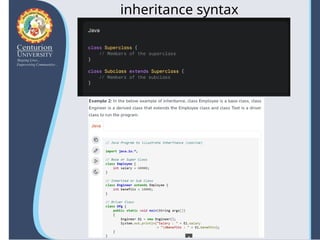
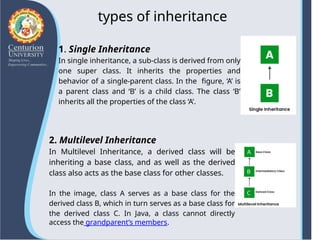
The document provides an overview of inheritance in Java, highlighting its significance in object-oriented programming as a mechanism for code reuse and class hierarchy organization. It explains key concepts including parent and child classes, types of inheritance such as single and multilevel, and important principles like method overriding and access modifiers. Additionally, the text discusses the benefits of inheritance in software development, such as modularity and extensibility.