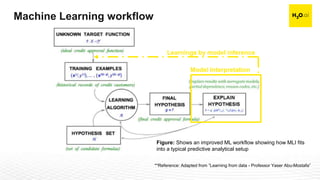
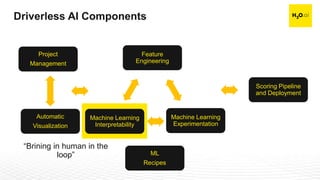
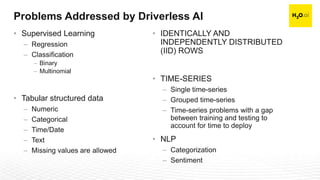
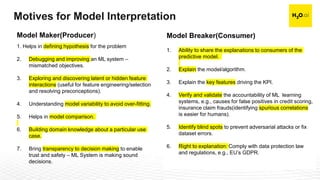
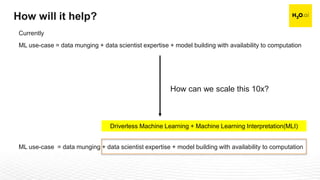
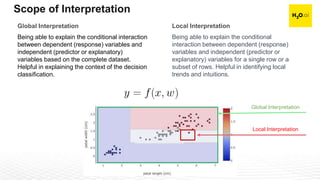
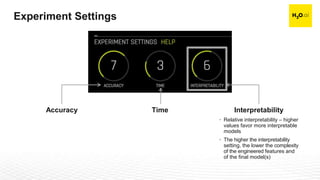
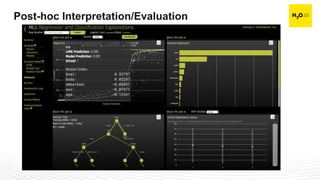
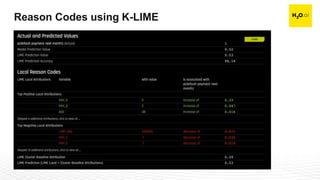
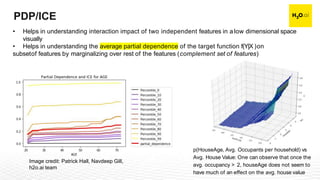
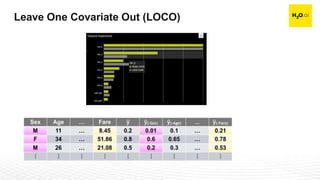
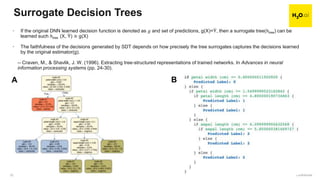
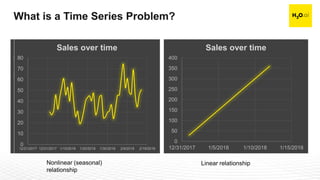
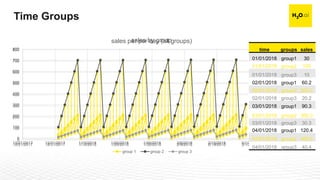
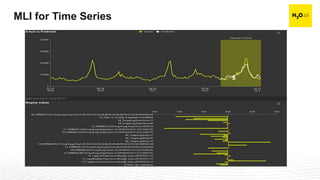
The document discusses machine learning interpretability and its integration within predictive modeling, emphasizing tools and workflows provided by H2O.ai. It outlines the significance of model interpretation for debugging, model improvement, and ensuring transparency, while detailing methods like local and global interpretation, Shapley values, and surrogate decision trees. Additionally, it highlights the potential of driverless machine learning in enhancing interpretability and scaling workflows effectively.