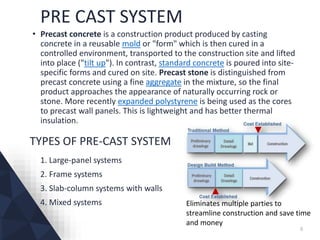
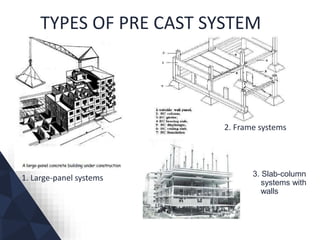
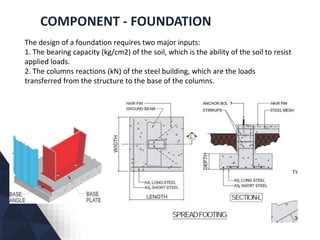
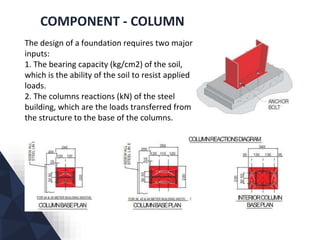
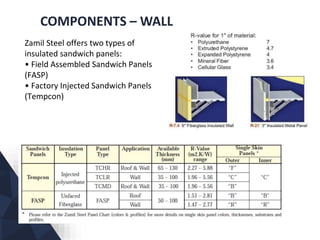
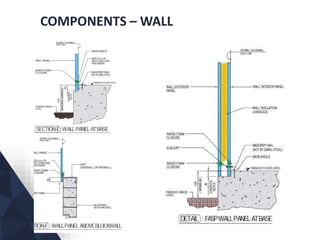
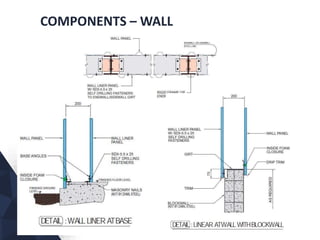
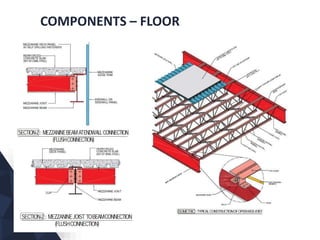
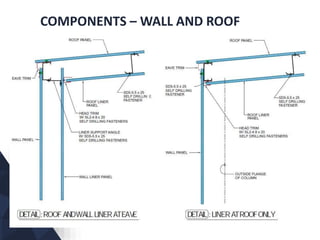
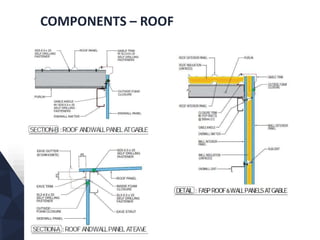
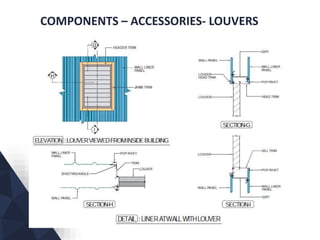
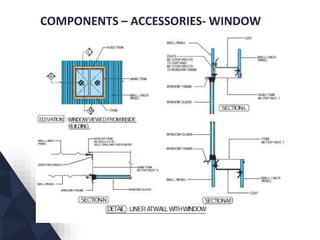
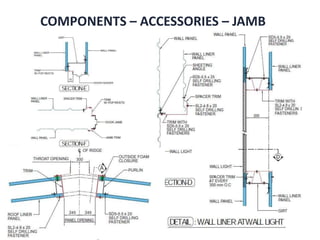
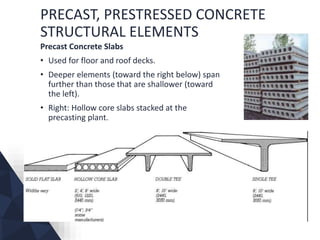
The document discusses prefabricated, precast, and prestressed concrete, emphasizing the advantages such as high quality, efficiency, and time savings, as well as disadvantages like careful handling and potential transportation costs. It outlines various applications, types of systems, and components involved in the construction of industrial and commercial buildings. Additionally, it details methods of prestressing concrete, including pre-tensioning and post-tensioning, along with their respective pros and cons.