This document describes the procedure for preparing a metal specimen for microscopic observation. Key steps include:
1) Cutting a piece of metal, mounting it, and grinding opposite faces flat and parallel.
2) Polishing the specimen using emery paper or disks to remove scratches.
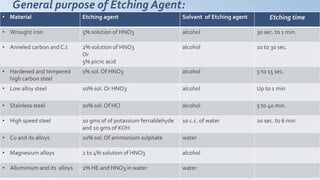
3) Etching the specimen by immersing it in a chemical agent or swabbing it to reveal internal structures.
4) Washing the specimen, drying it, and examining it under a microscope. The goal is to determine properties like material phases, strength, hardness, and failure reasons.