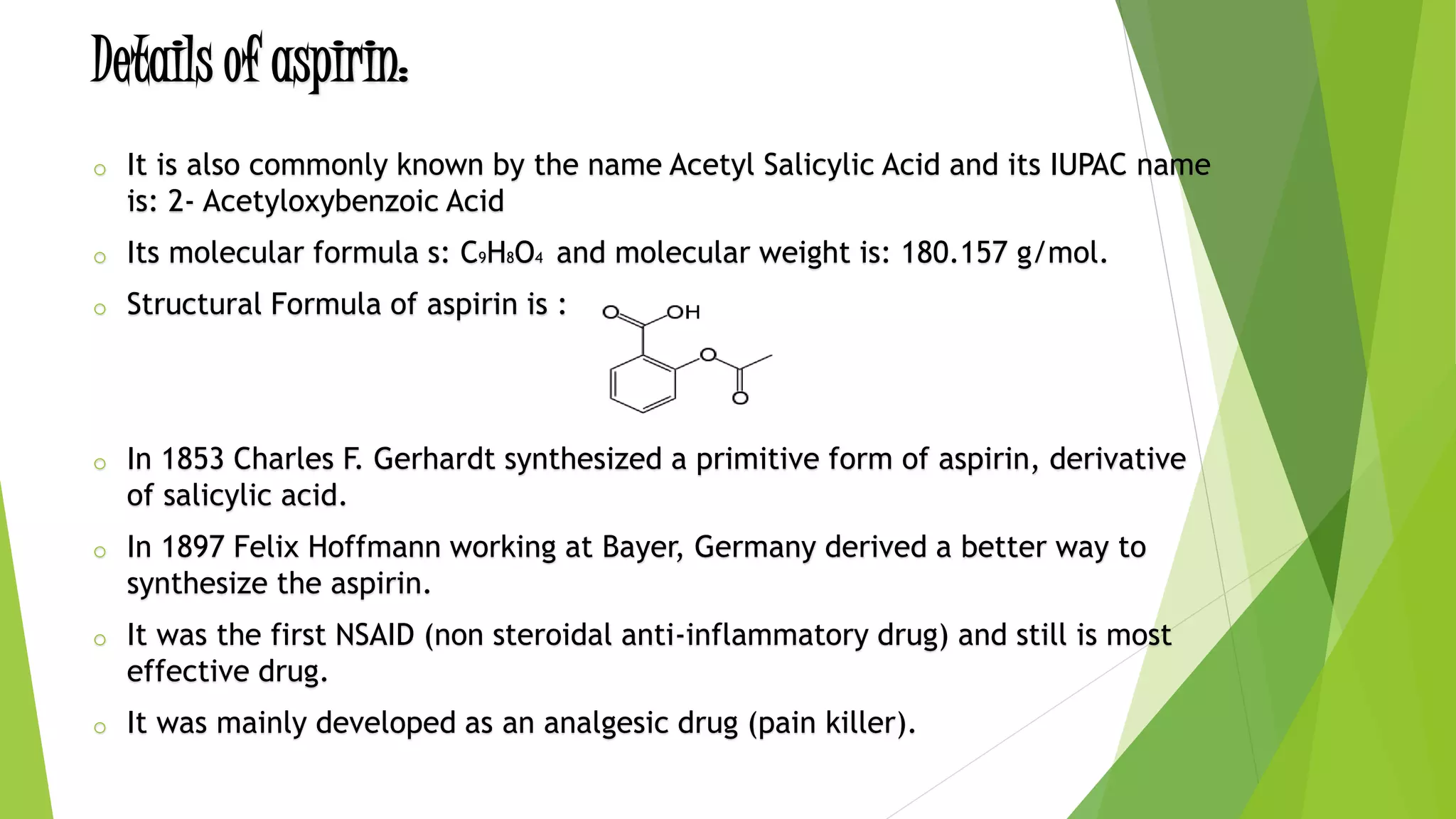
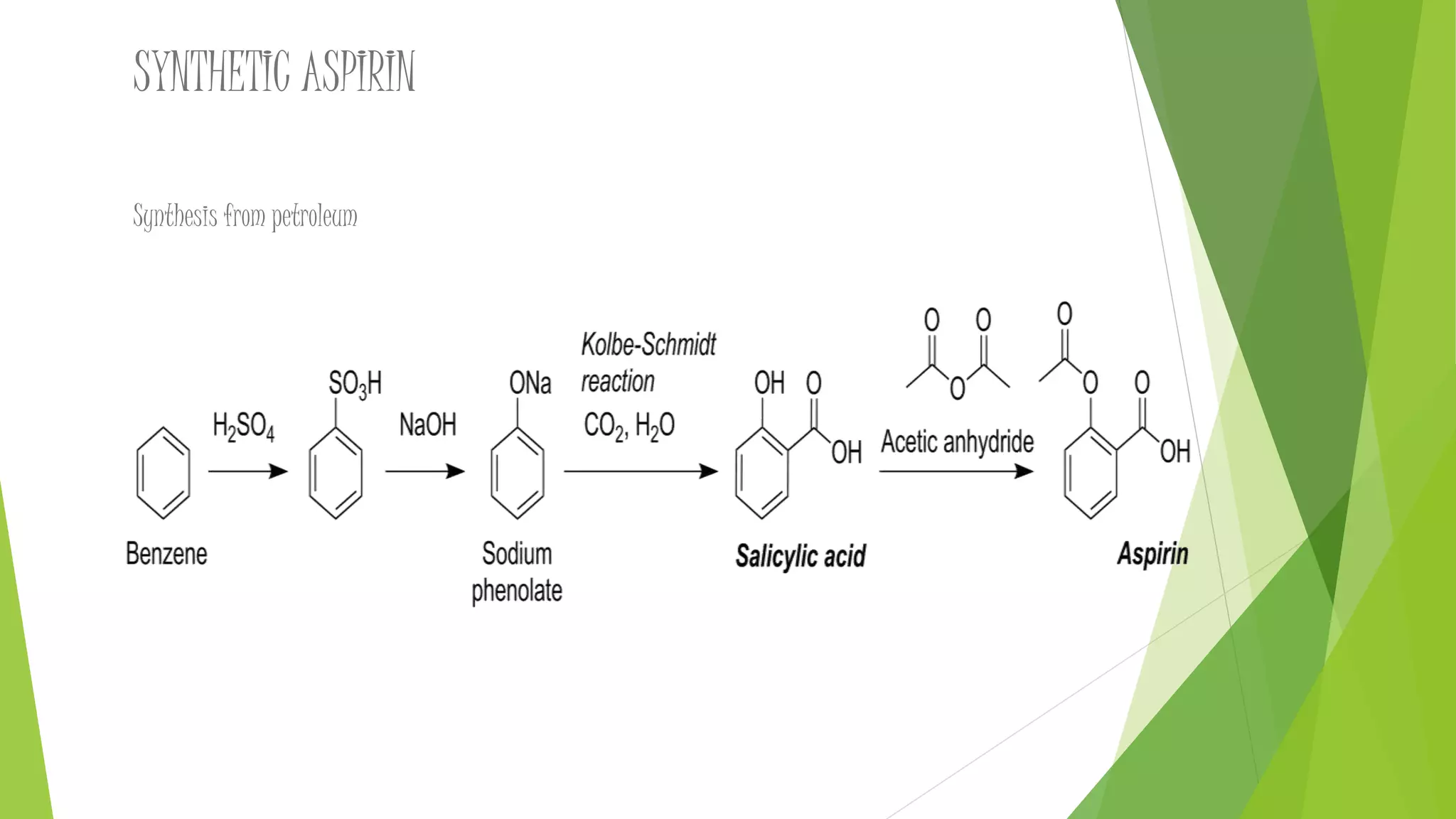
The document discusses the preparation and synthesis of aspirin. Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, is synthesized through the esterification reaction of salicylic acid and acetic anhydride. This reaction converts the hydroxyl group of salicylic acid into an ester group, yielding aspirin and acetic acid as a byproduct. A small amount of sulfuric or phosphoric acid is used as a catalyst. The document also outlines the history, uses, and potential side effects of aspirin.