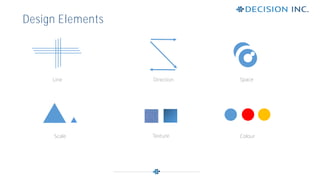
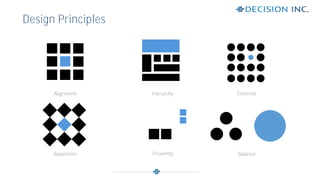
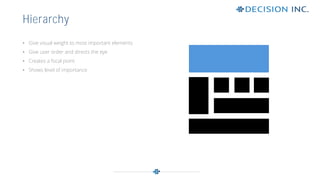
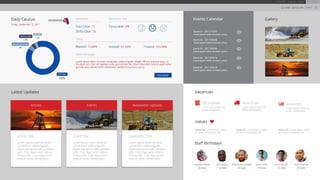
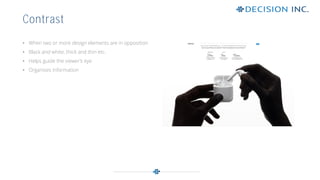
This document discusses design principles for user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design. It defines design as the visual communication of ideas through logical visual elements that are essential to a user's experience. It then discusses key design elements like line, shape, size, and color. It also outlines important design principles for applying the elements, including alignment, hierarchy, contrast, repetition, proximity, and balance. These principles help create structure, order, and focus when applied to the visual elements of a design.