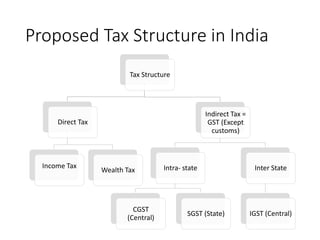
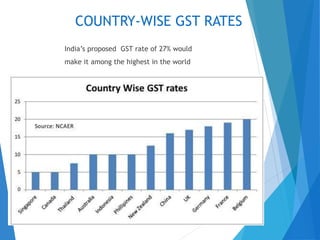
GST stands for Goods and Services Tax, which will be levied on the sale or purchase of goods and services. It will replace existing indirect taxes and create a single, national tax system to help drive economic growth. Implementing GST is an important reform that will simplify taxation, boost consumption, and have widespread impacts by streamlining India's tax structure and market. While it aims to reduce costs, some disadvantages include its complexity for individuals and lack of infrastructure.