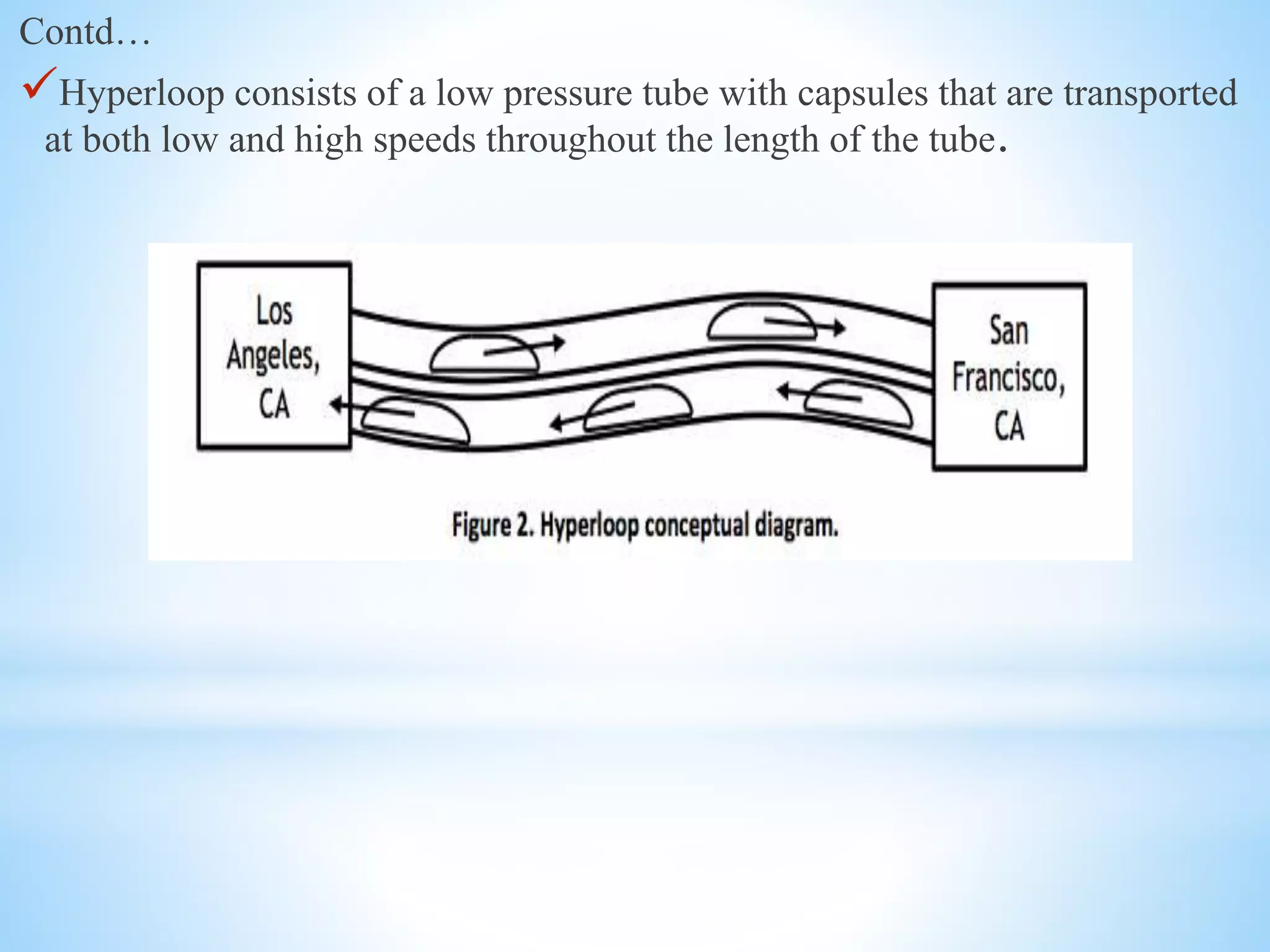
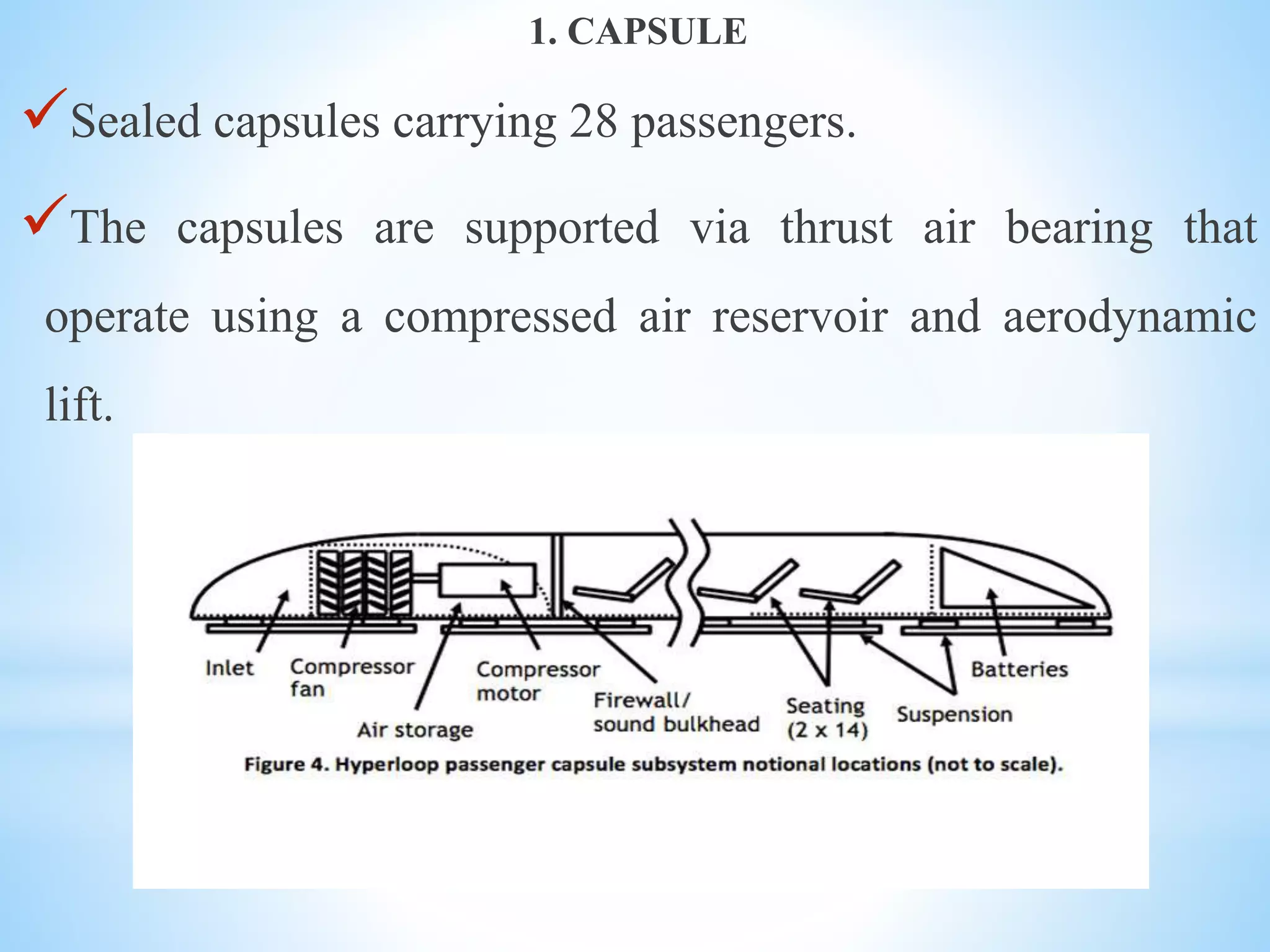
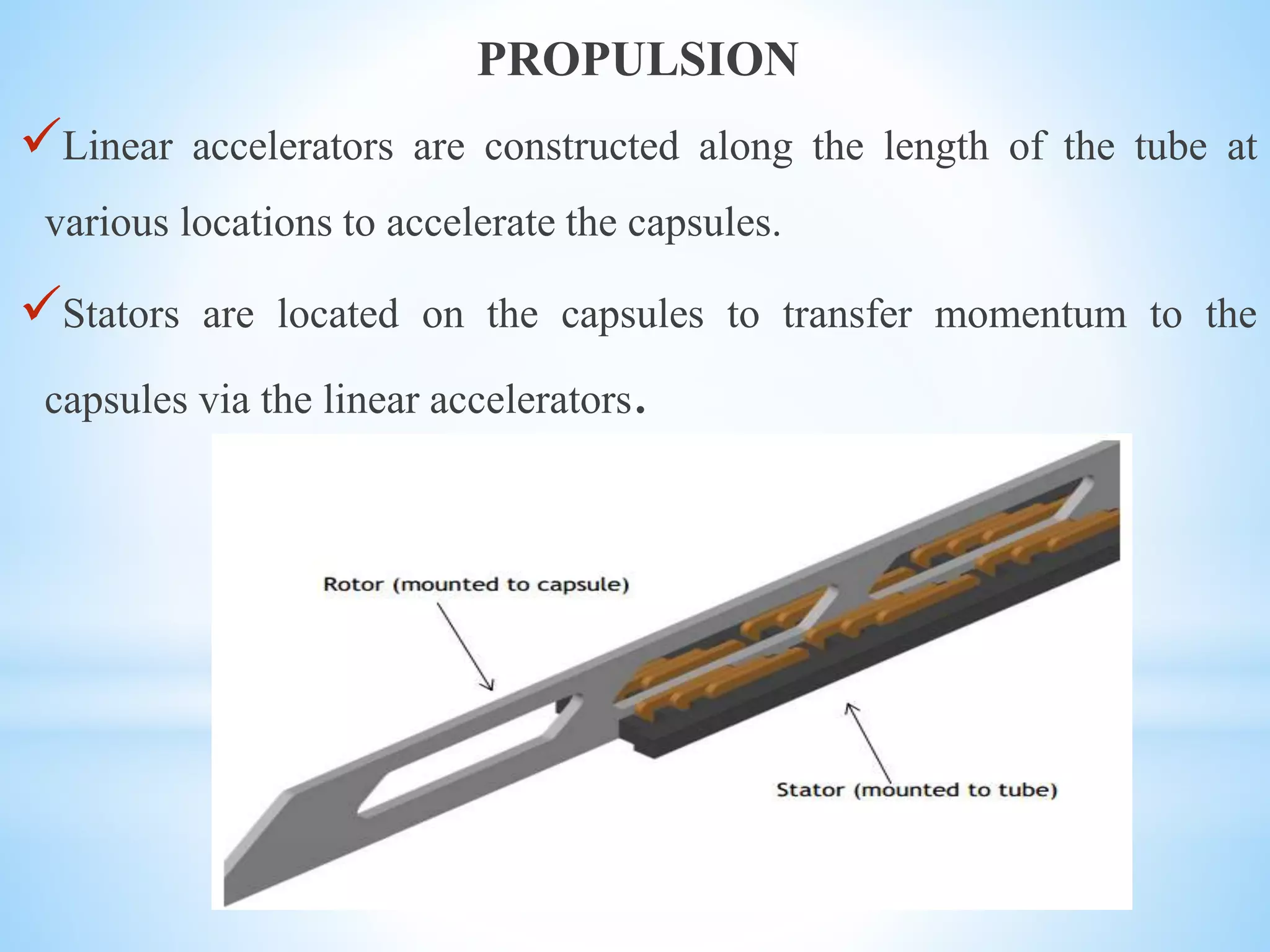
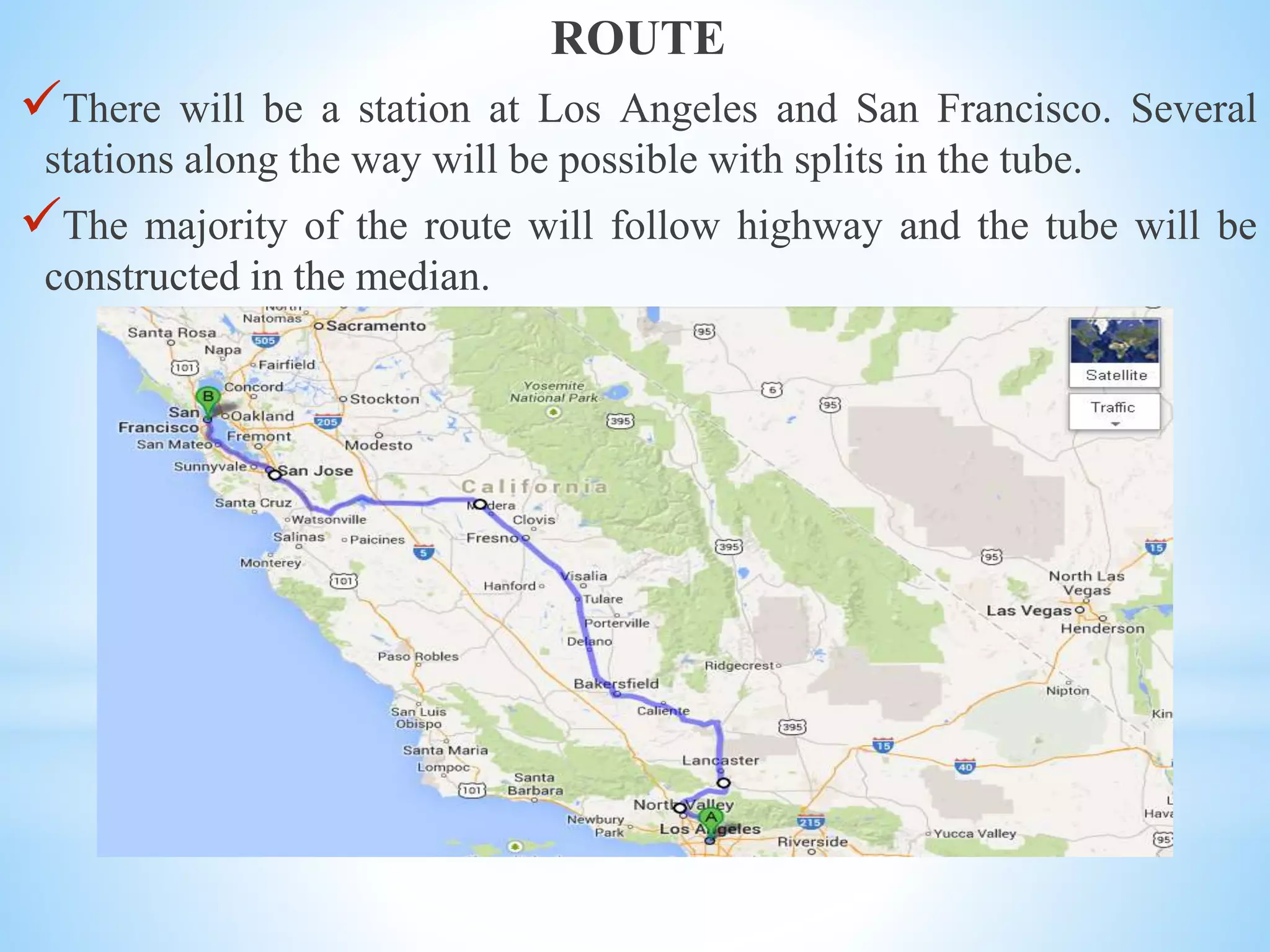
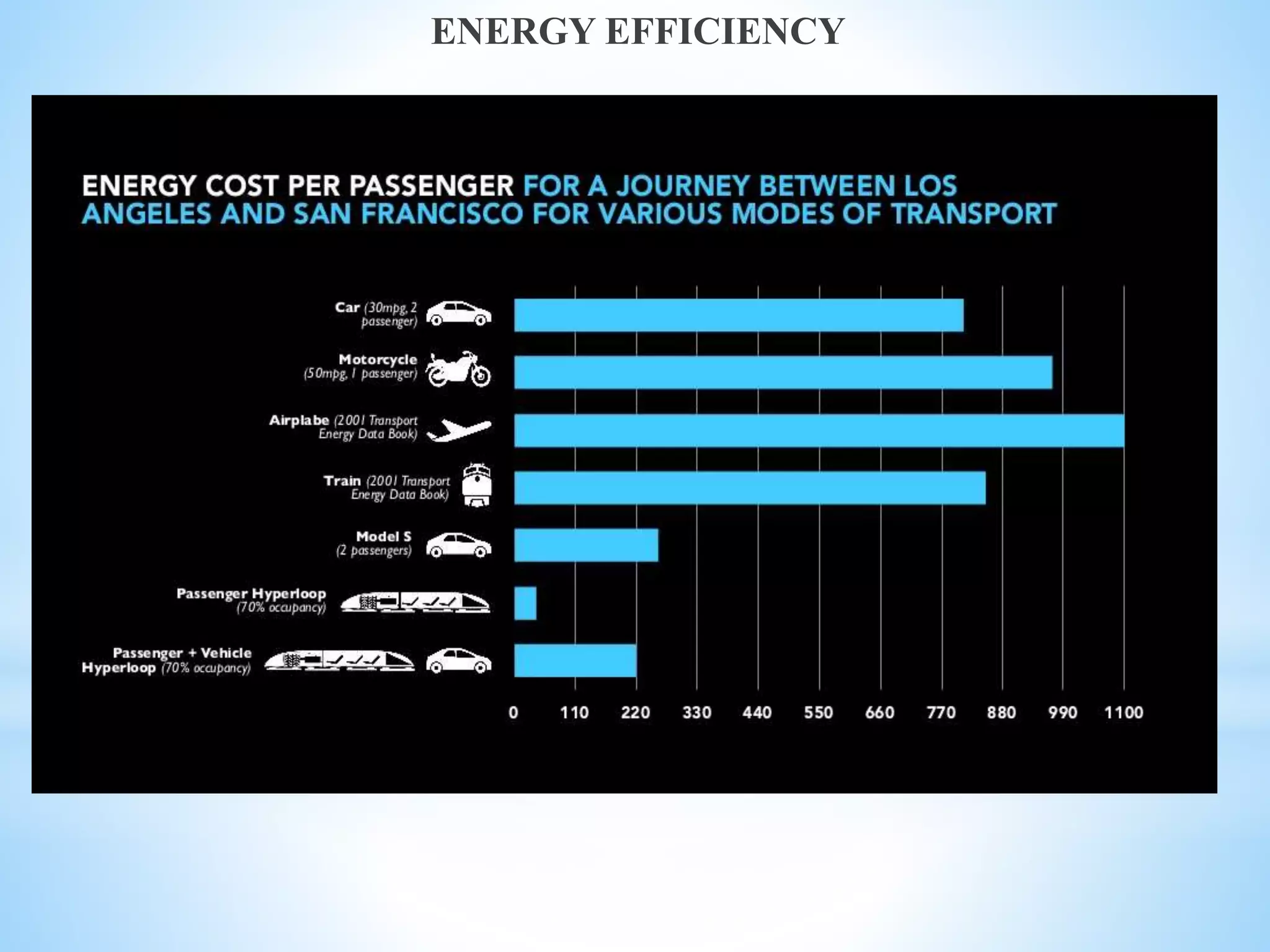
The document discusses the Hyperloop transportation system proposed by Elon Musk as a new mode of transportation that could transport passengers from Los Angeles to San Francisco in just 30 minutes. The Hyperloop would use low-pressure tubes to move capsules carrying passengers at speeds up to 760 mph using linear electric motors. It has the potential to be faster and less expensive than existing modes like high-speed rail, while being more energy efficient and generating less pollution than air travel. Some challenges to implementing the Hyperloop include developing the tube pressurization and capsule turning technologies and addressing passenger space constraints within the small diameter tubes.