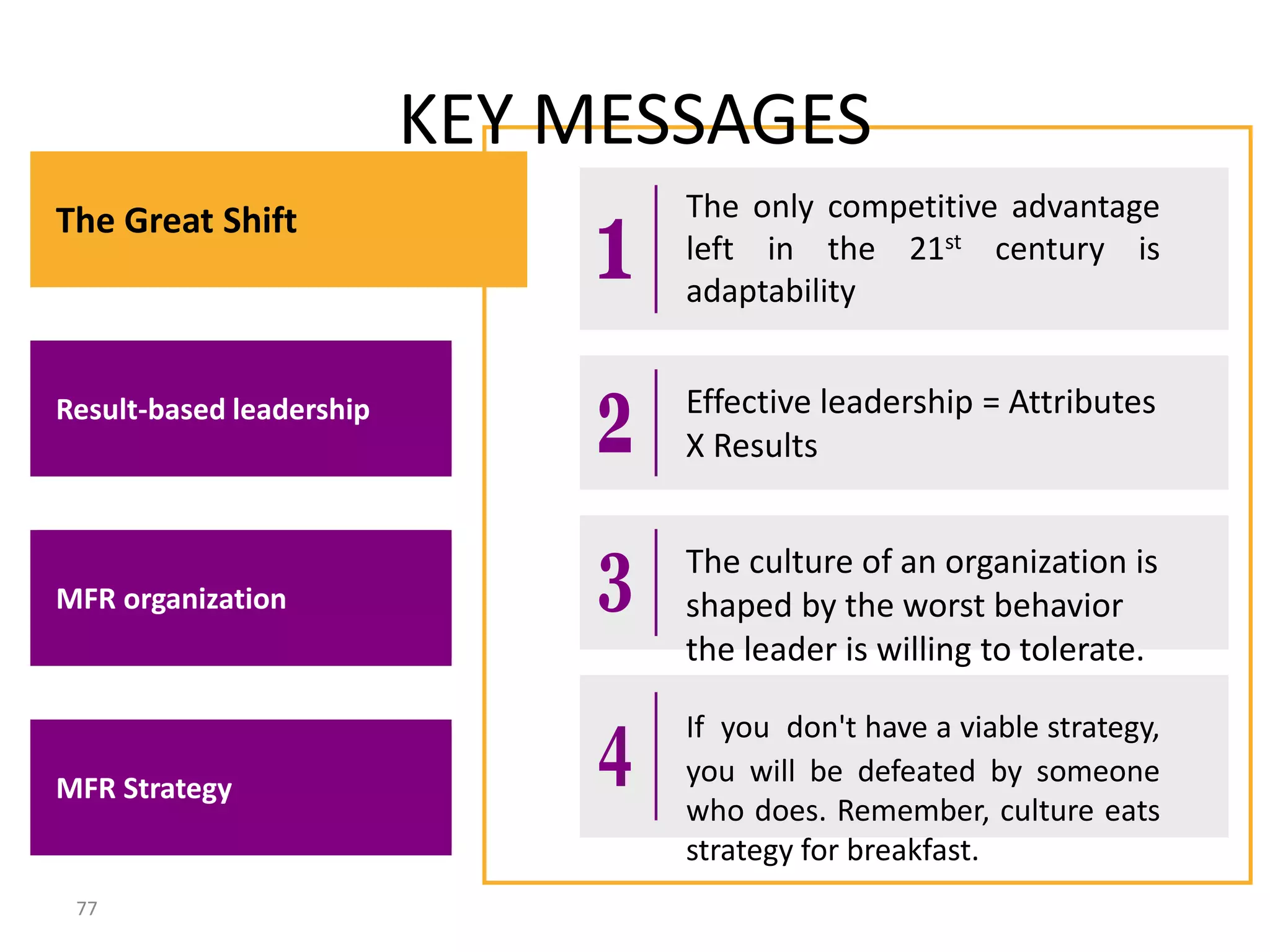
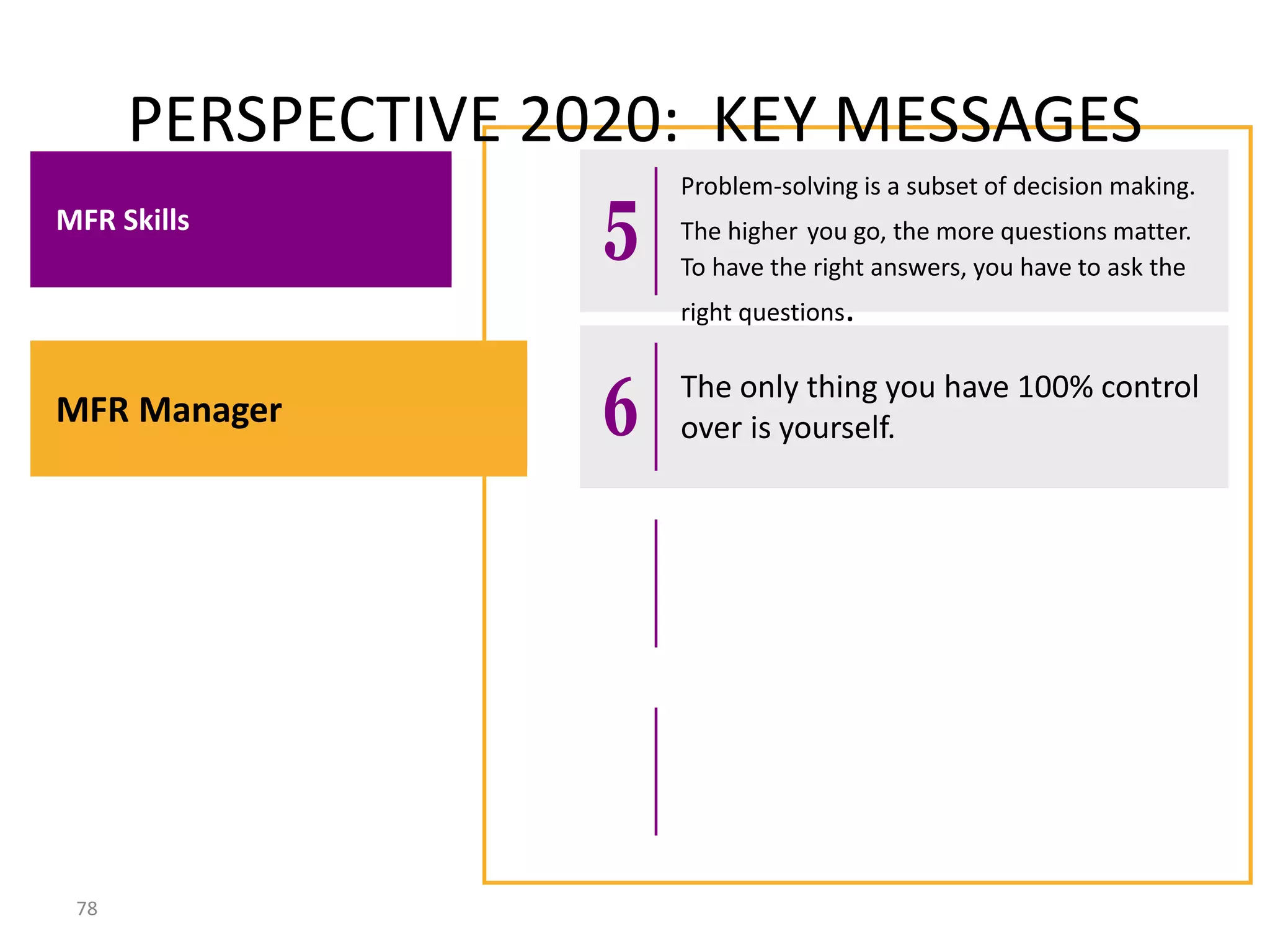
The document summarizes key concepts around leading and managing for results. It discusses:
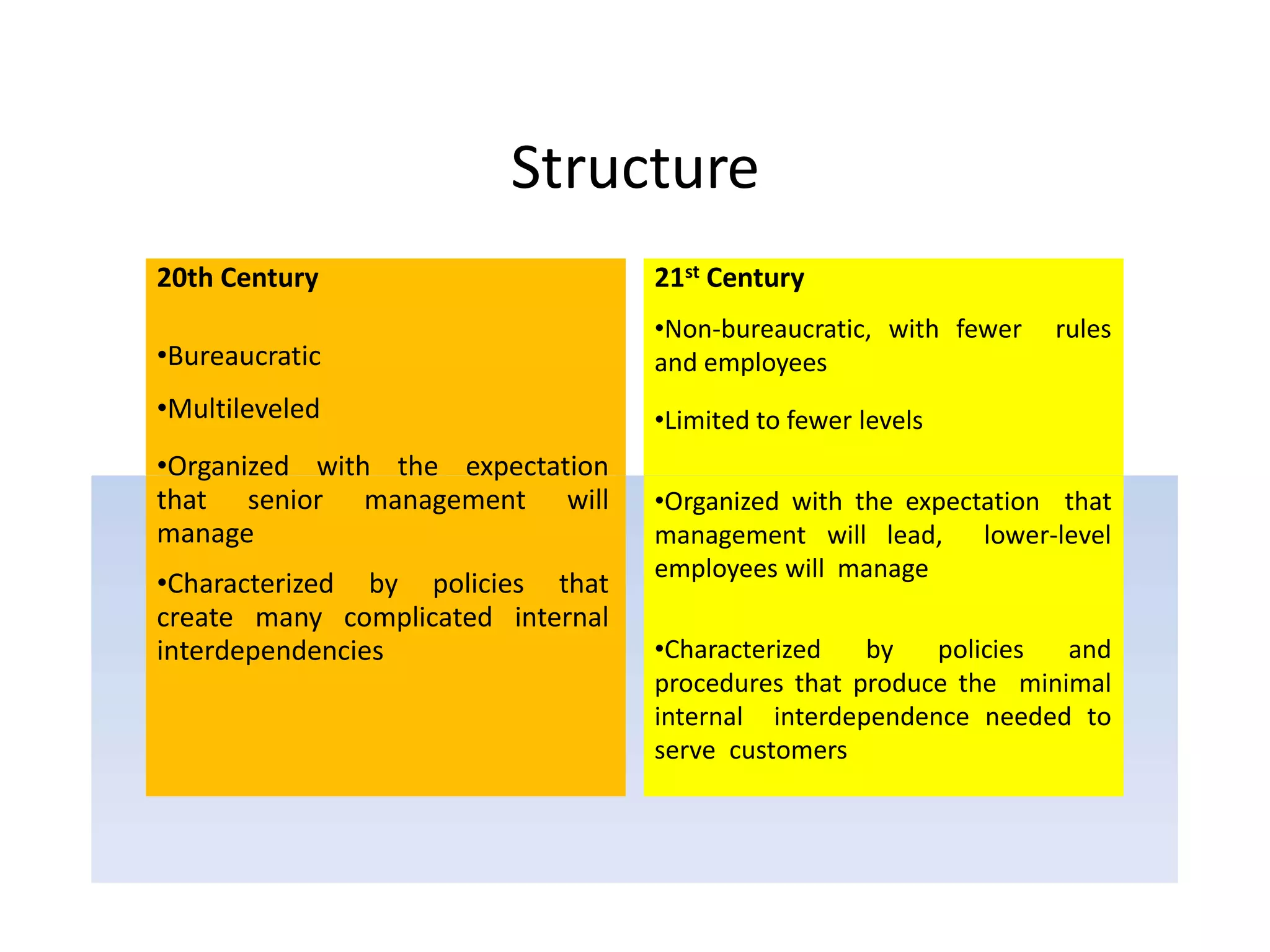
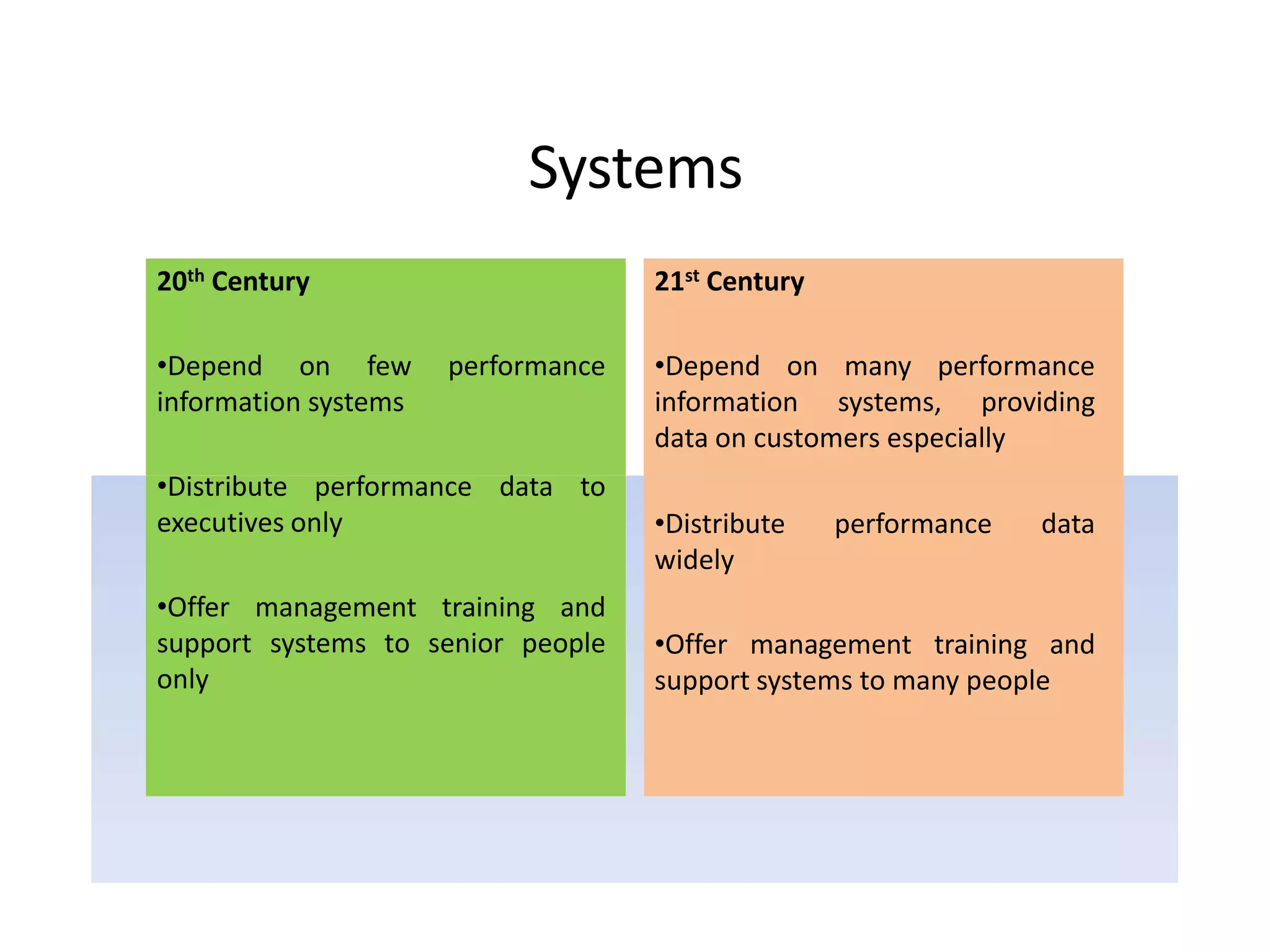
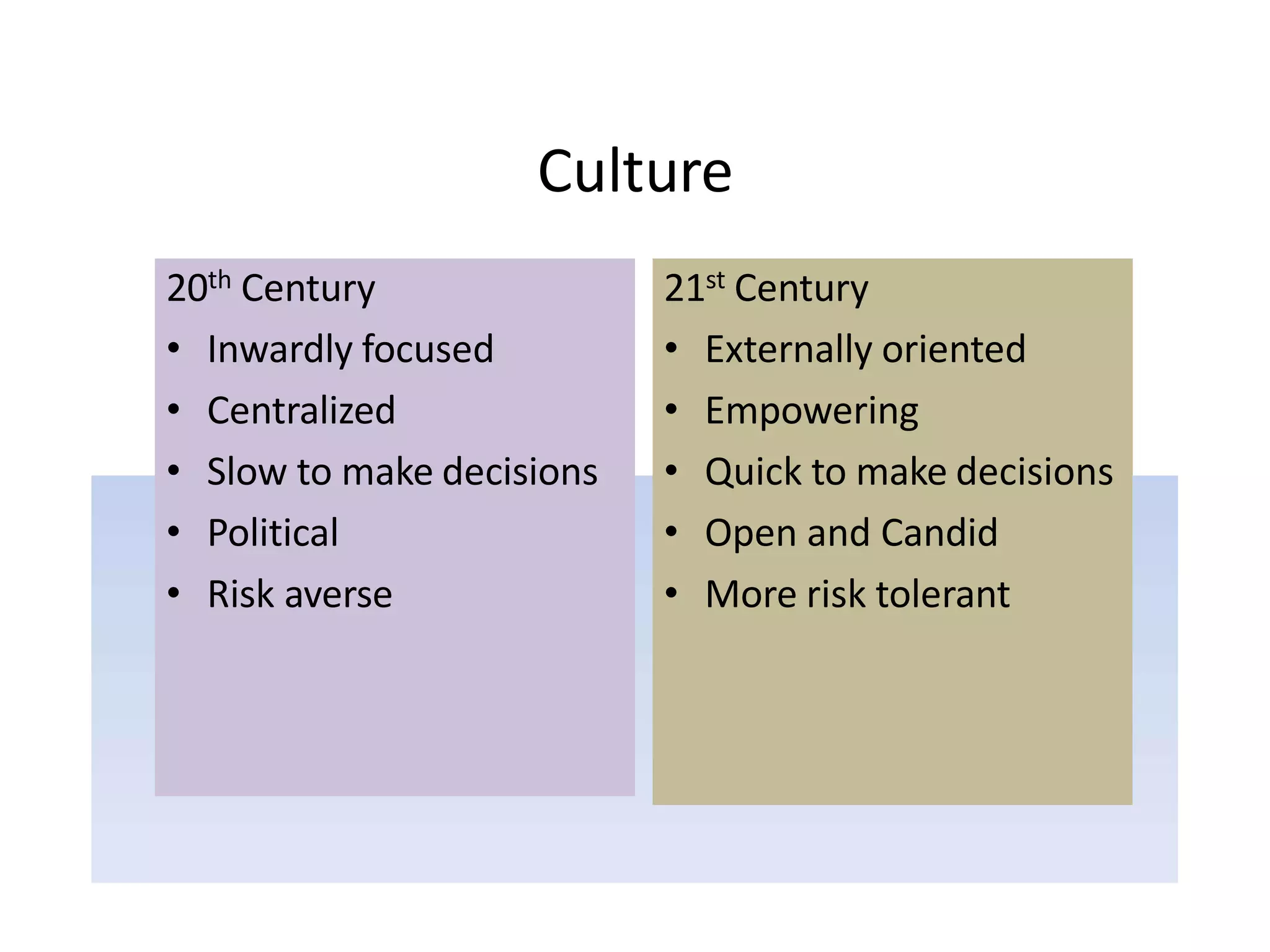
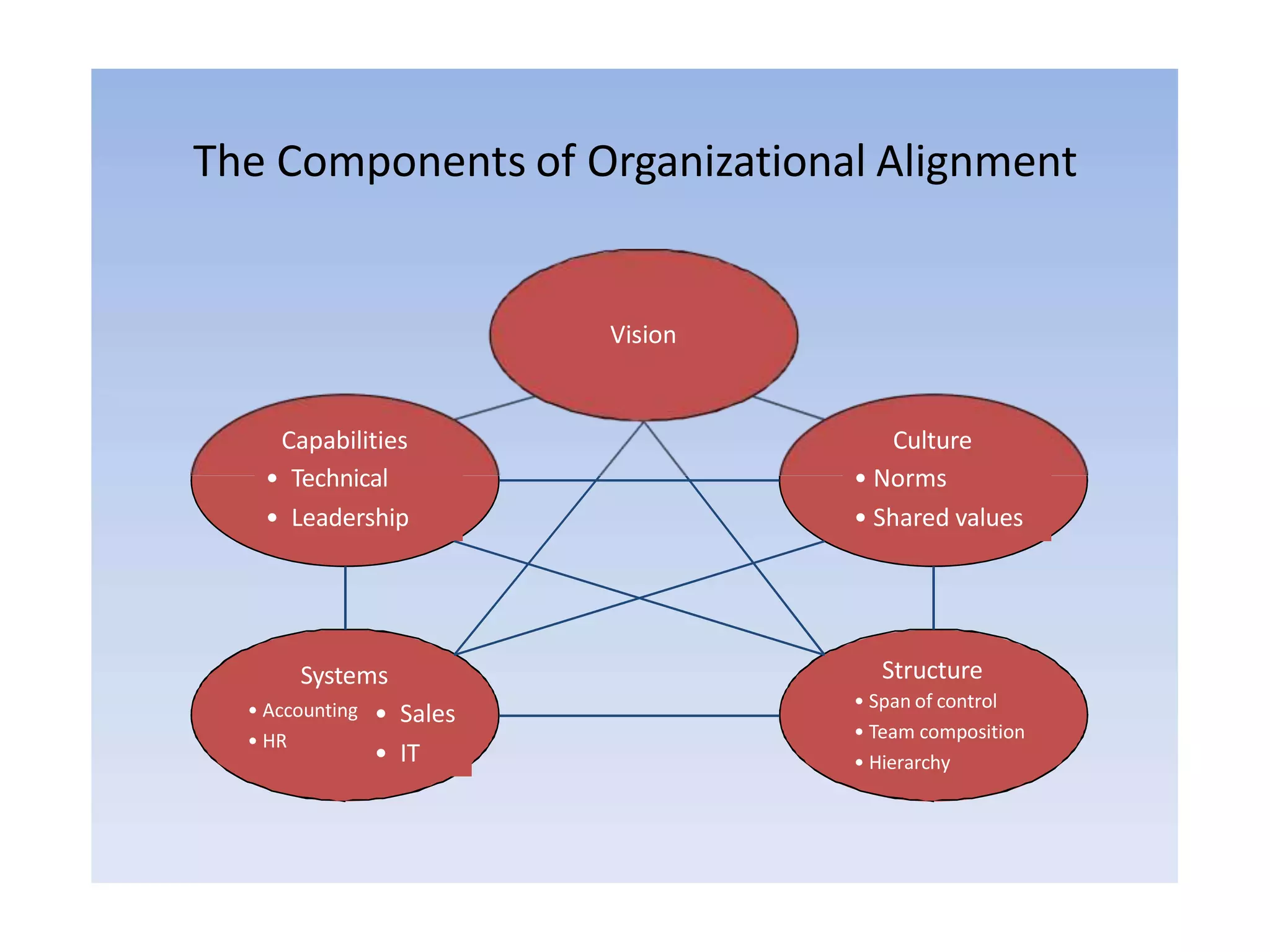
1) The shift from 20th to 21st century organizations, moving from bureaucratic structures to more flexible, non-bureaucratic structures focused on customers and empowering employees.
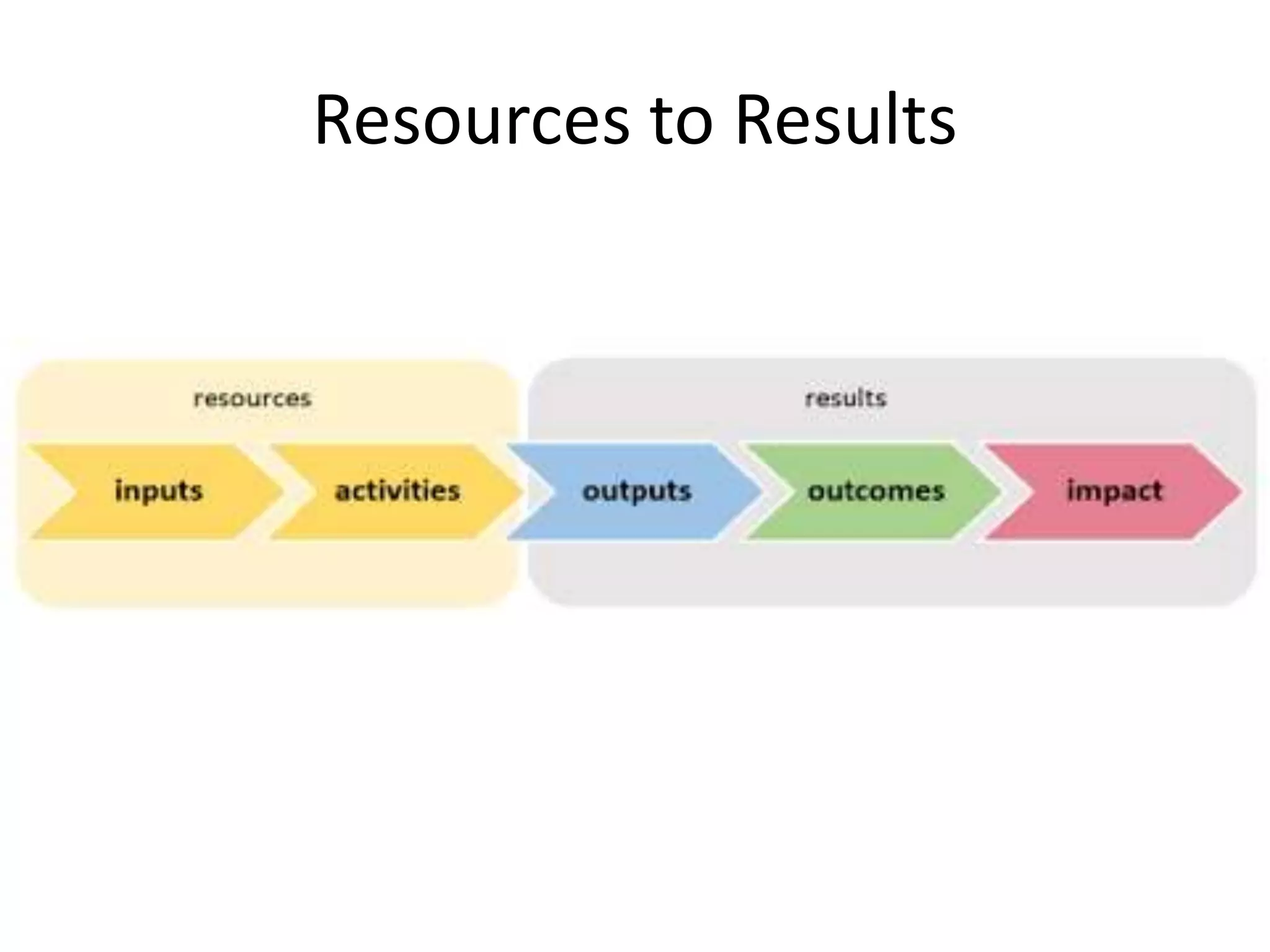
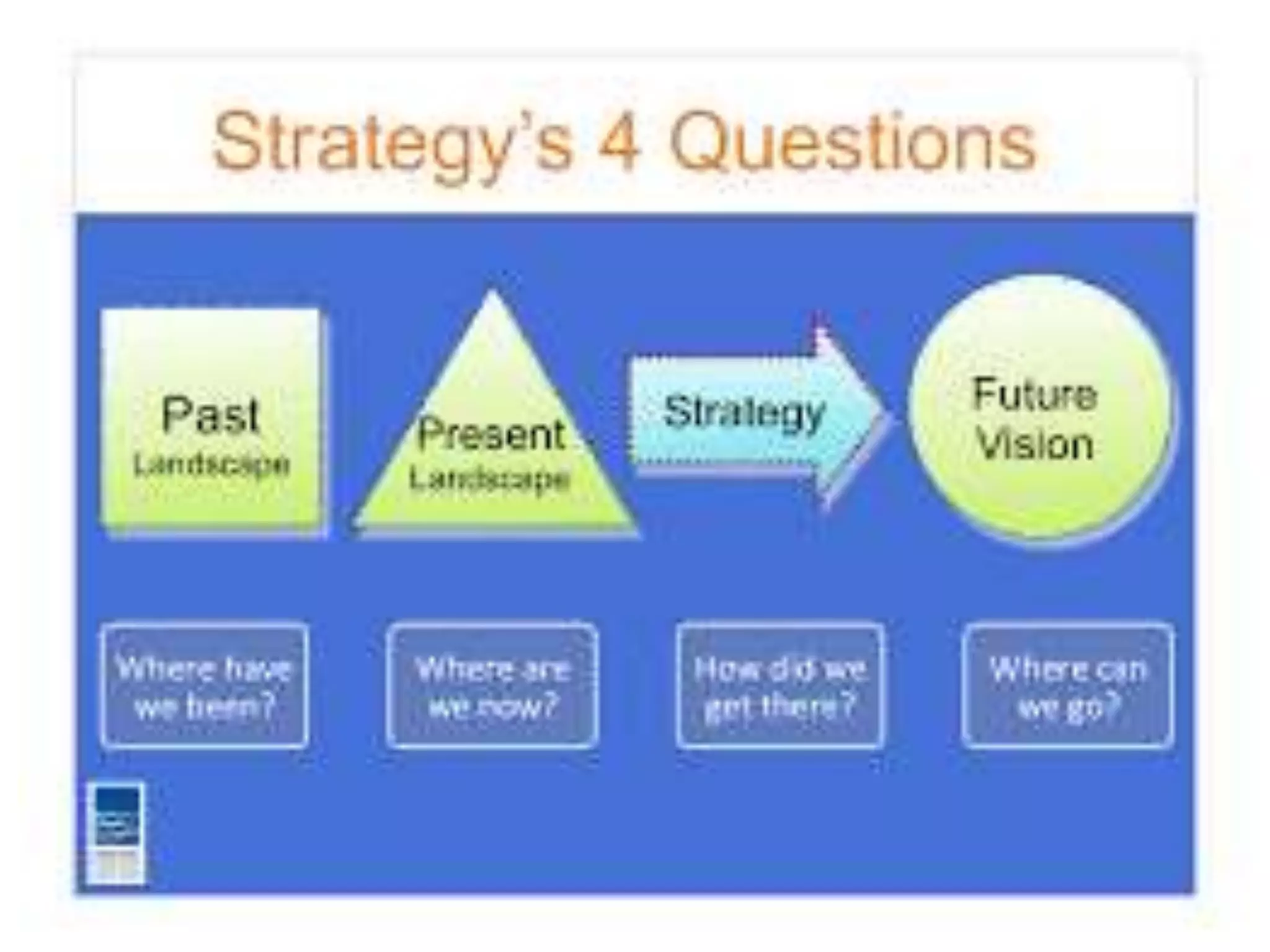
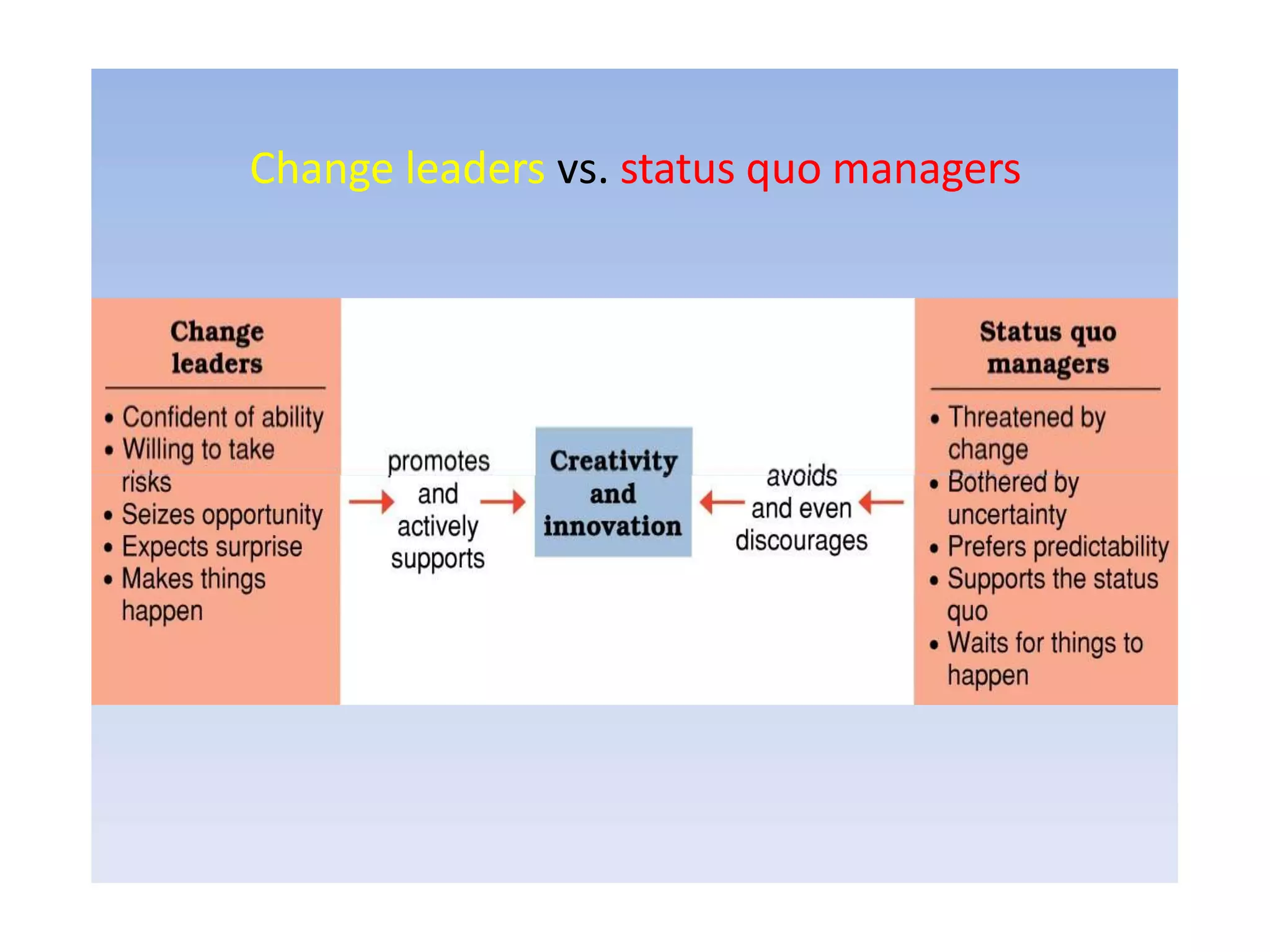
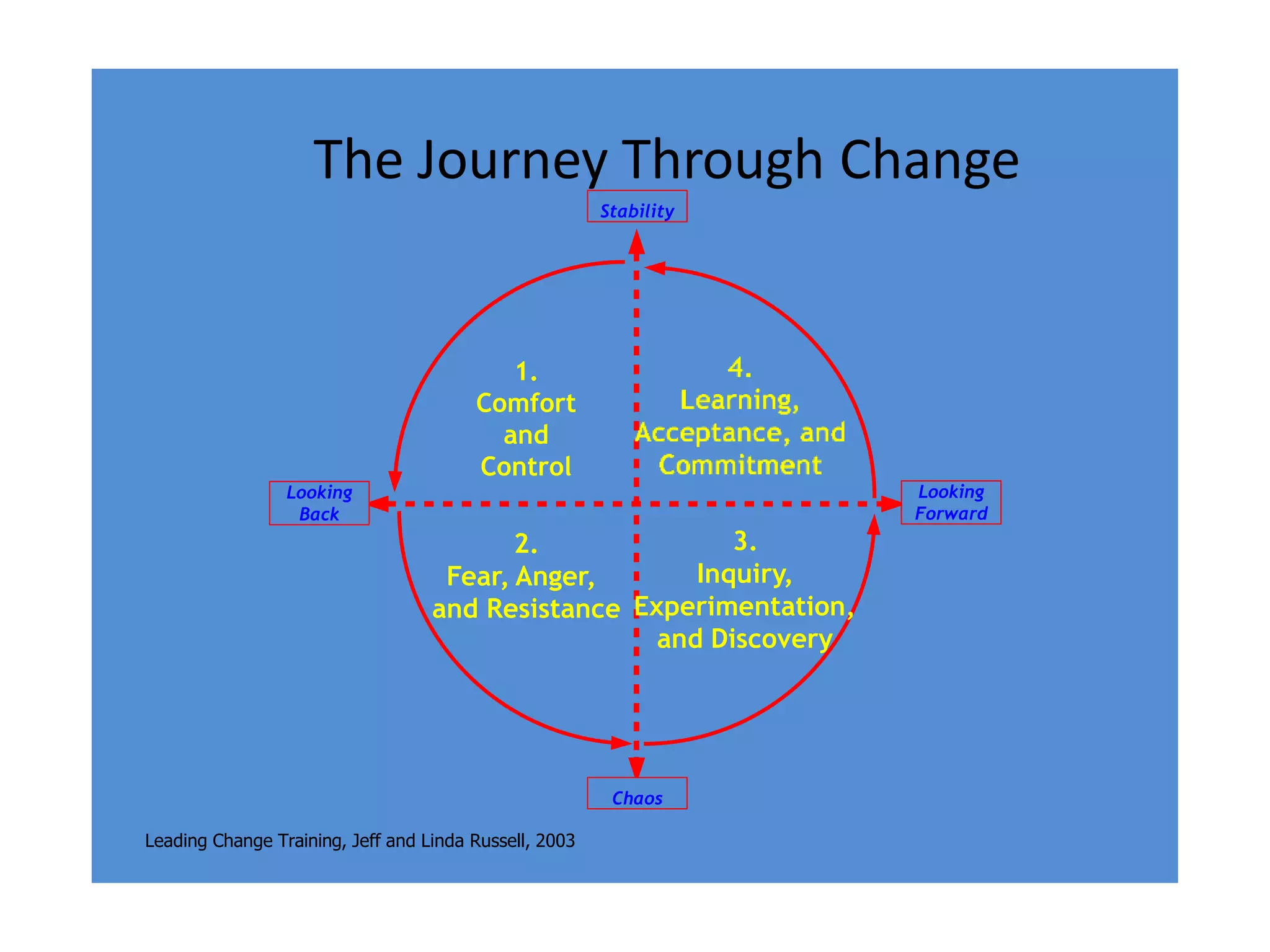
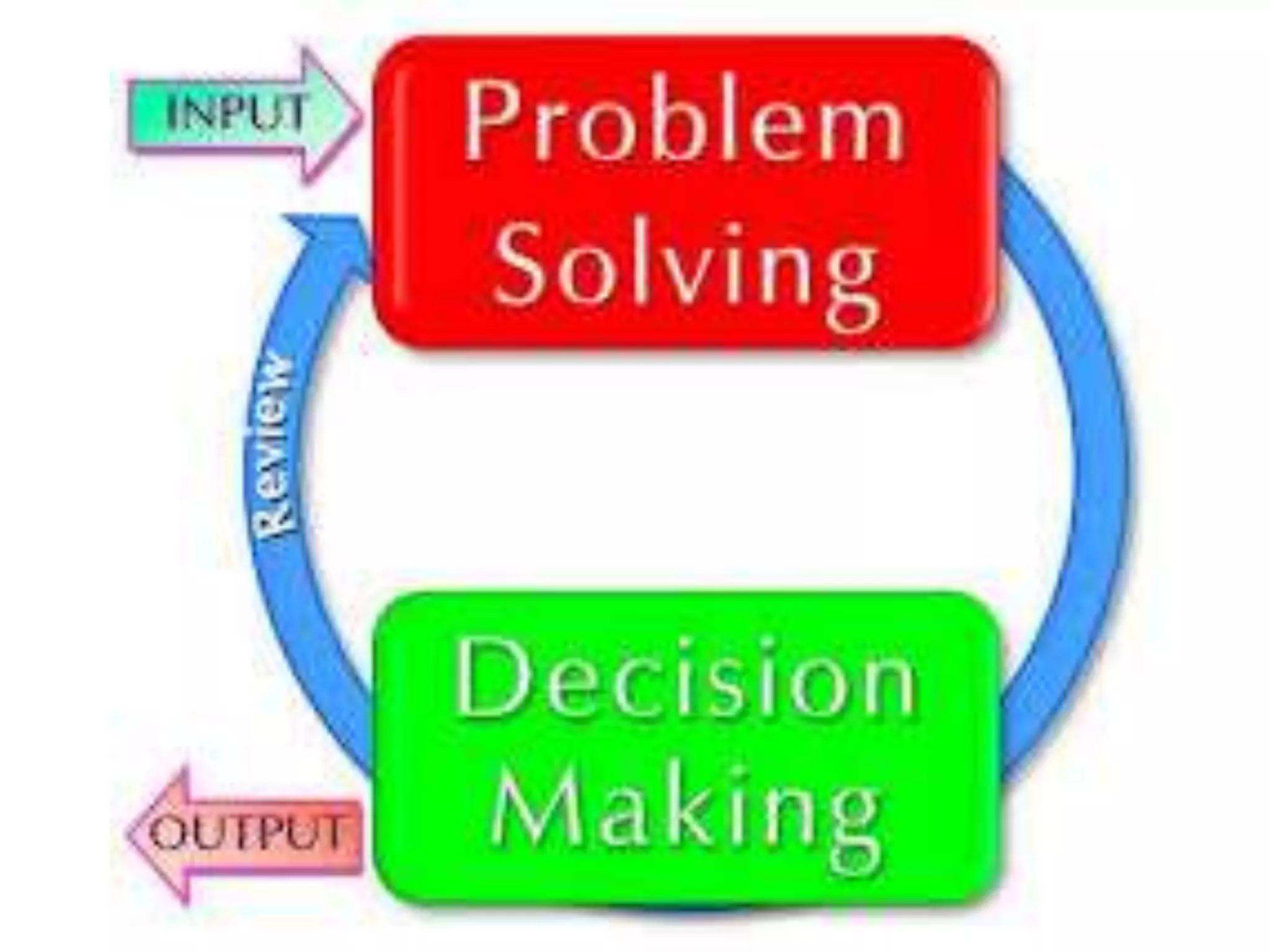
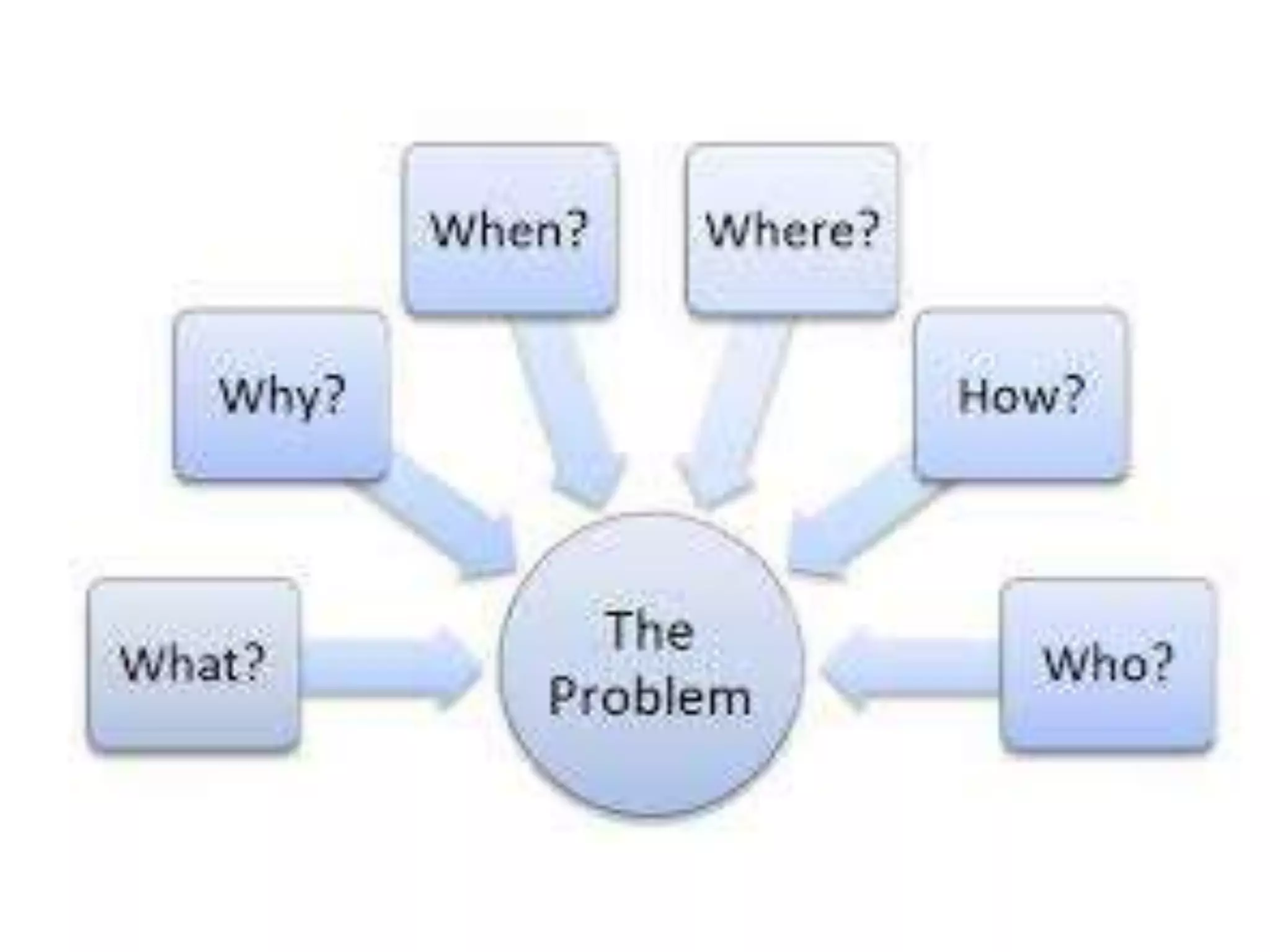
2) The difference between leadership which promotes vision and change, and management which promotes stability and problem-solving. Managing for results focuses on determining important goals and using performance data to improve.
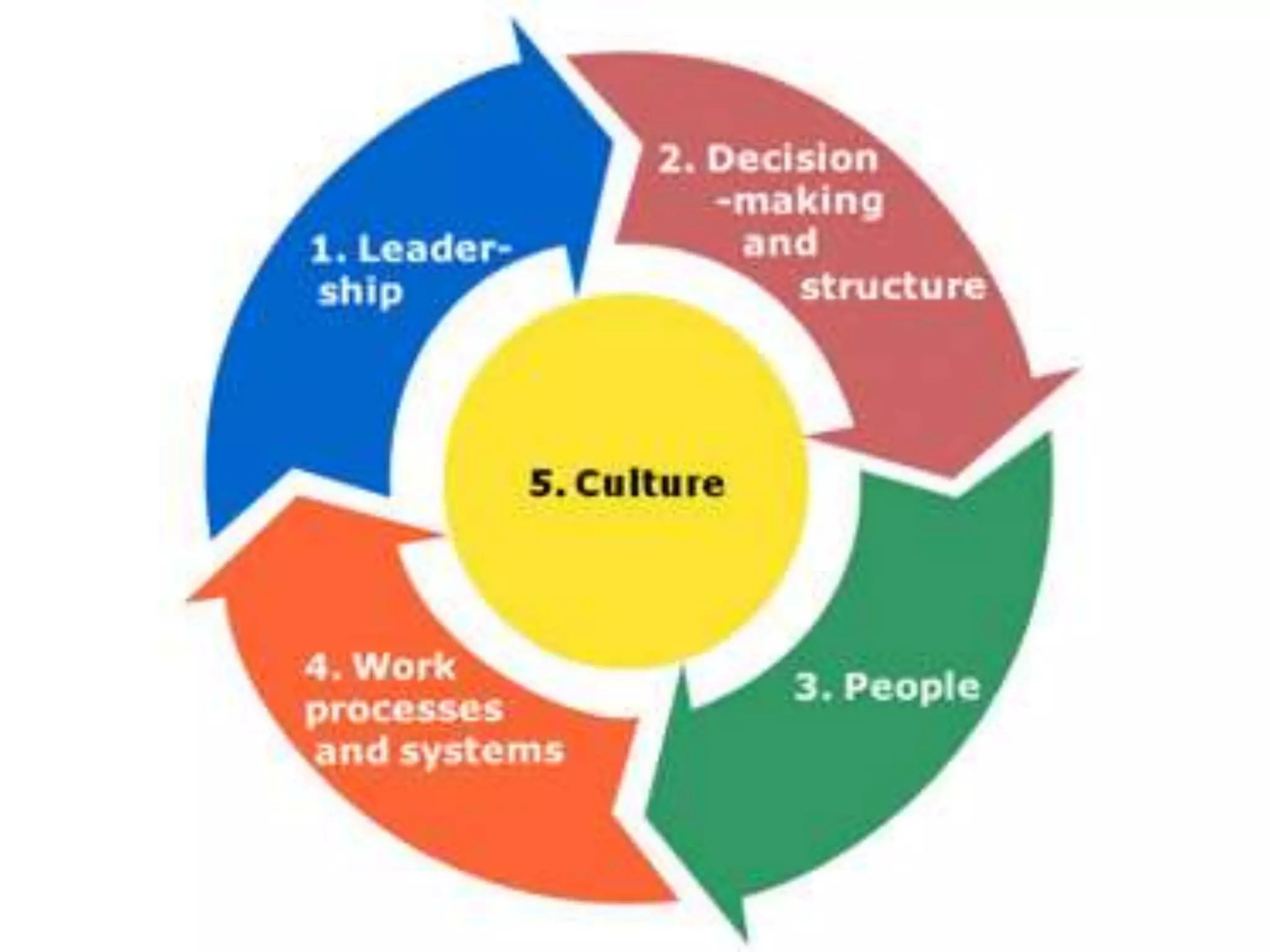
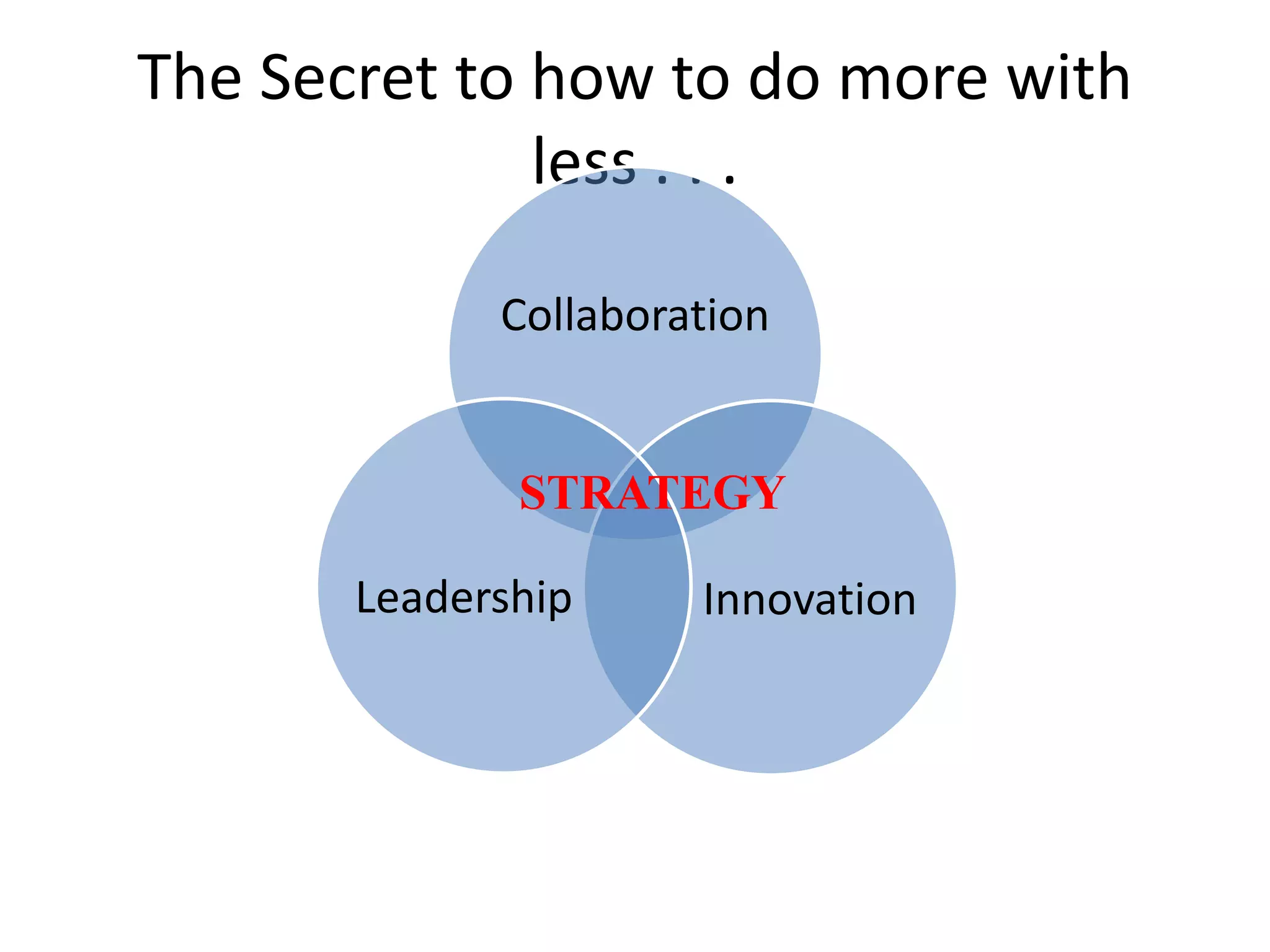
3) Important skills for managing for results including synergy, problem-solving, decision-making, delegation, collaboration, change leadership, and focus.
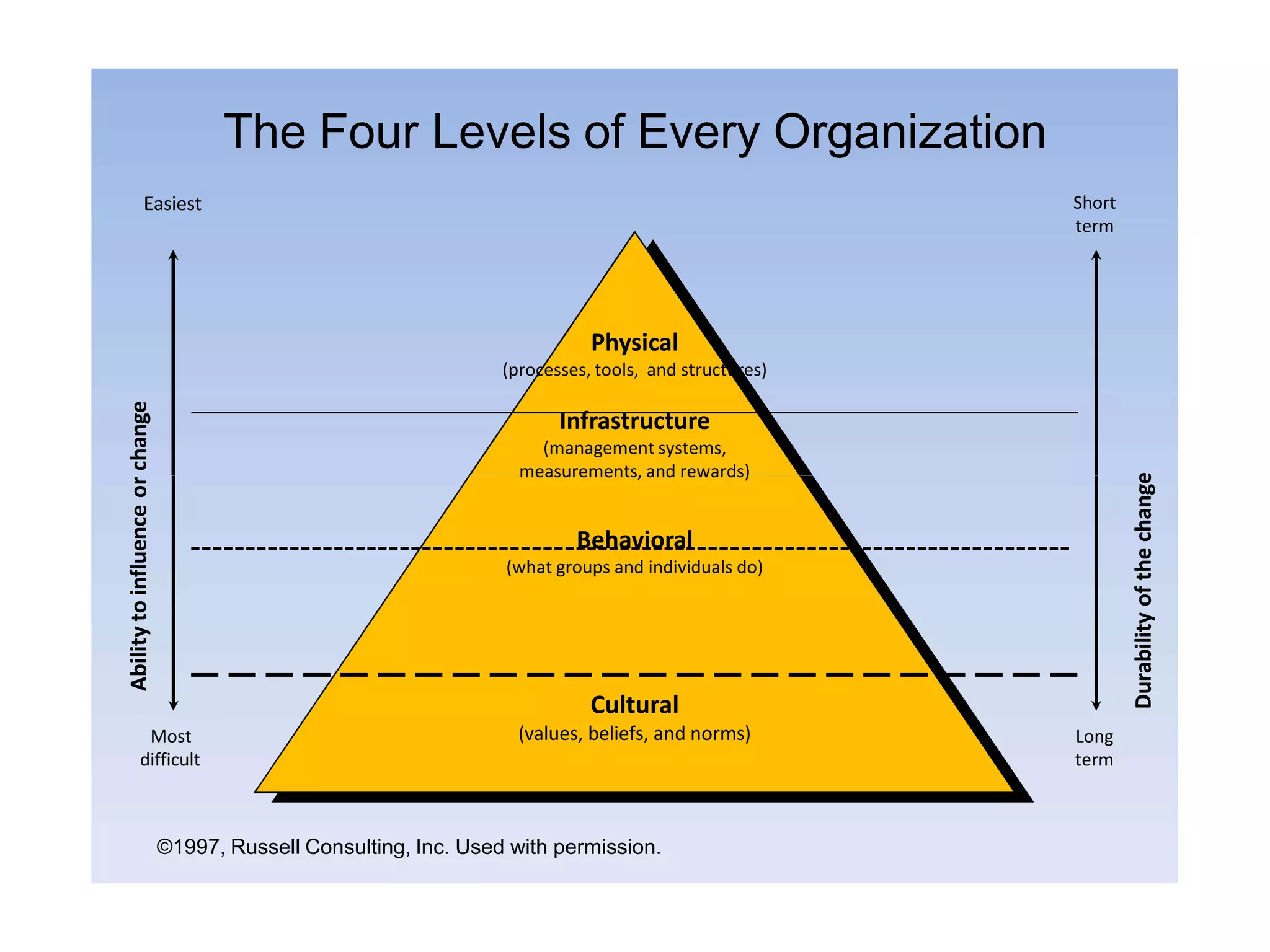
4) How organizations have four levels - cultural, physical, infrastructure, and behavioral - and