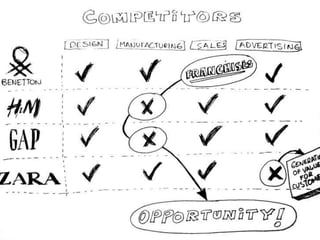
Zara is a Spanish clothing and accessories retailer known for its fast and affordable fashion, founded in 1975 by Amancio Ortega and Rosalía Mera. The company has a unique business model focusing on quick reaction to customer feedback and minimal marketing, relying on strategic store locations and frequent inventory turnover. With global outreach and a strong competitive strategy, Zara is poised for sustainable growth, although it faces challenges such as fierce competition and potential brand dilution.