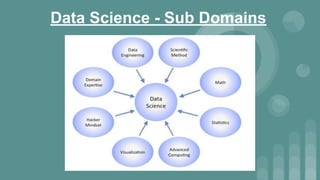
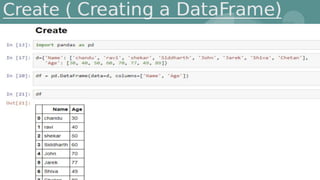
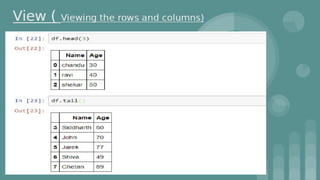
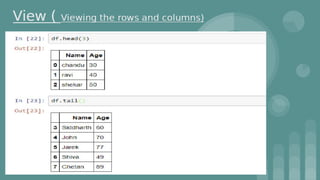
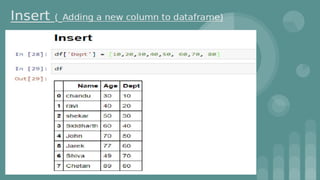
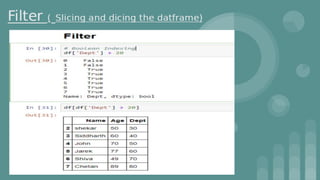
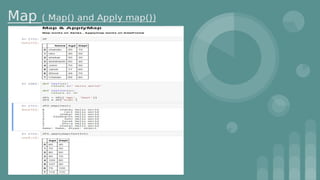
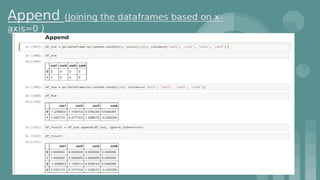
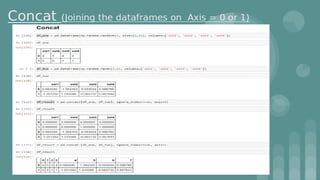
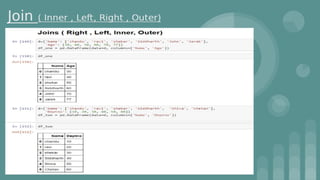
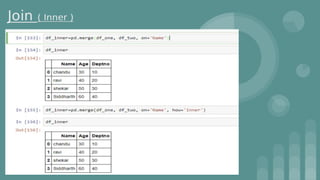
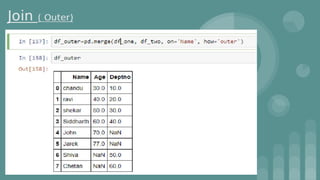
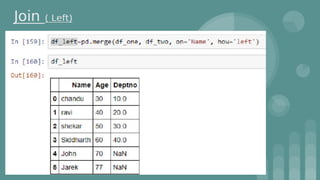
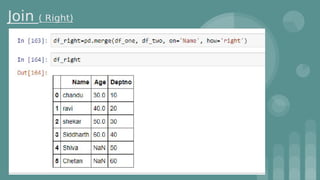
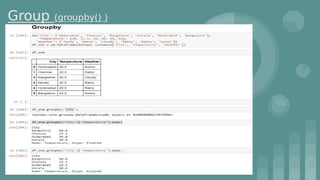
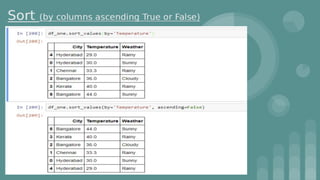
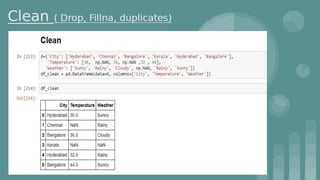
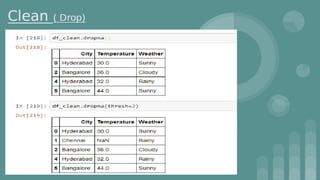
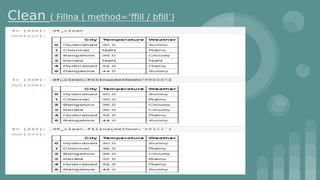
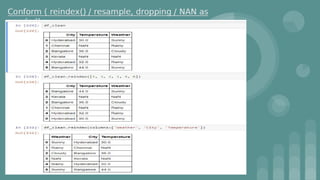
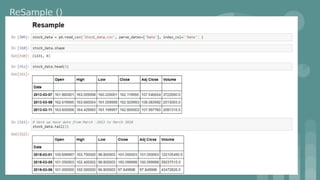
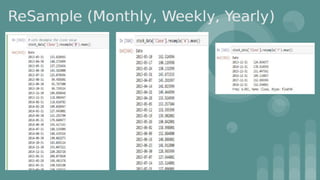
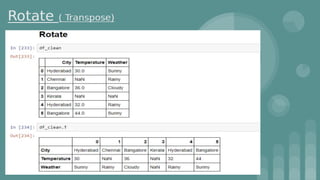
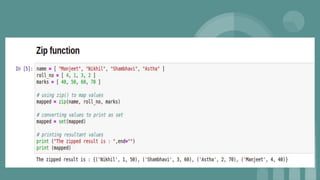
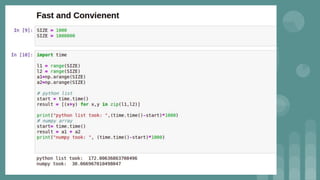
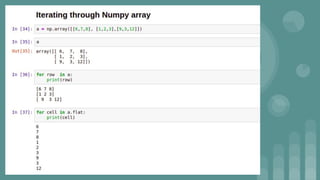
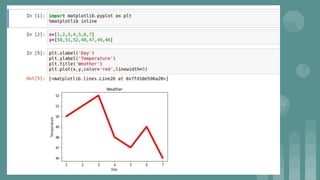
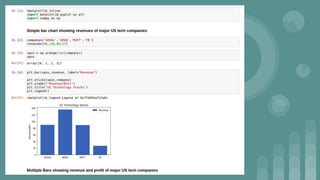
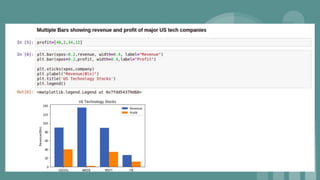
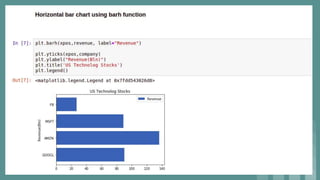
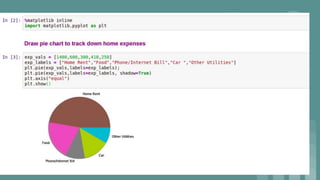
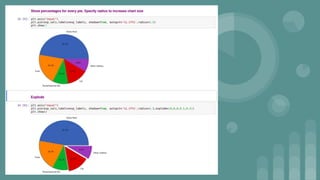
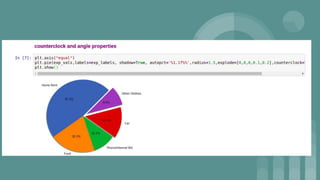
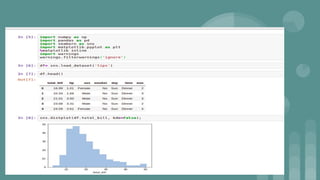
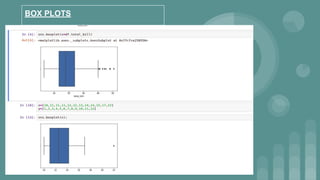
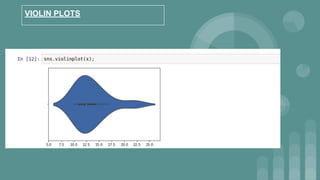
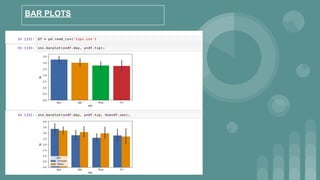
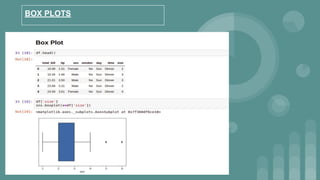
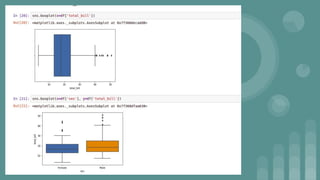
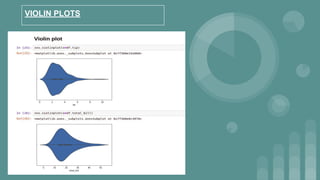
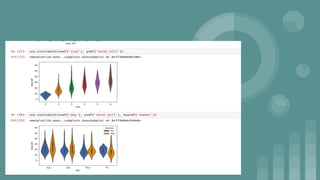
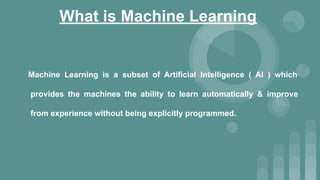
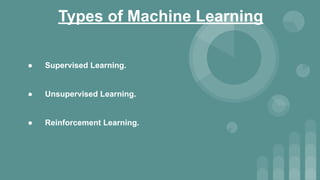
This document provides an introduction to data science. It discusses what data science is, the data life cycle, key domains that benefit from data science and why Python is well-suited for data science. It also summarizes several important Python libraries for data science - Pandas for data analysis, NumPy for scientific computing, Matplotlib and Seaborn for data visualization, and introduces machine learning concepts like supervised and unsupervised learning. Example algorithms like linear regression and K-means clustering are also covered.