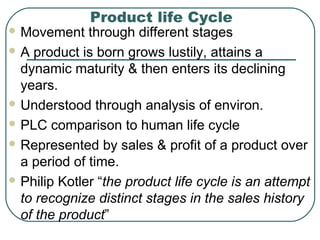
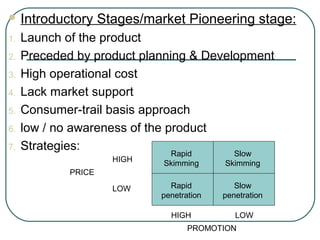
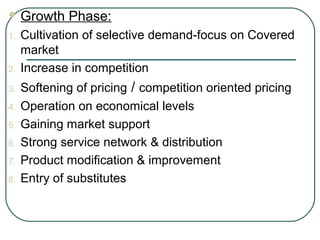
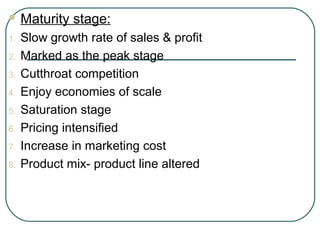
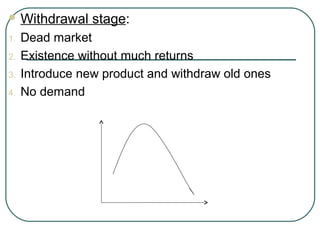
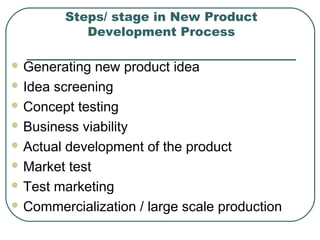
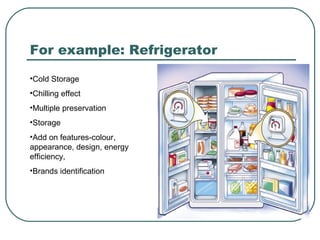
The document discusses key concepts related to product management including definitions of a product, components of a product, product mix, product life cycle, and new product development. It defines a product as a bundle of benefits that satisfies customer needs and discusses the core benefit, actual product, augmented product, and future product. It also outlines the stages of the product life cycle as introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and withdrawal. Finally, it lists the steps in new product development as generating ideas, screening, testing, development, market testing, and commercialization.




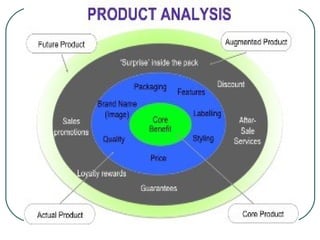
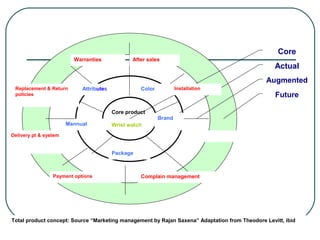
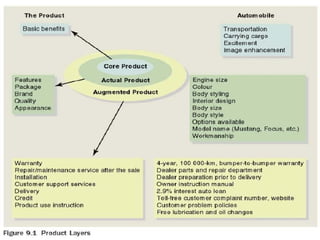
![What constitutes of a product?
[Component/Levels of product]
A product planner should think about the
product at three levels:
first needs- identify the core consumer
needs the product will satisfy.
Then design the actual products
And find ways and means to augment it
further to create bundle of satisfy
consumers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptproductmanagementchap89-130902022129-phpapp01/85/Product-management-PLC-7-320.jpg)