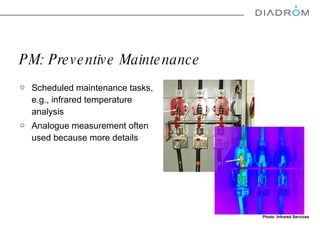
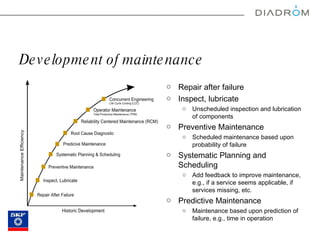
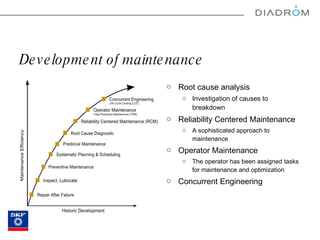
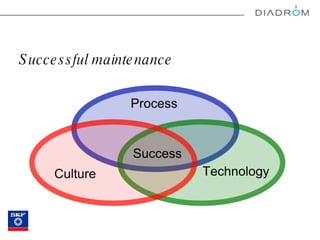
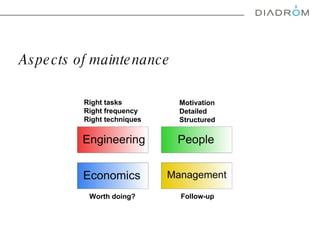
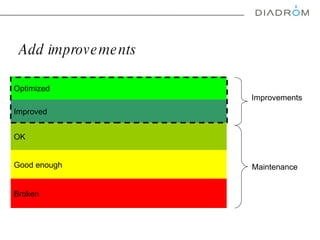
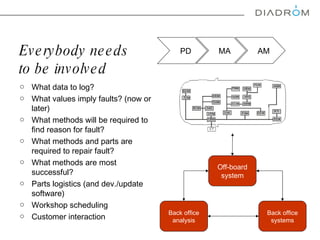
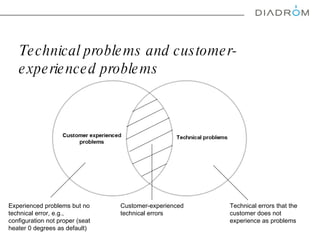
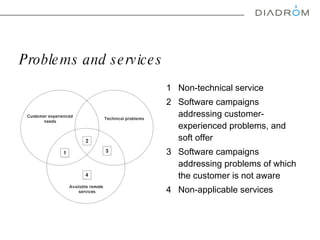
The document discusses various maintenance strategies, focusing on predictive maintenance (PdM), preventive maintenance (PM), and condition-based maintenance (CBM). It highlights examples from the automotive industry, specifically BMW and Volvo, illustrating how these strategies can improve customer satisfaction and service efficiency. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of sophisticated maintenance approaches in enhancing product reliability and customer service while reducing operational costs.
![Predictive Maintenance Fredrik Ljungberg [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/predictivemaintenance-100113103705-phpapp01/75/Predictive-Maintenance-1-2048.jpg)