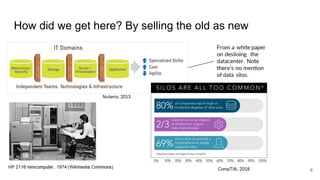
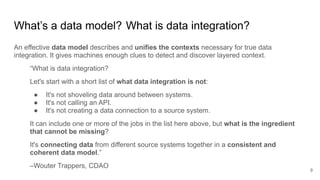
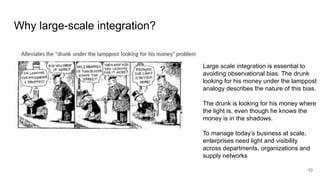
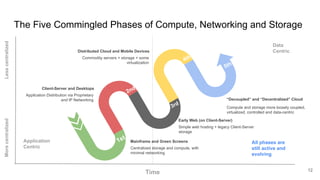
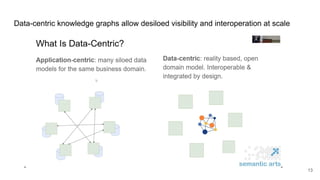
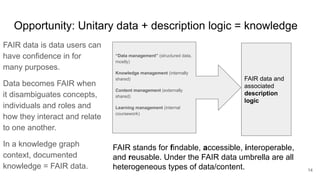
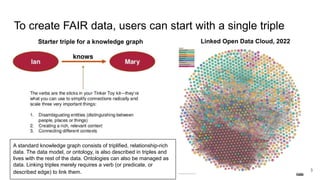
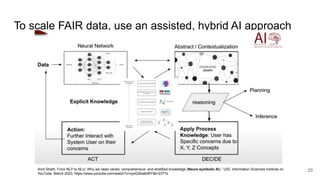
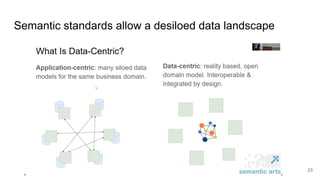
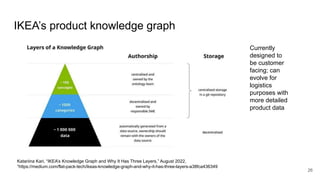
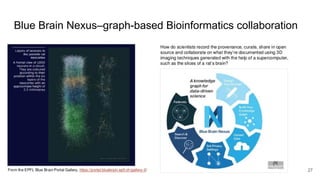
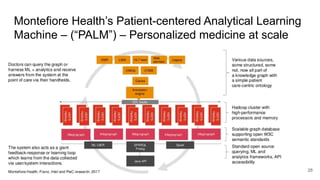
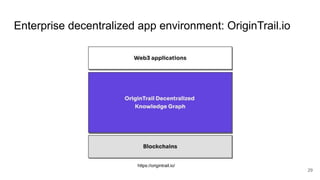
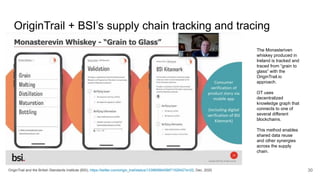
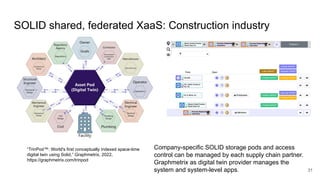
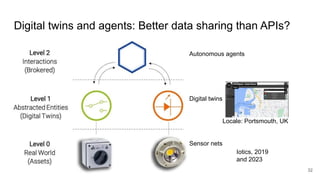
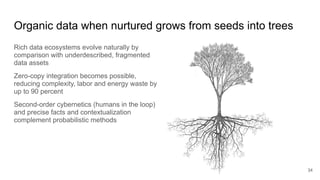
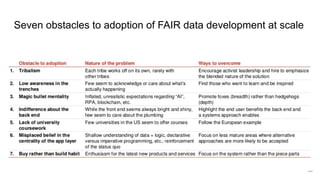
The document discusses the limitations of traditional data warehousing, particularly in addressing data siloing and integration challenges. It proposes a 'fair data' approach using knowledge graphs to improve data visibility and interoperation while highlighting several case studies that illustrate the benefits of adopting a data-centric architecture. The presentation emphasizes the potential for organic, decentralized systems that reduce integration complexity and enhance data quality across enterprises.