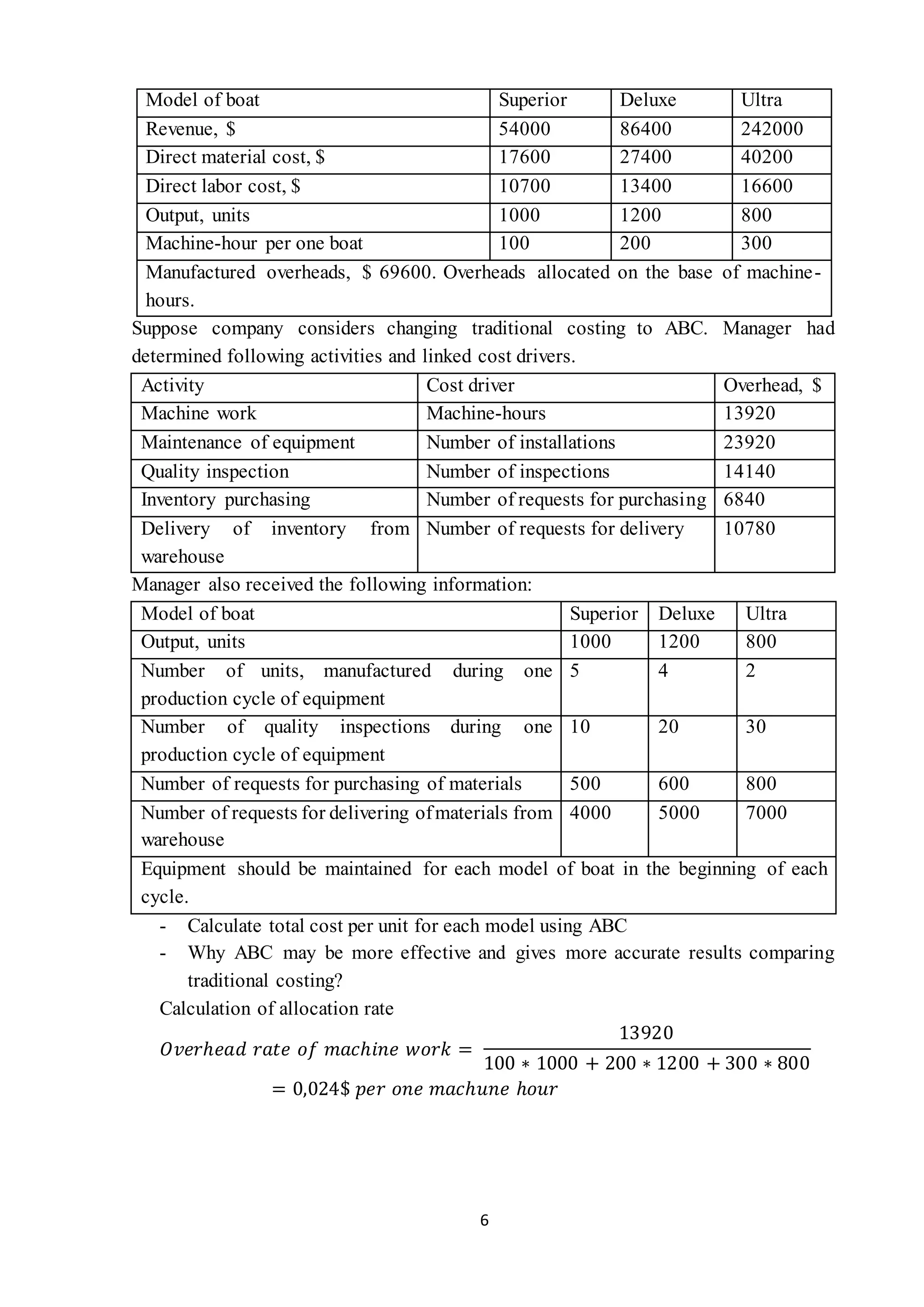
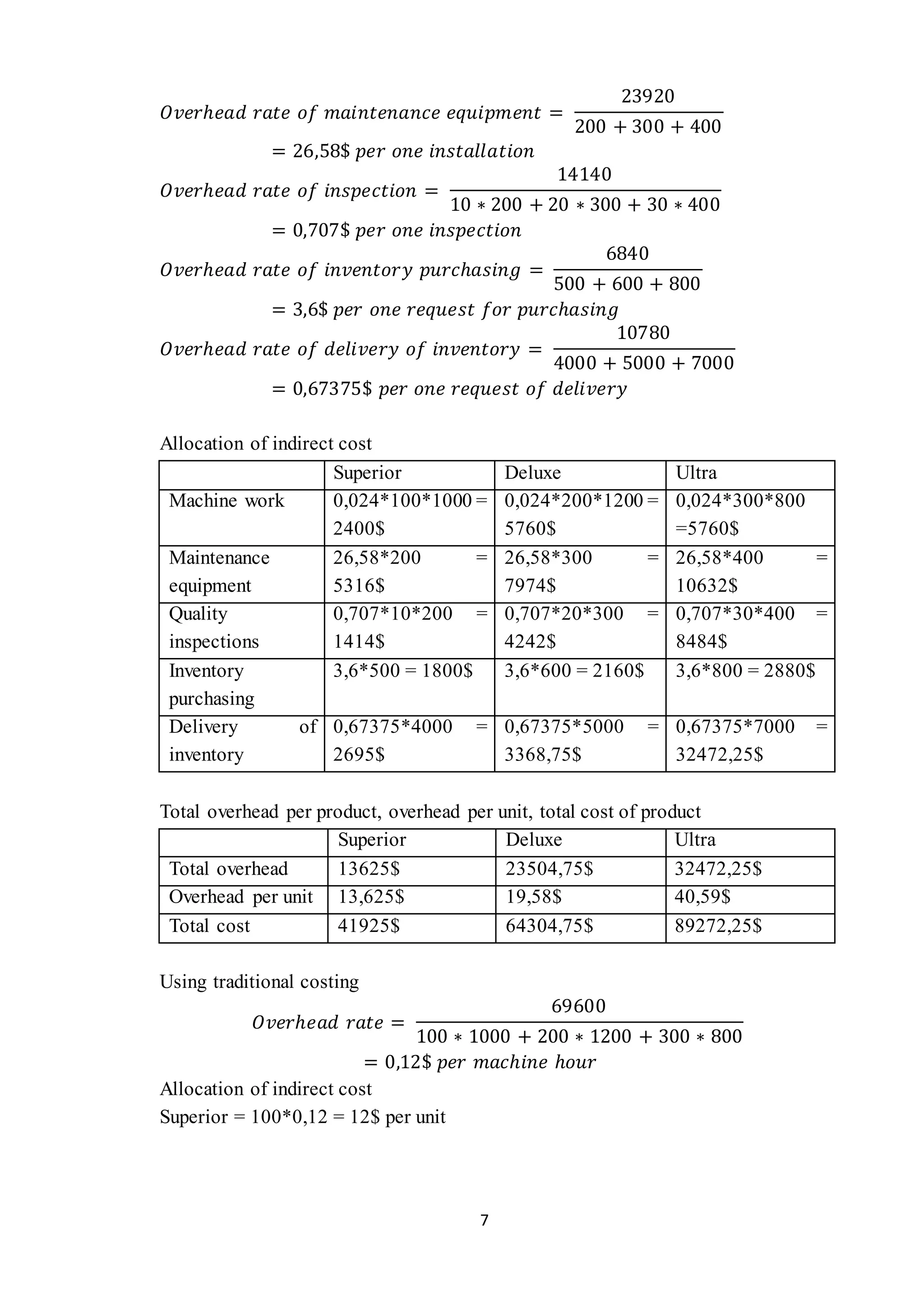
The document provides information on cost allocation and absorption costing for several companies. It includes:
- Calculating total cost per unit for a company using absorption and marginal costing, finding inventory value differs between the two methods.
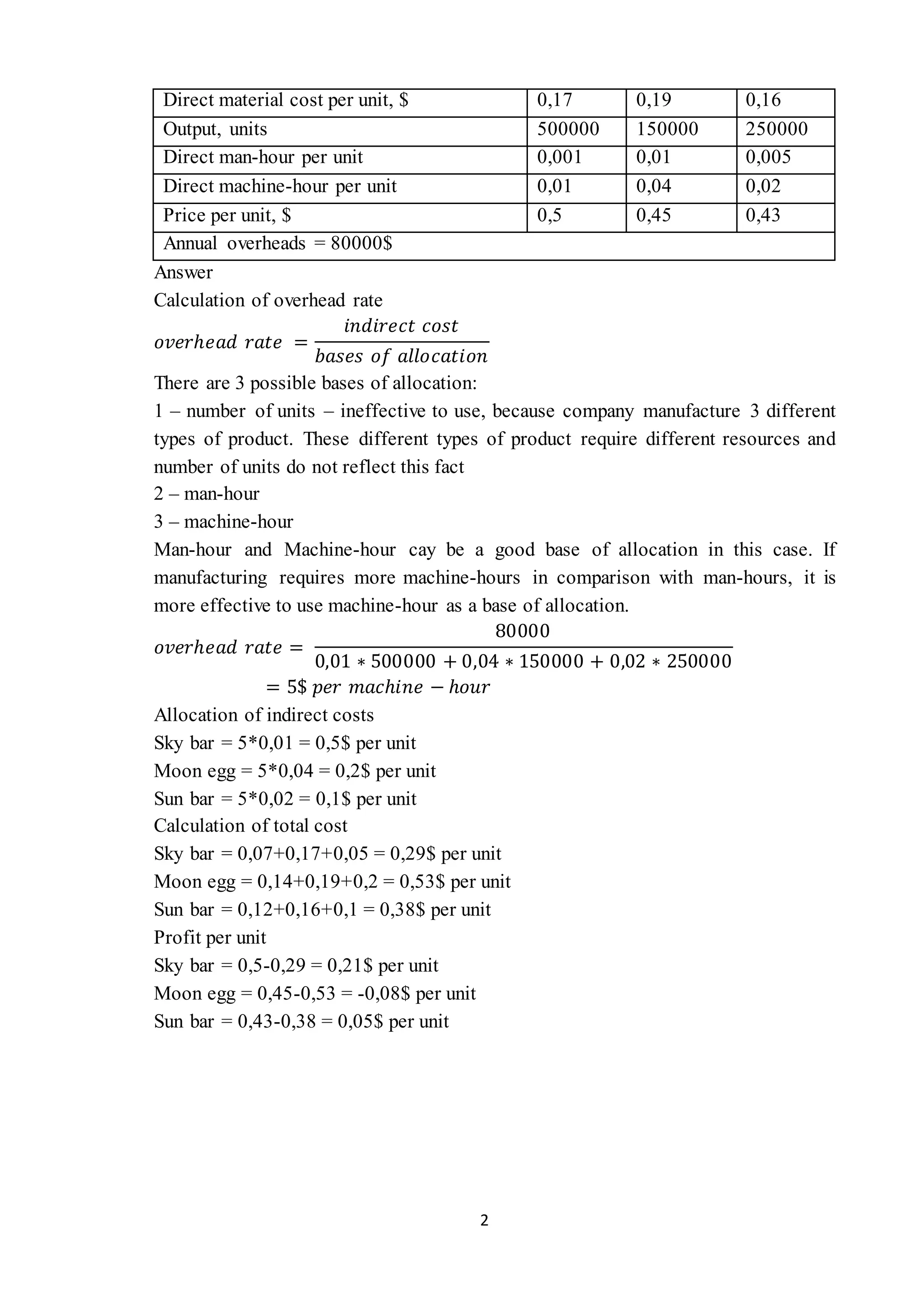
- Analyzing production costs and profitability of different chocolate products using absorption costing, finding one product is unprofitable.
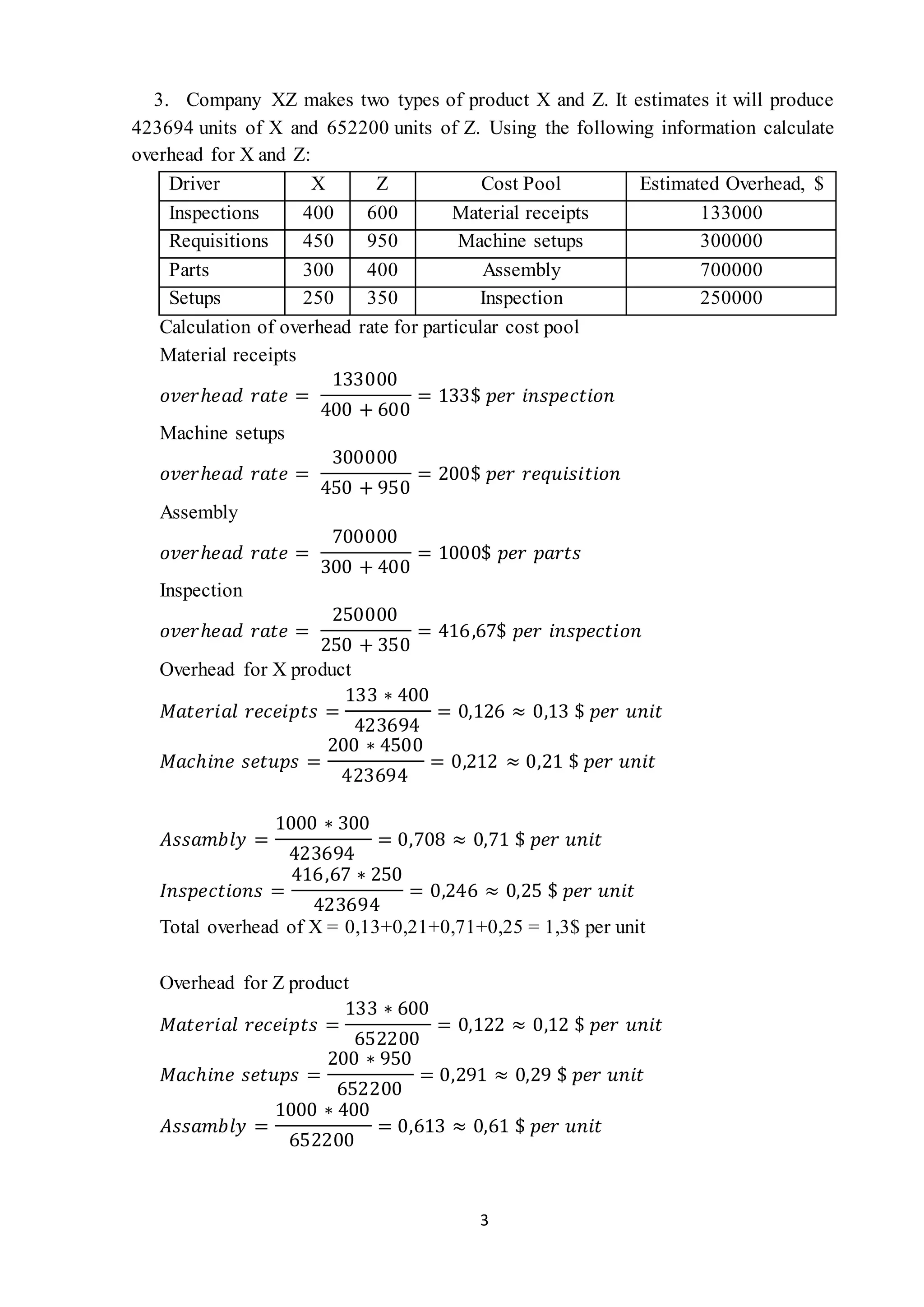
- Calculating overhead rates allocated to different cost pools and products for two companies, determining total overhead costs per unit for each product.
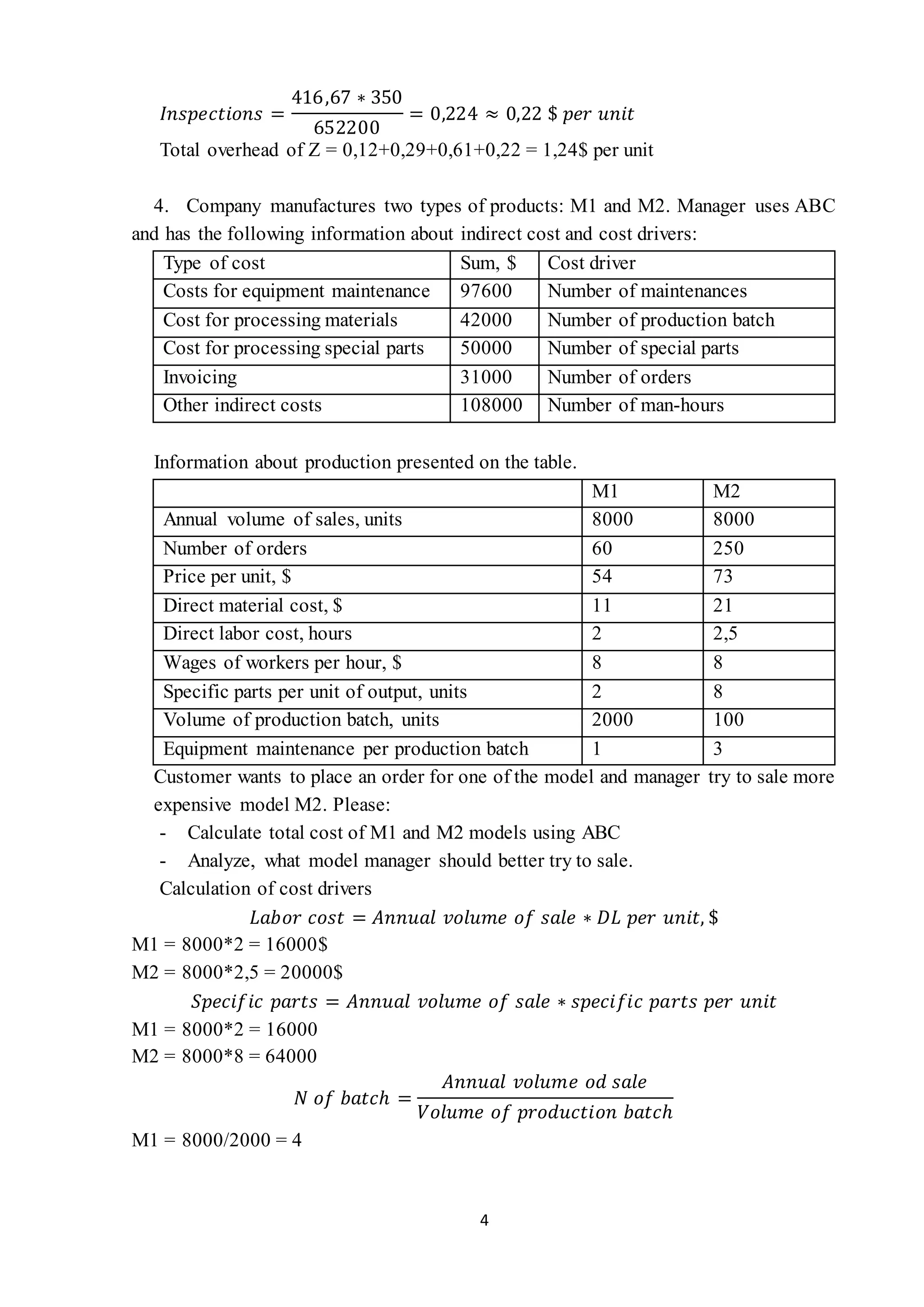
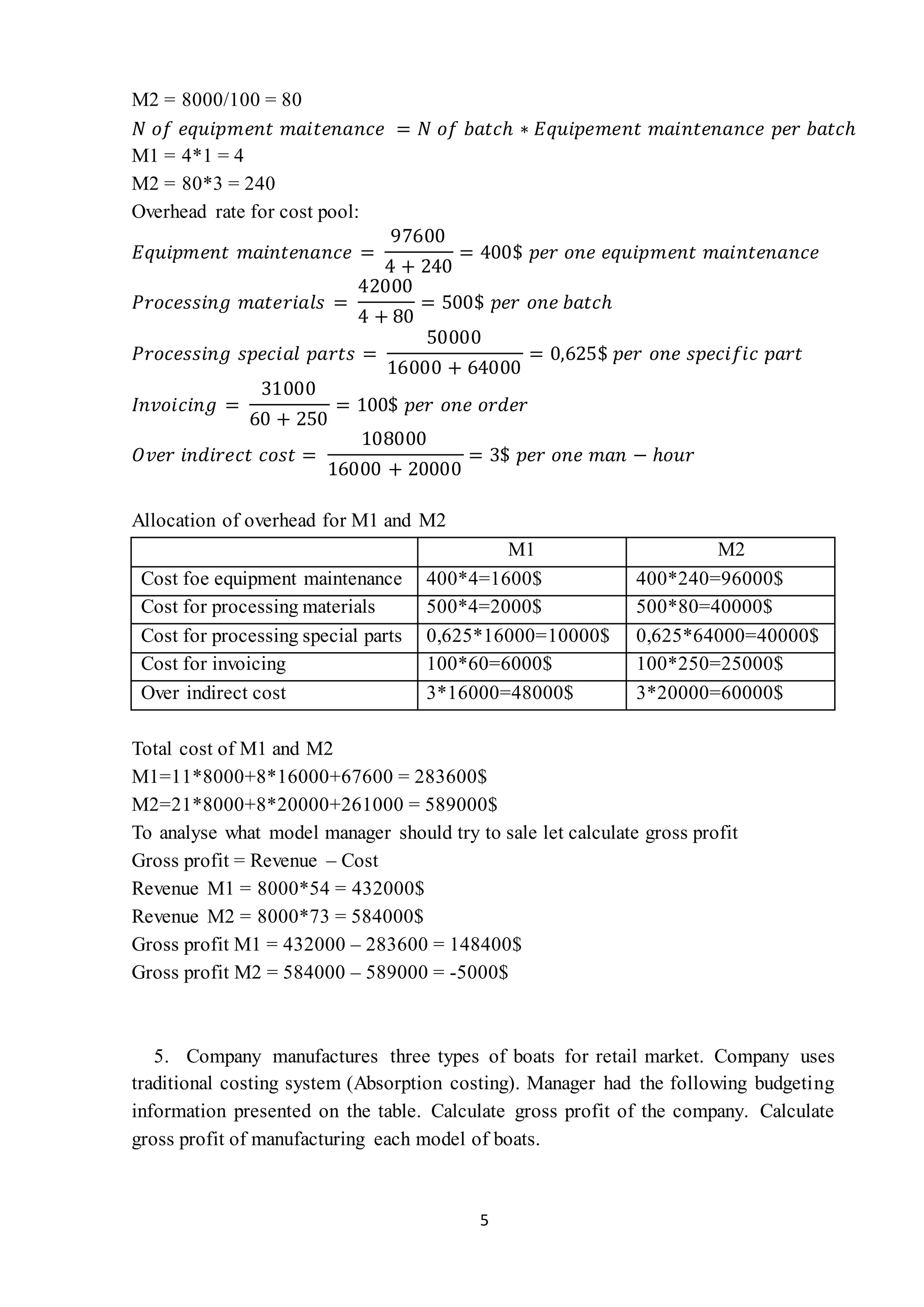
- Calculating overhead costs for two models using activity-based costing and drivers, finding one model is more expensive to produce.