This document discusses principles of instructional design and the process of developing instructional materials. It covers:
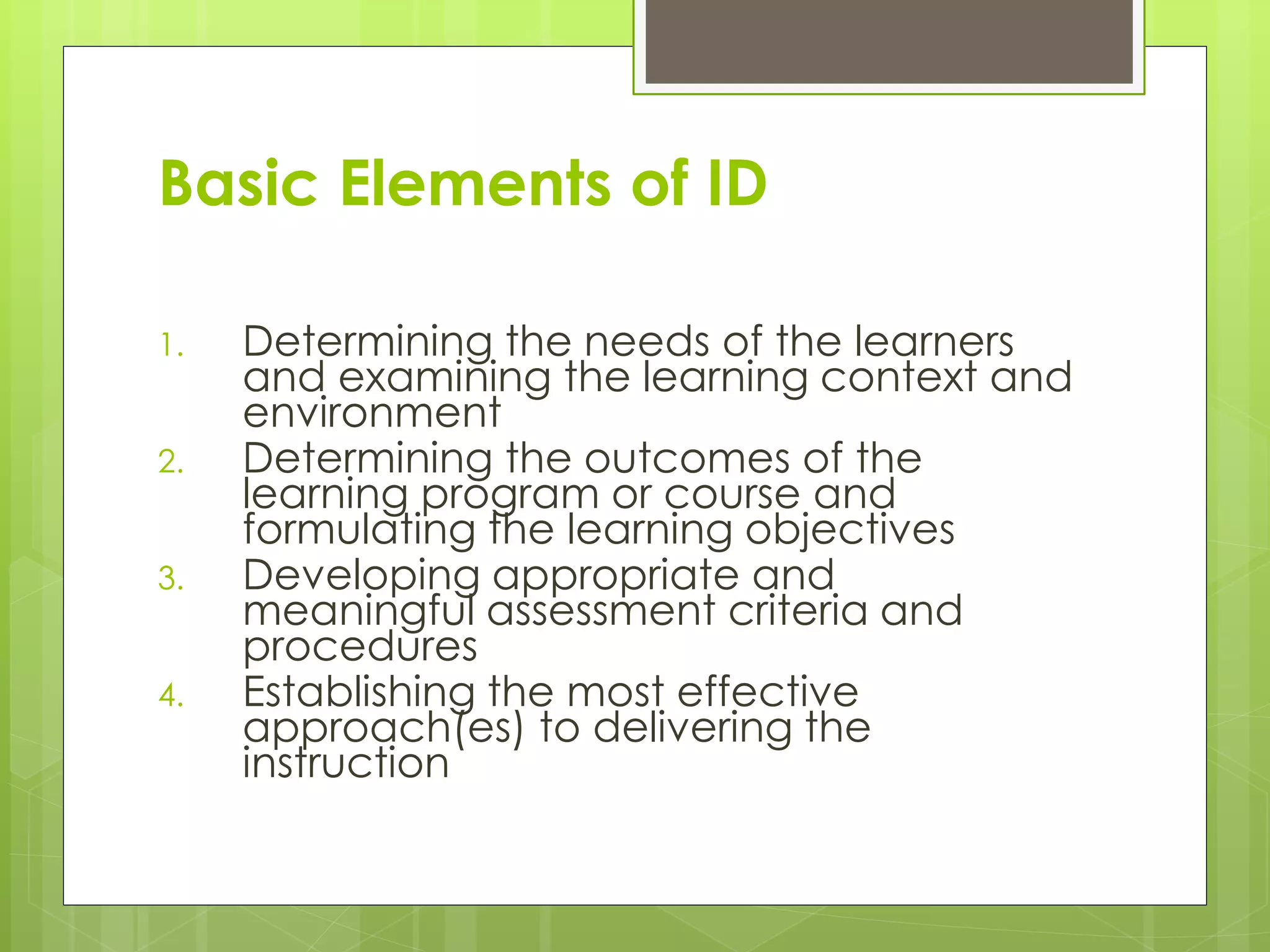
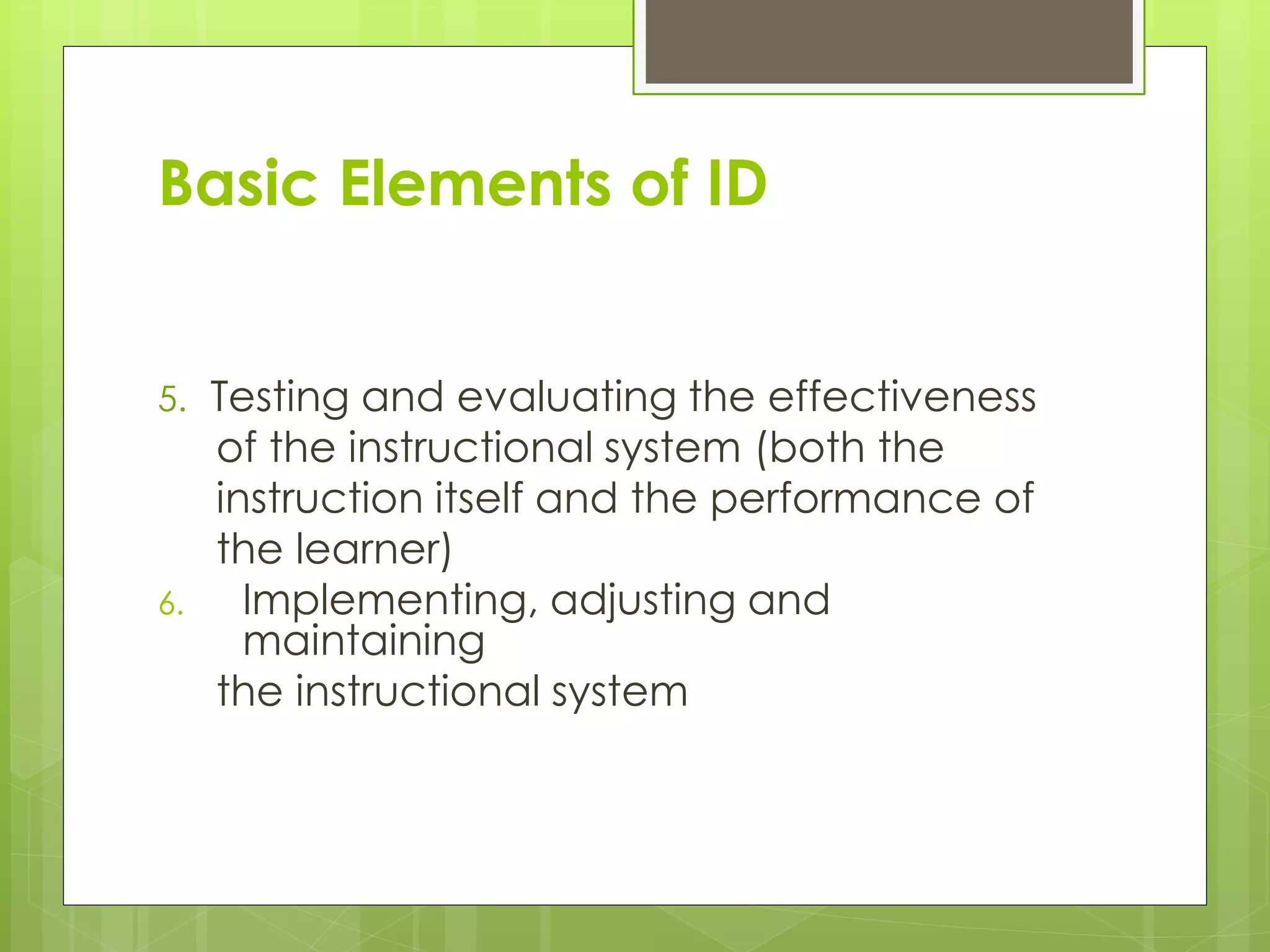
1) The basic elements of instructional design which include determining learner needs, learning objectives, assessments, instructional approaches, testing effectiveness, and maintaining materials.
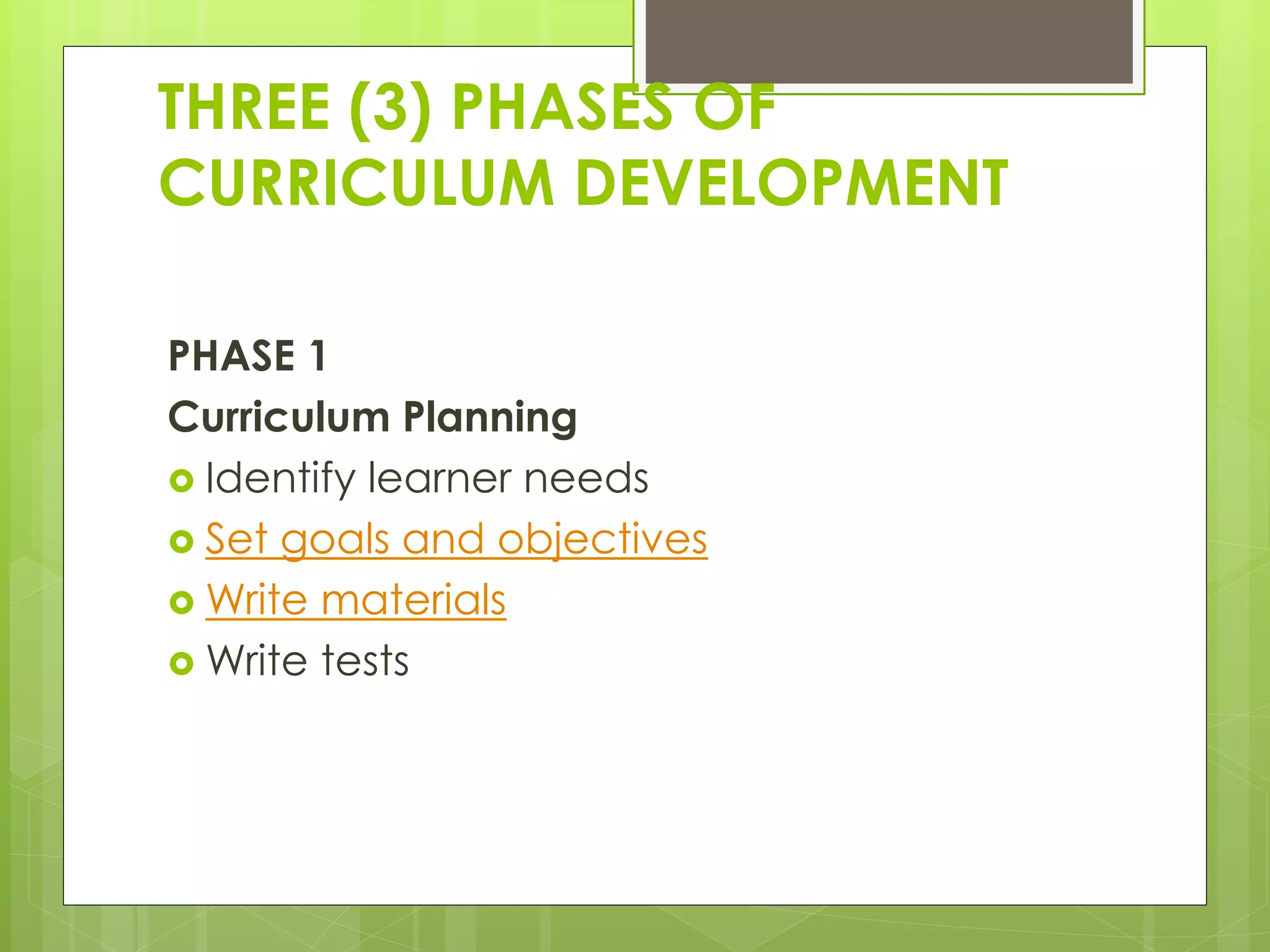
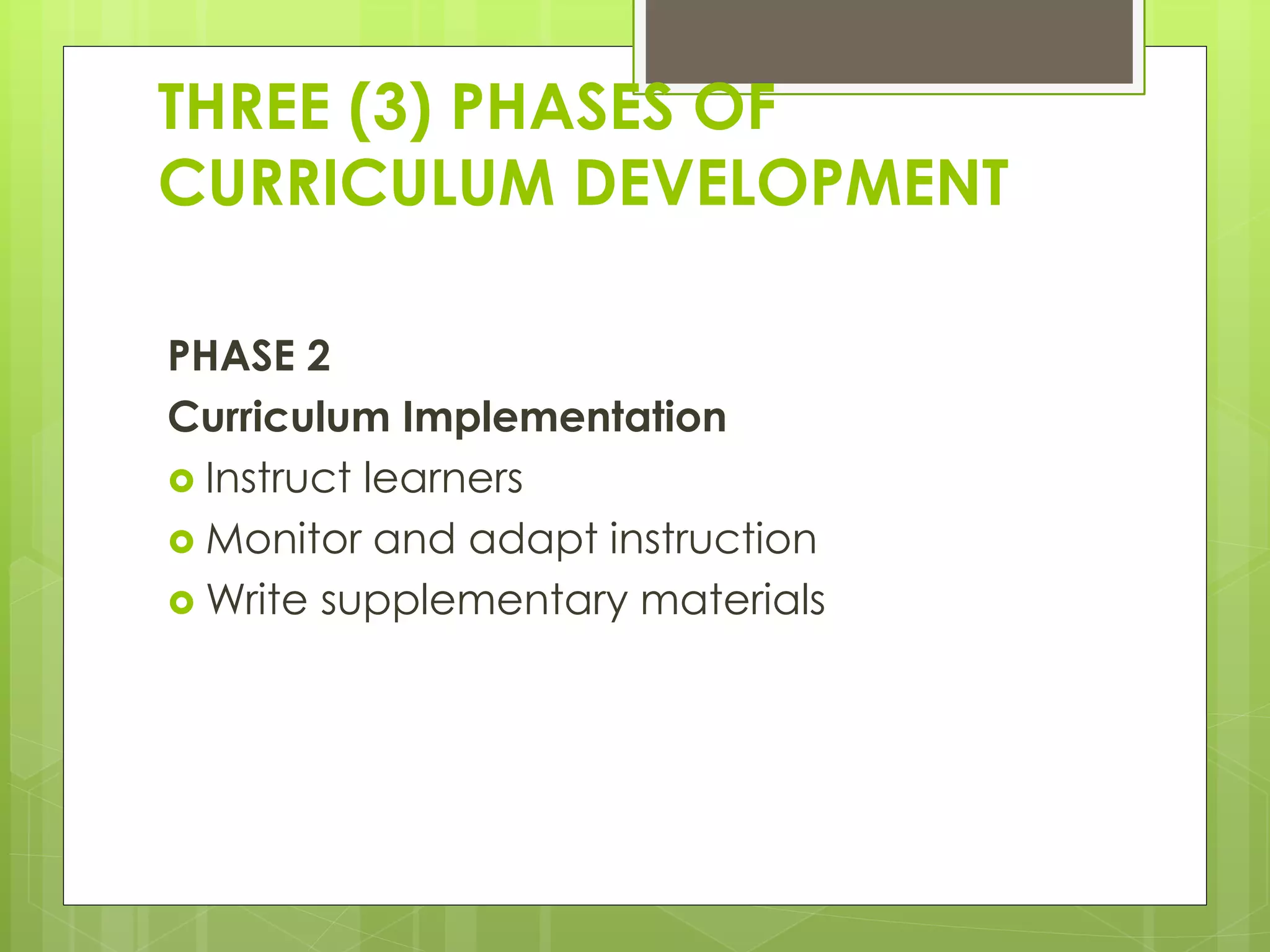
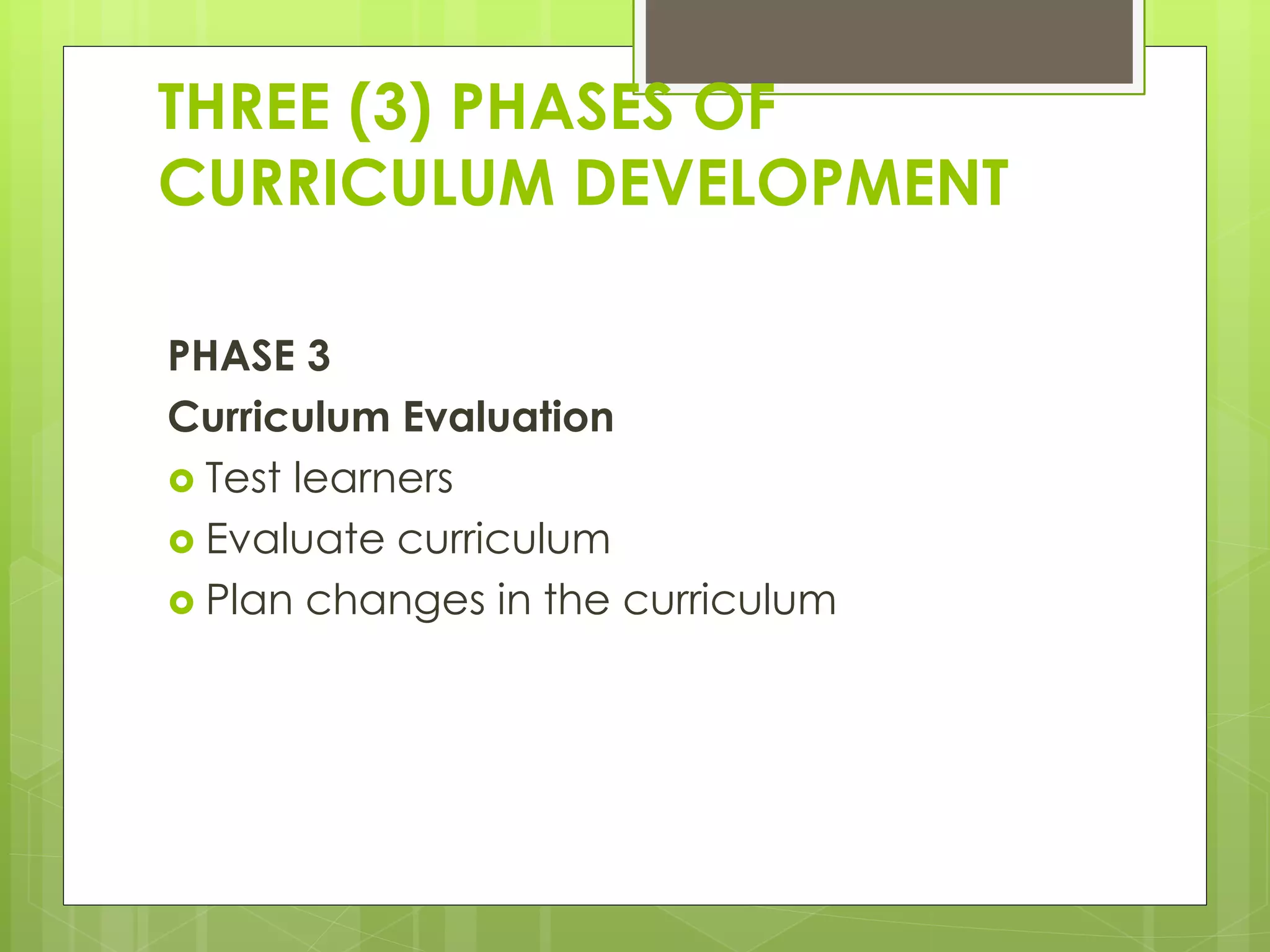
2) The three phases of curriculum development - planning, implementation, and evaluation.
3) Factors to consider in materials design such as learning theories, specifications, formats, and authentic versus created materials.