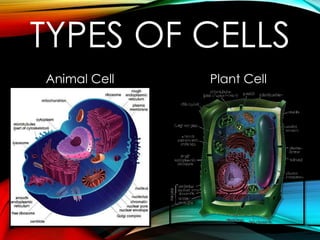
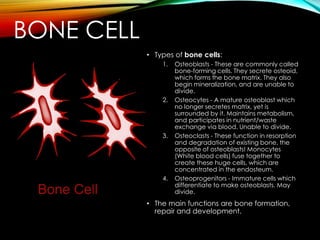
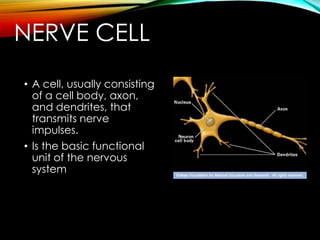
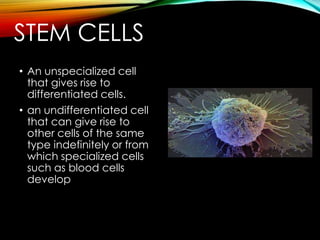
This document describes several types of cells in the human body. It discusses animal cells and plant cells at a high level. It then provides more detail on specific cell types, including connective tissue cells, muscle cells, cartilage cells, bone cells, red blood cells, nerve cells, and stem cells. For each cell type, it outlines their basic function and characteristics. The overall document serves to introduce and compare different cell types found in human and animal tissue.