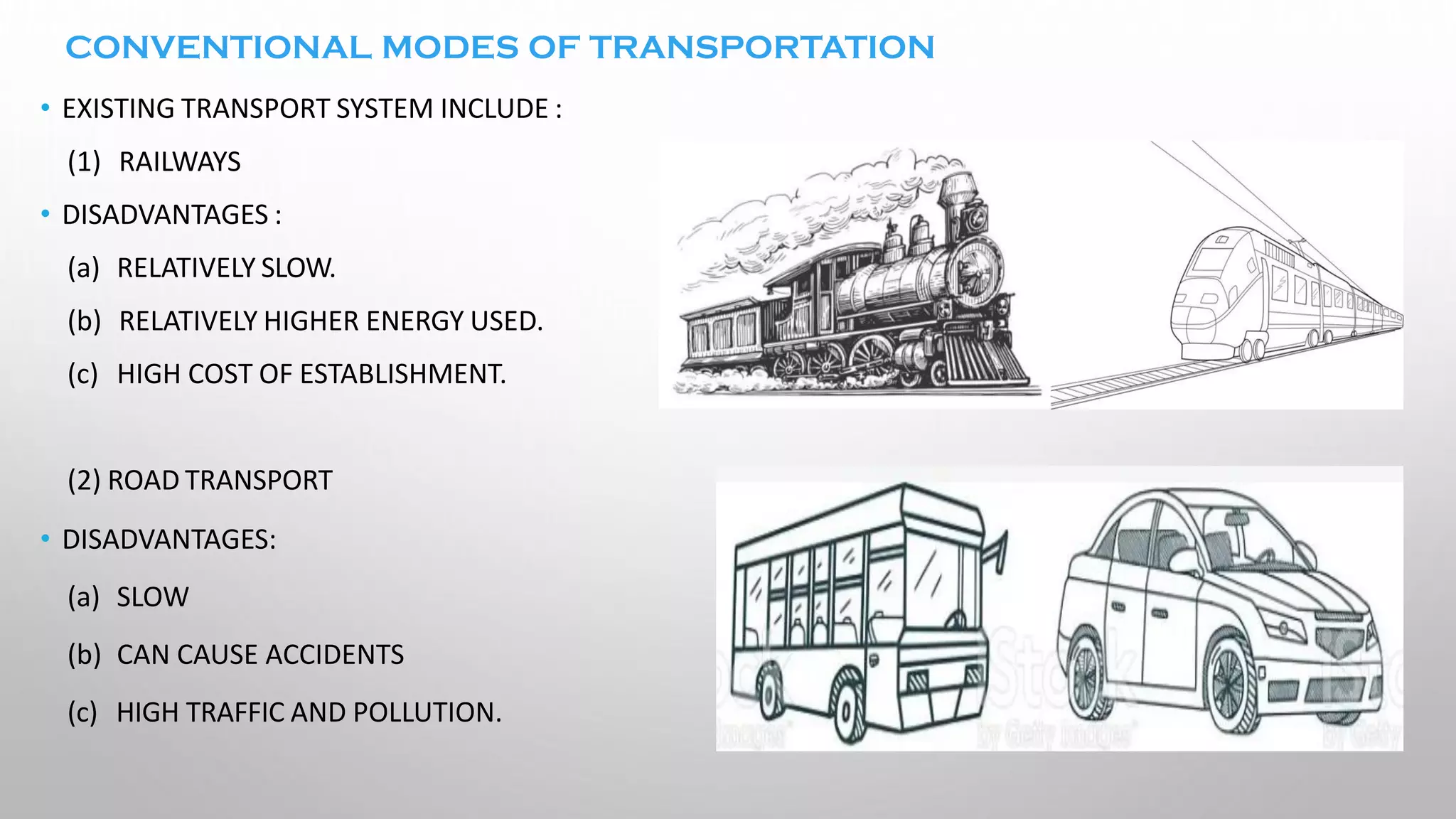
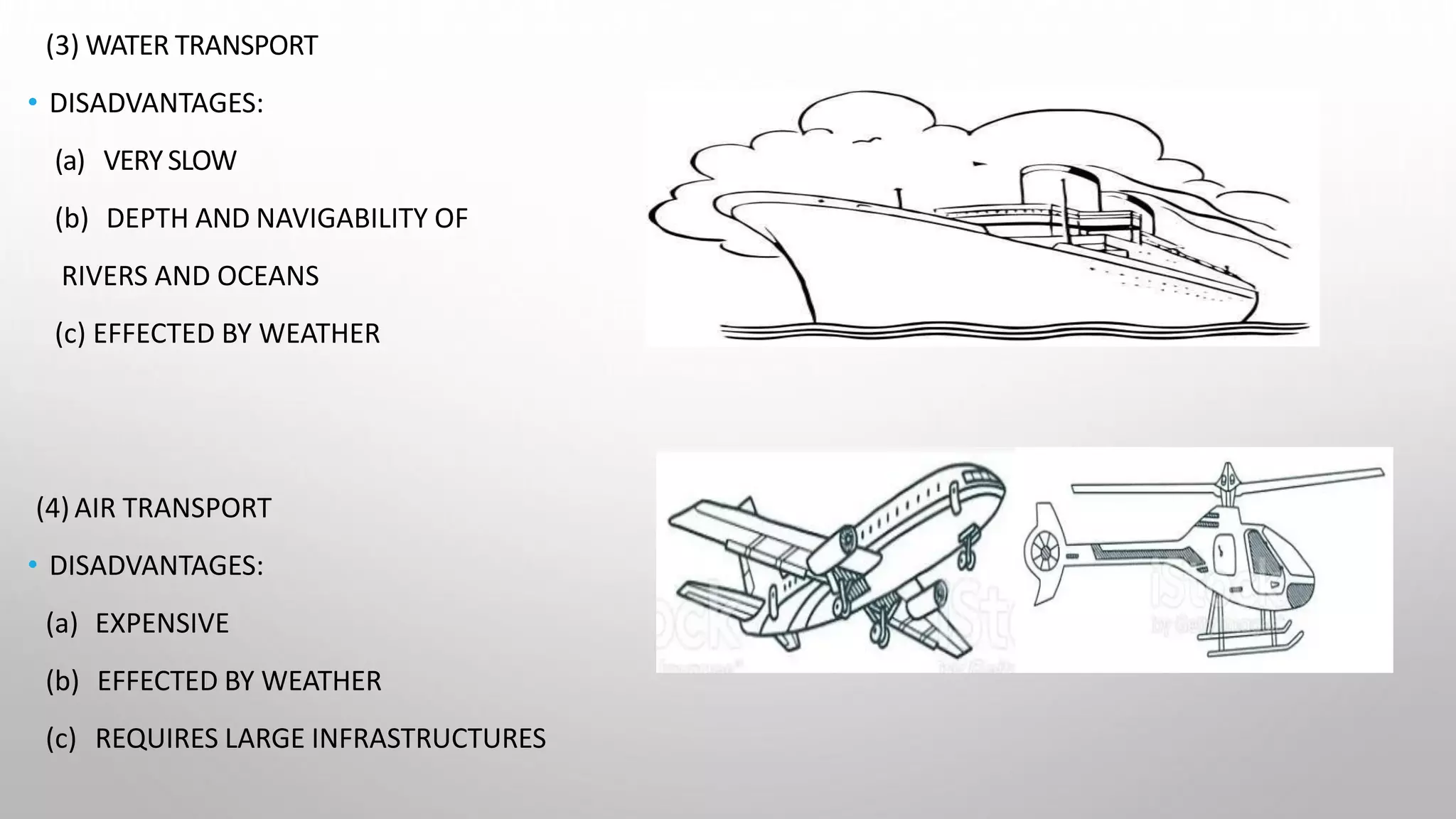
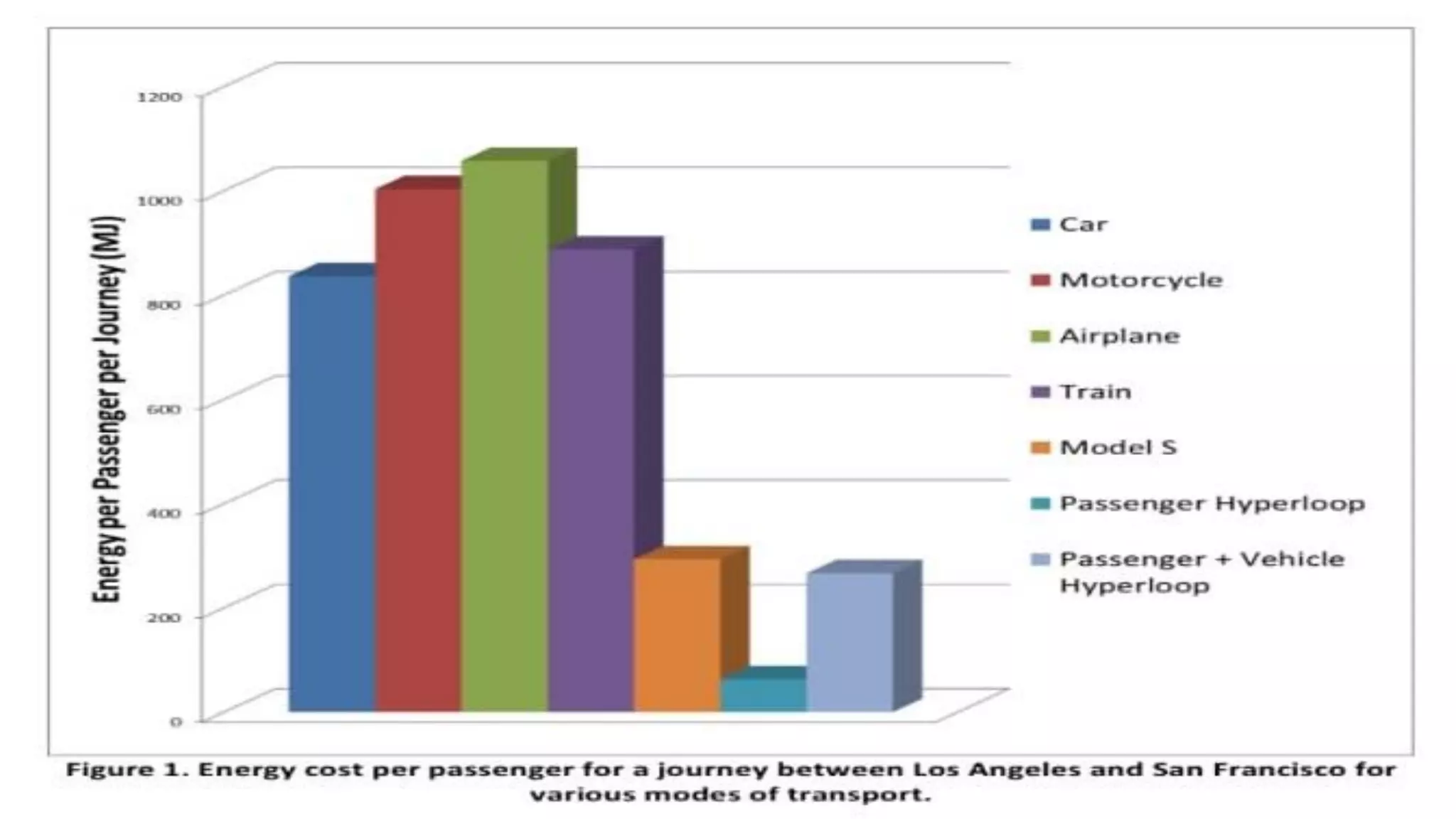
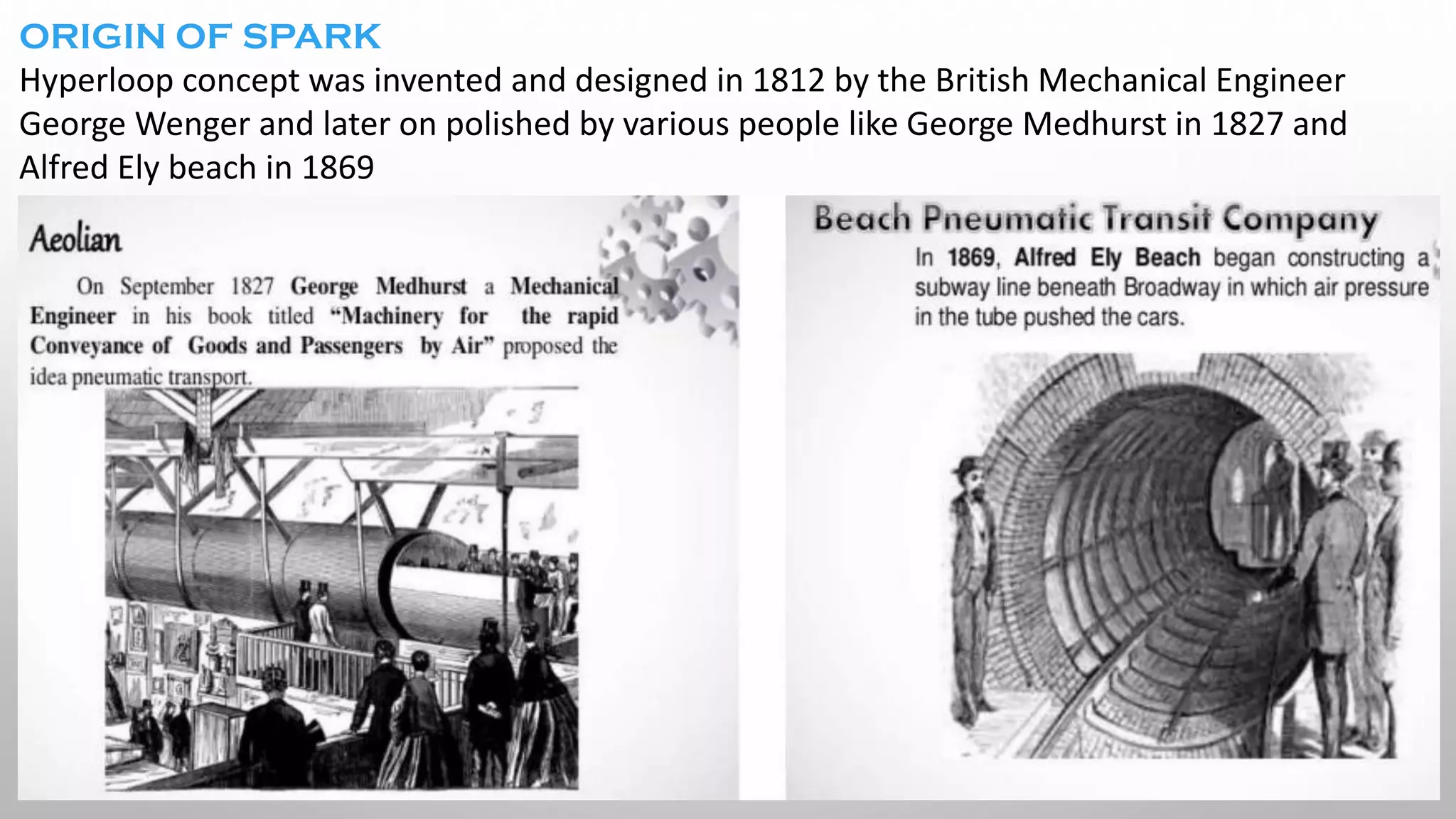
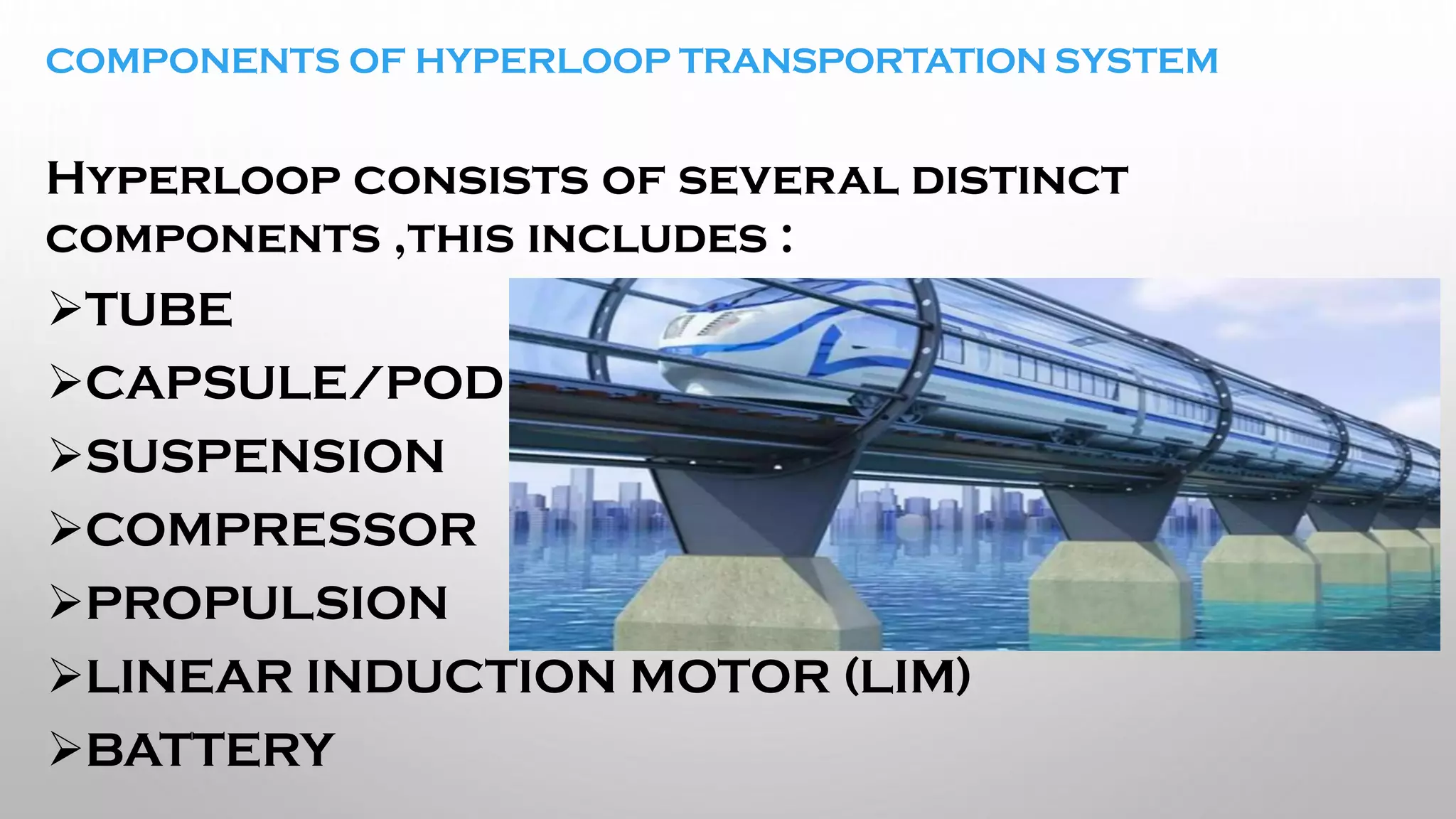
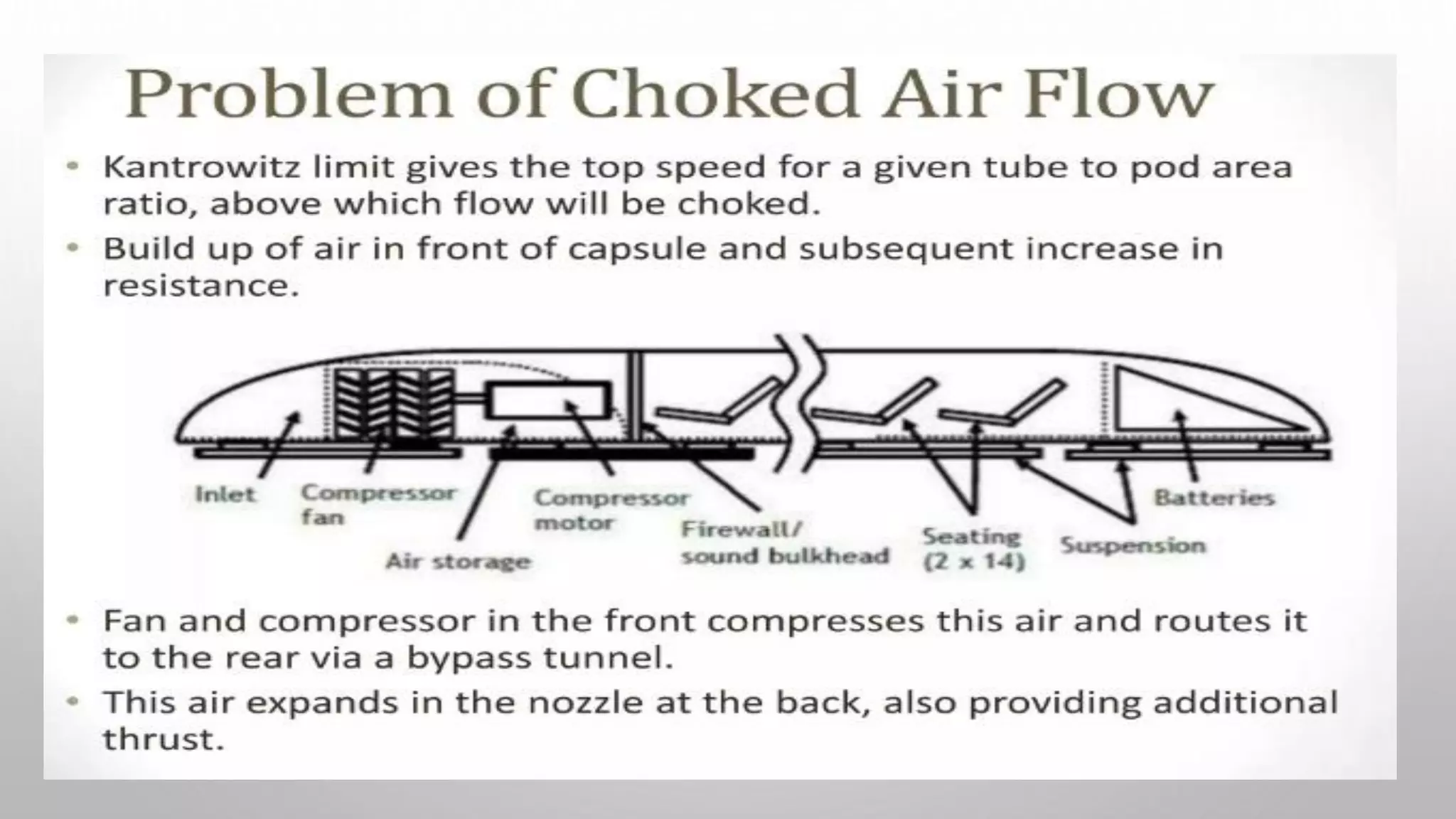
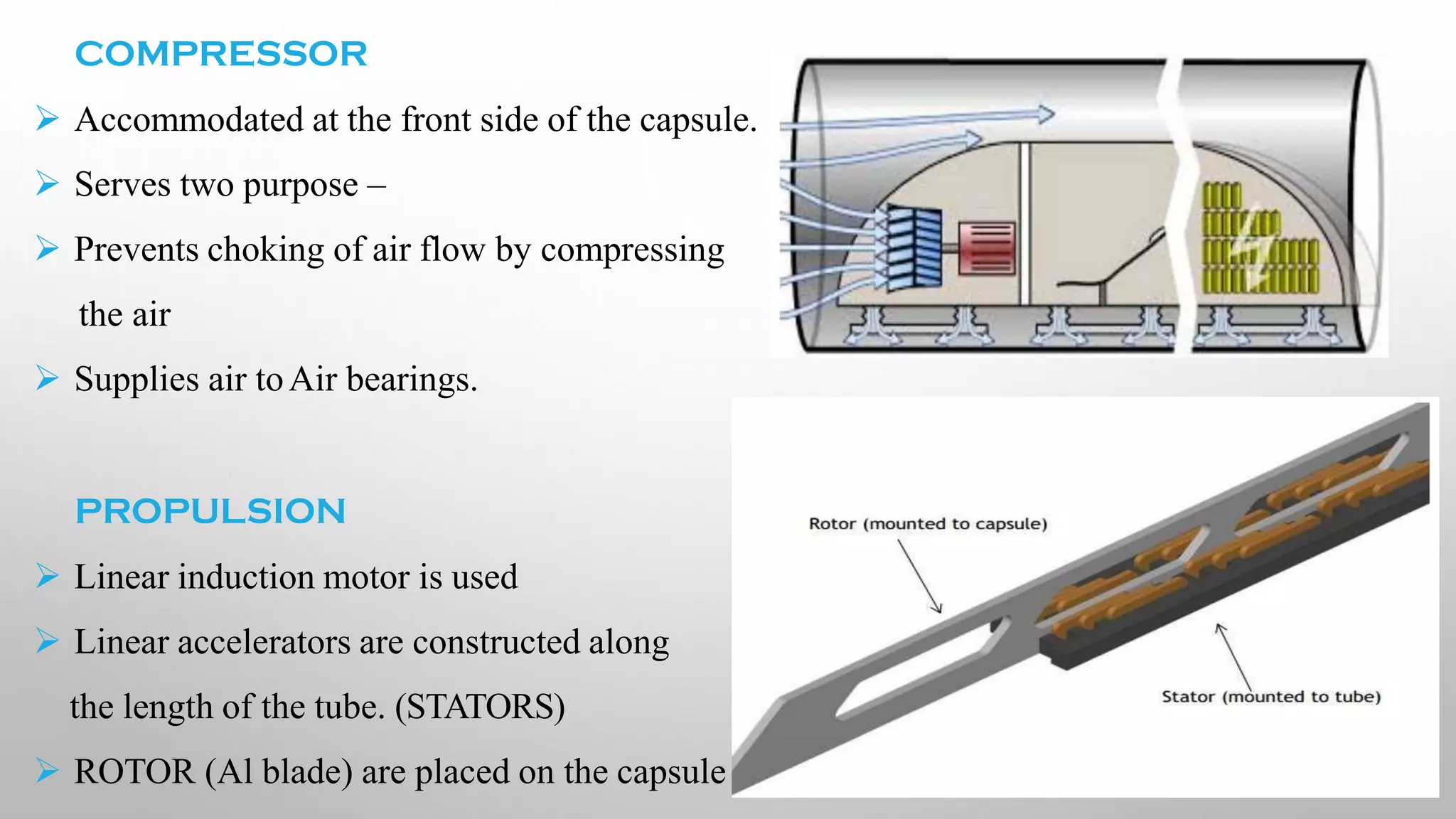
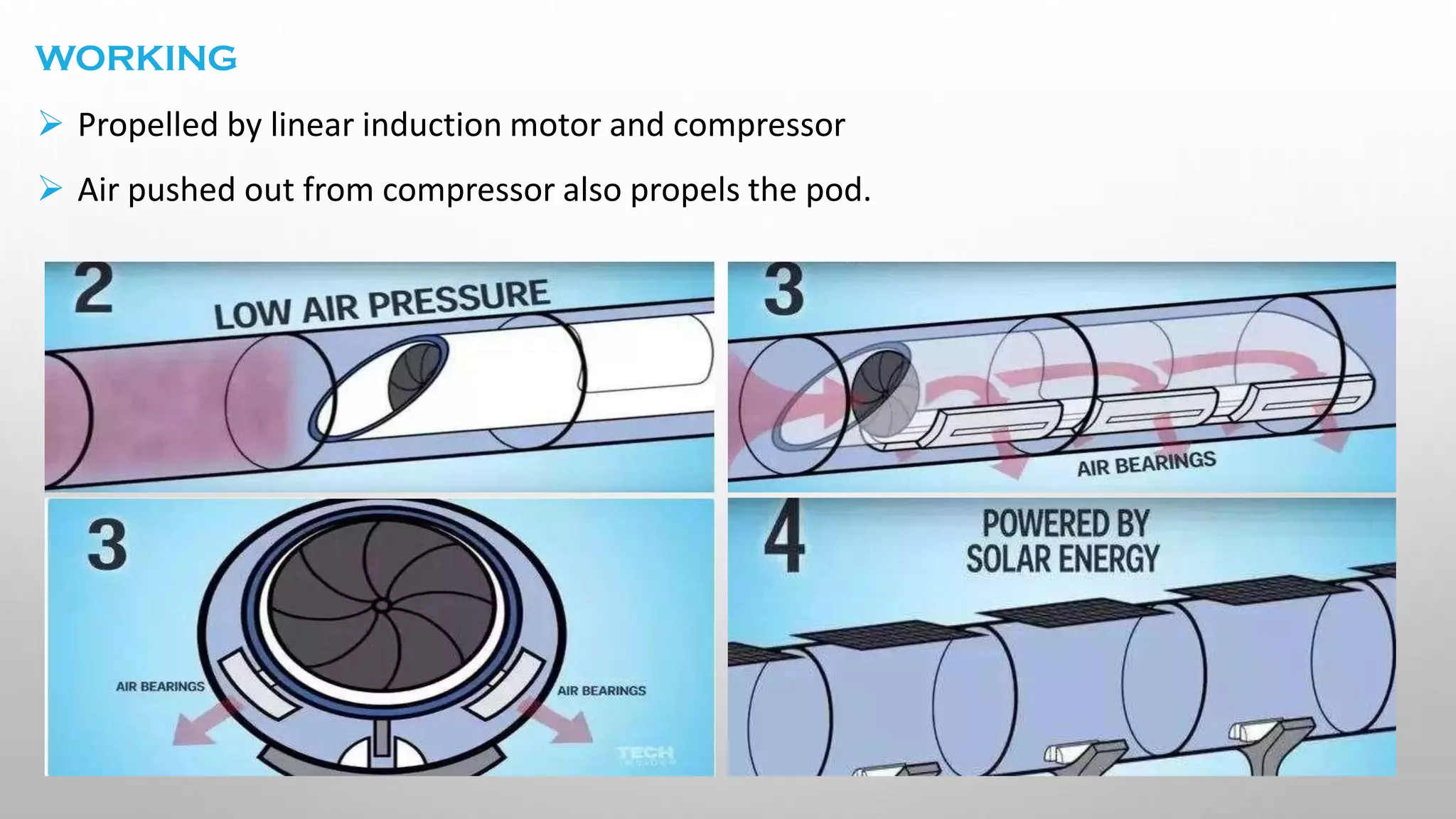
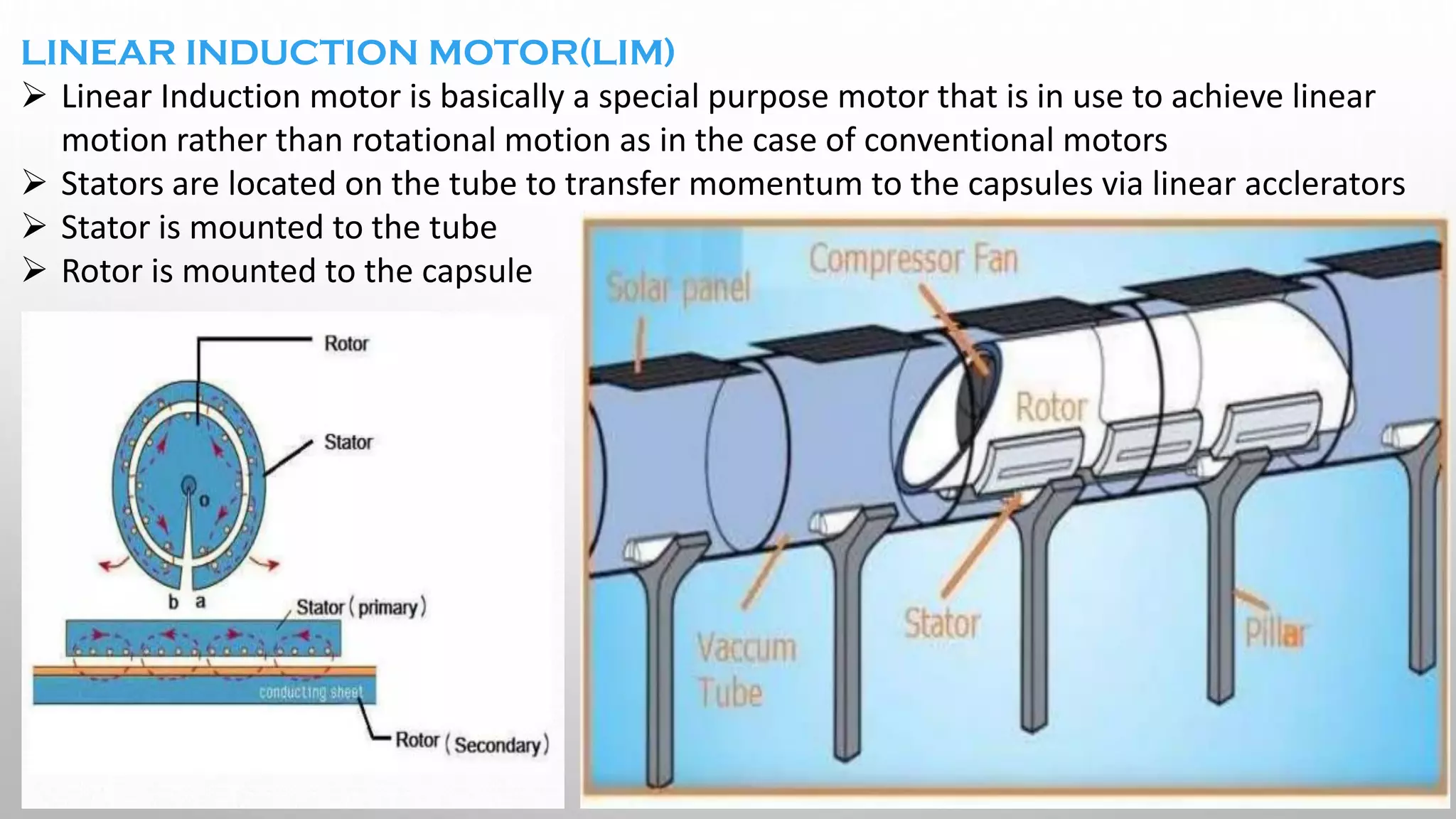
This document presents information on the Hyperloop, a proposed 5th mode of transportation invented by Elon Musk. The Hyperloop involves capsules that would travel through low pressure tubes at over 700 mph, faster and cheaper than existing modes. It would use linear induction motors and air compressors to levitate and propel the capsules through the tubes. The document discusses the components, workings, benefits over high-speed rail, and developments aimed to implement the Hyperloop between major cities like LA and San Francisco by 2045.