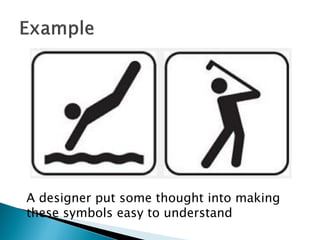
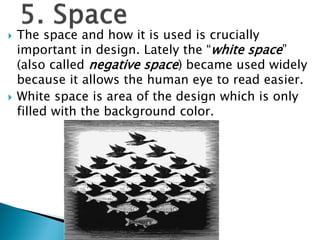
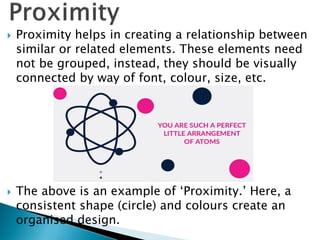
Graphic design uses visual elements like line, shape, color, and texture along with principles such as balance, hierarchy, and contrast to communicate ideas through visual compositions. Designers combine these elements following principles to achieve their communication goals effectively. Key elements include line, color, shape, texture, and space while principles like alignment, proximity, repetition and emphasis guide how elements are structured in a design. Together, thoughtful use of elements and principles allow designers to create visual representations that convey intended messages.