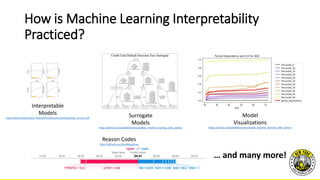
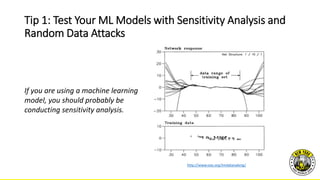
The document provides practical tips for interpreting machine learning models, emphasizing the importance of model interpretability for both social and commercial reasons. It outlines methods such as sensitivity analysis, human quality assessment, and various model visualization techniques to ensure trustworthy explanations. The document also discusses the relevance of explainability in regulated industries and offers specific guidelines for improving model transparency and understanding.