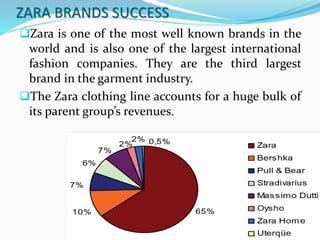
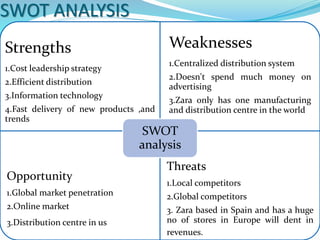
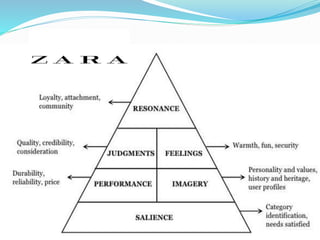
Zara is a Spanish clothing retailer known for its rapid response to new fashion trends. It is owned by Inditex Group and was founded in 1975 in A Coruña, Spain. Zara launches around 10,000 new designs each year and delivers new products to its 1,763 stores around the world twice each week. Through extensive market research and a vertically integrated supply chain located near its headquarters, Zara is able to quickly design, produce, and distribute new items to stores in response to emerging trends.