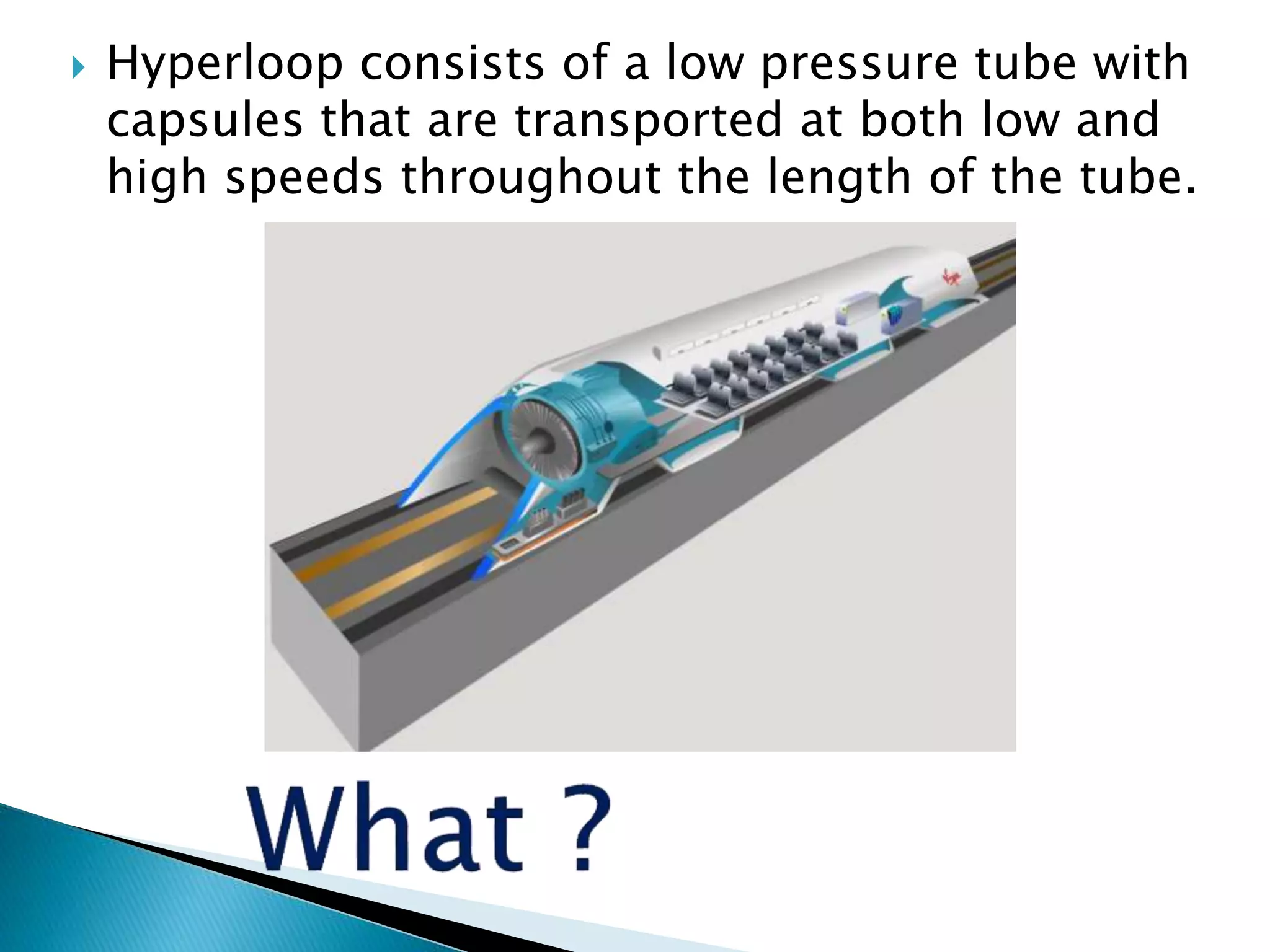
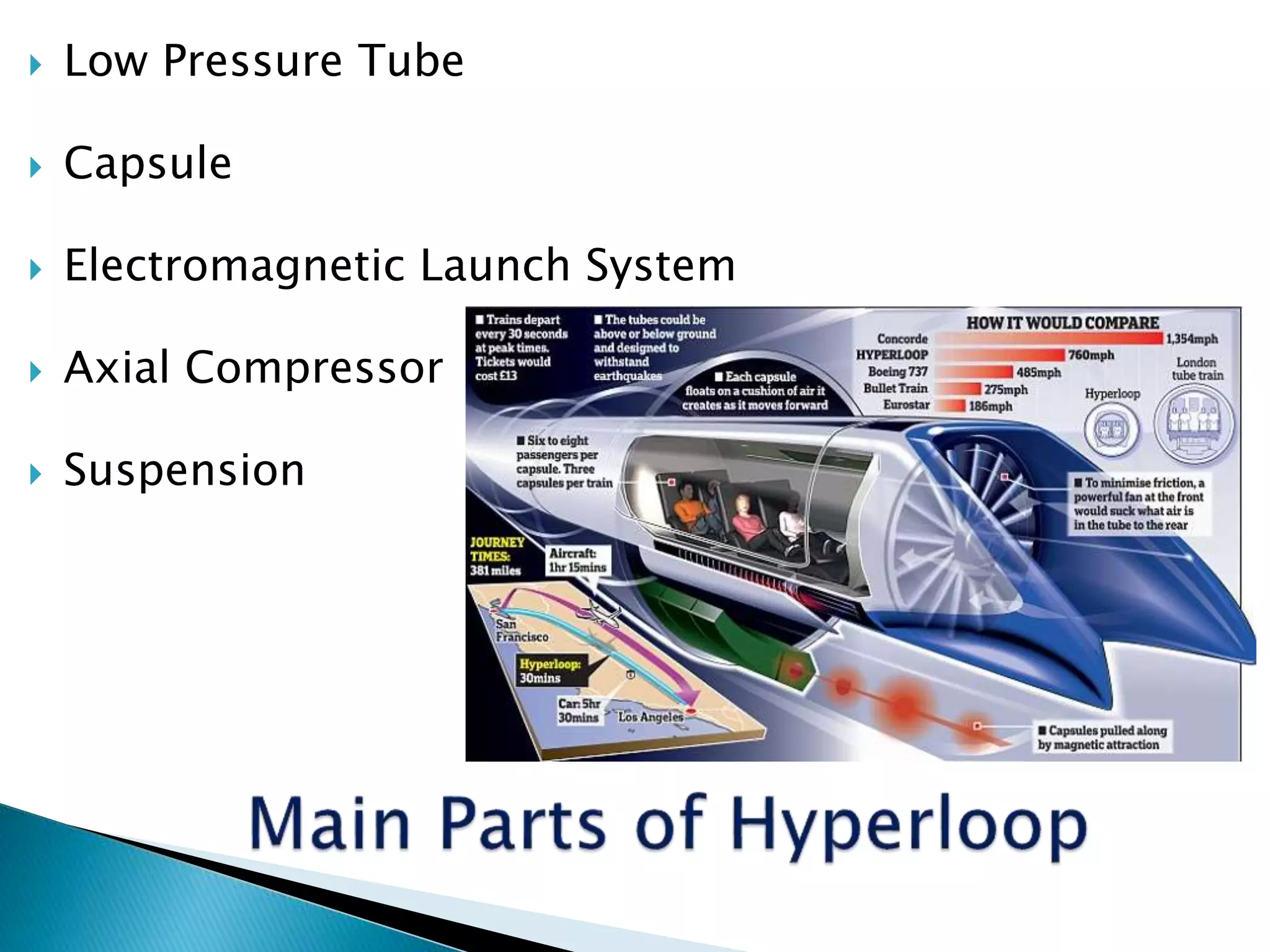
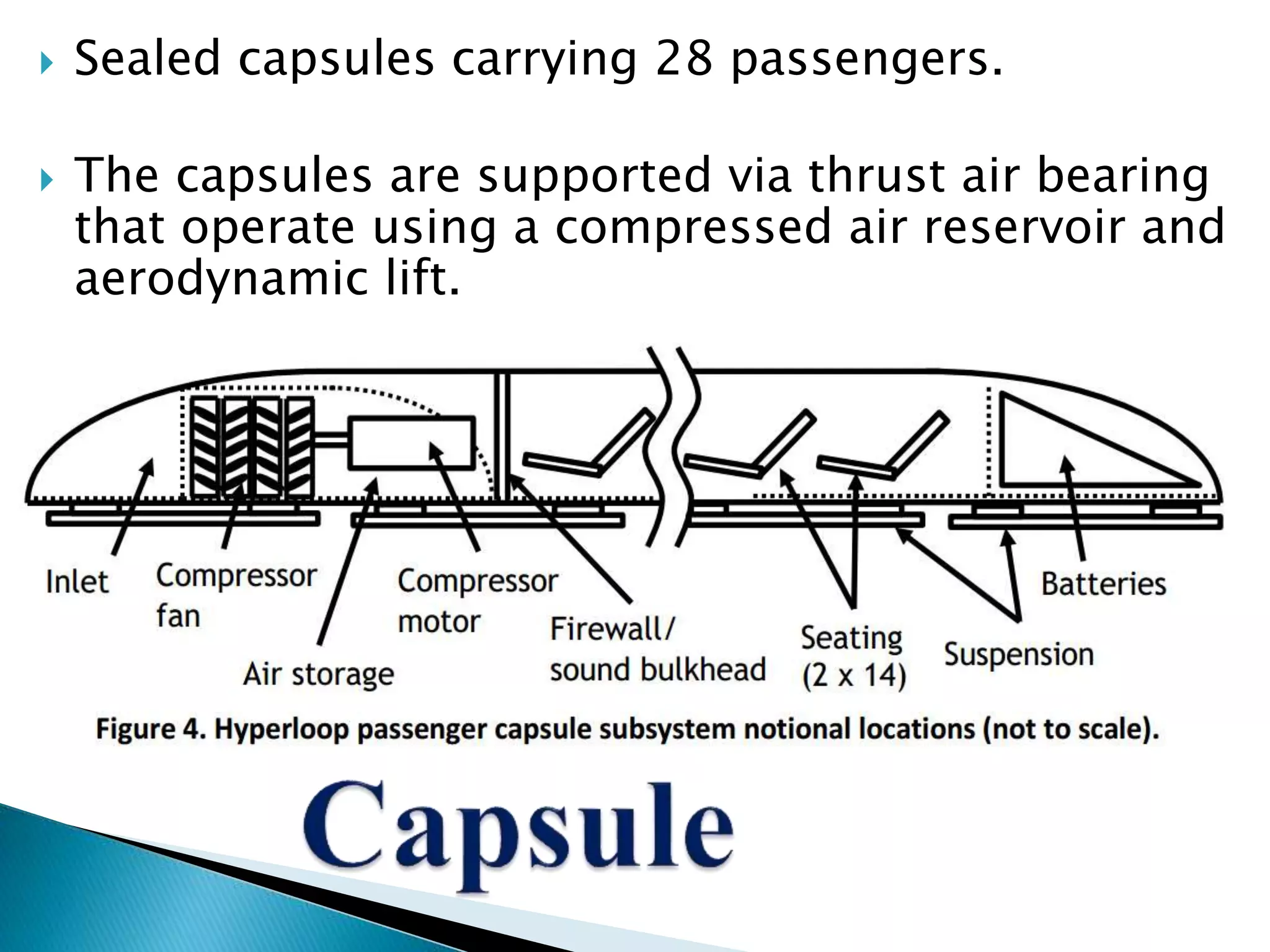
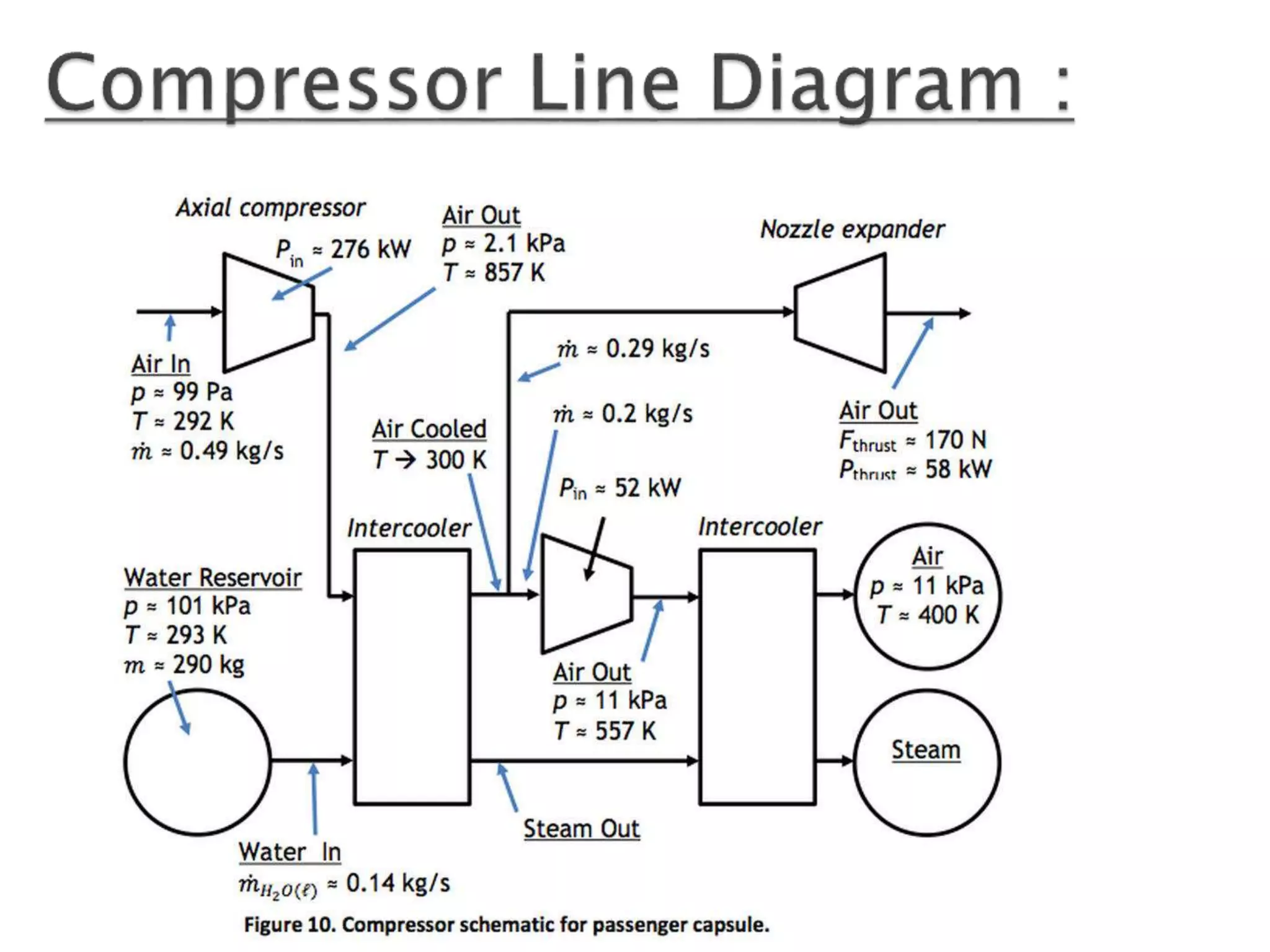
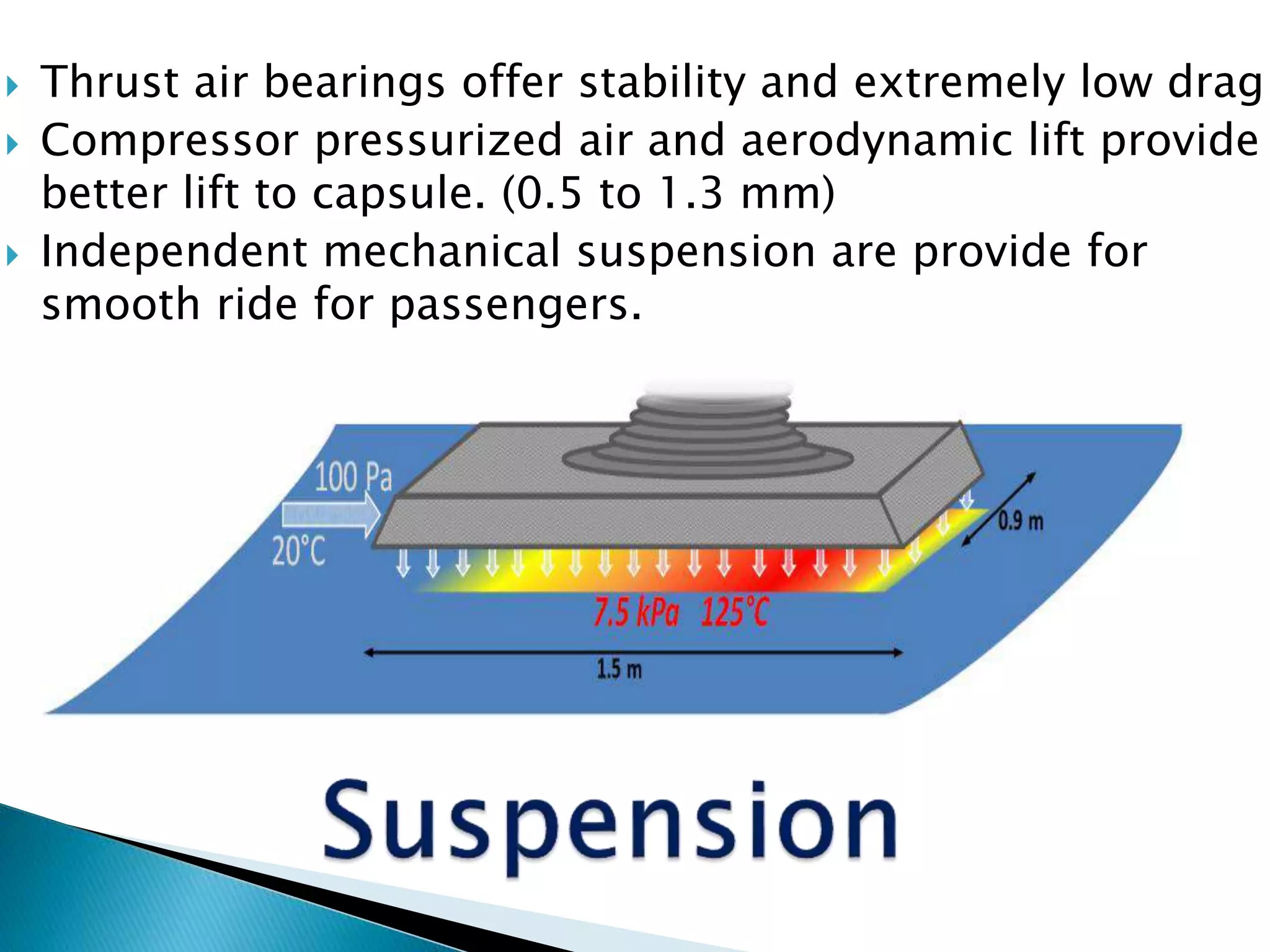
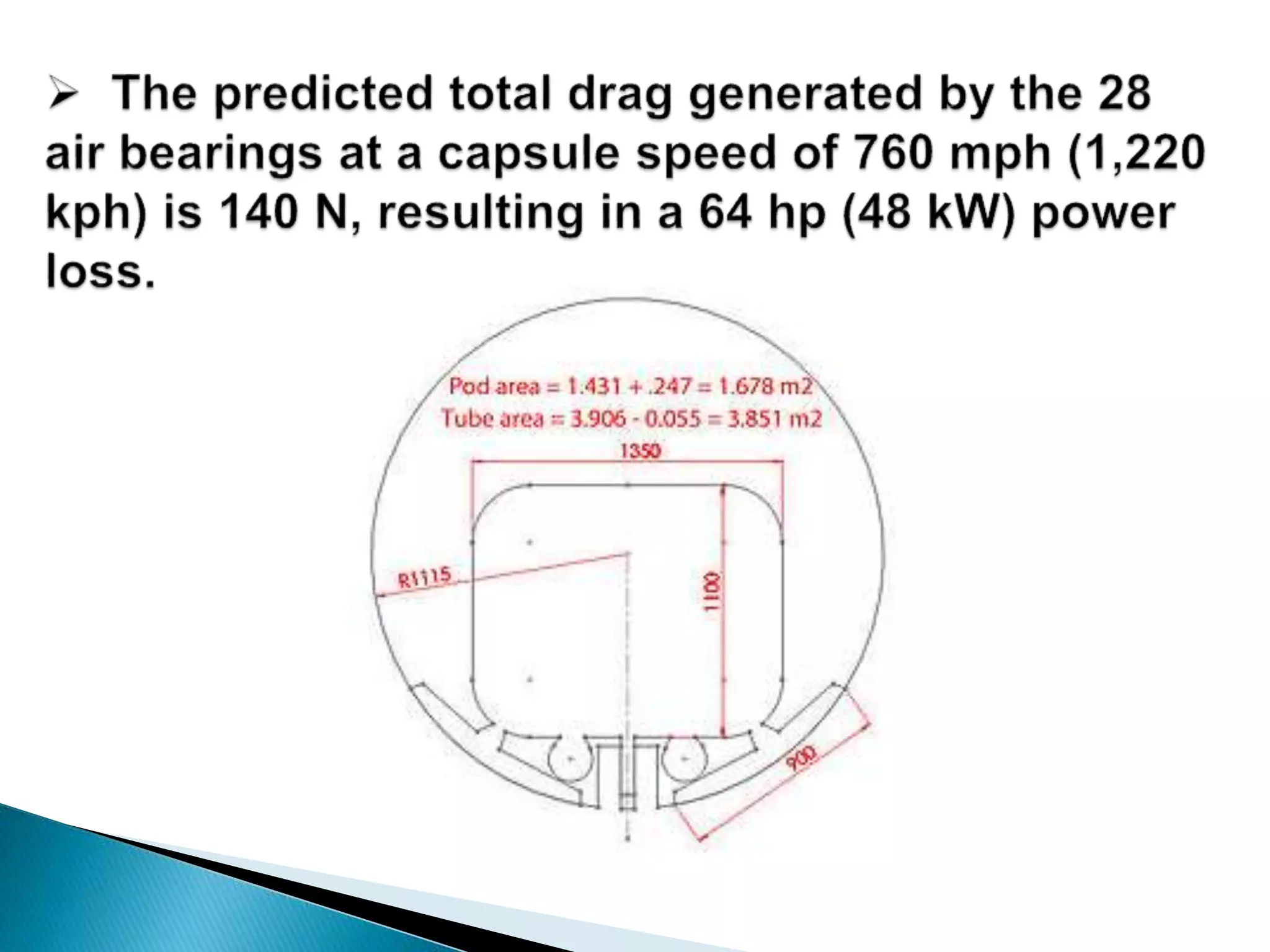
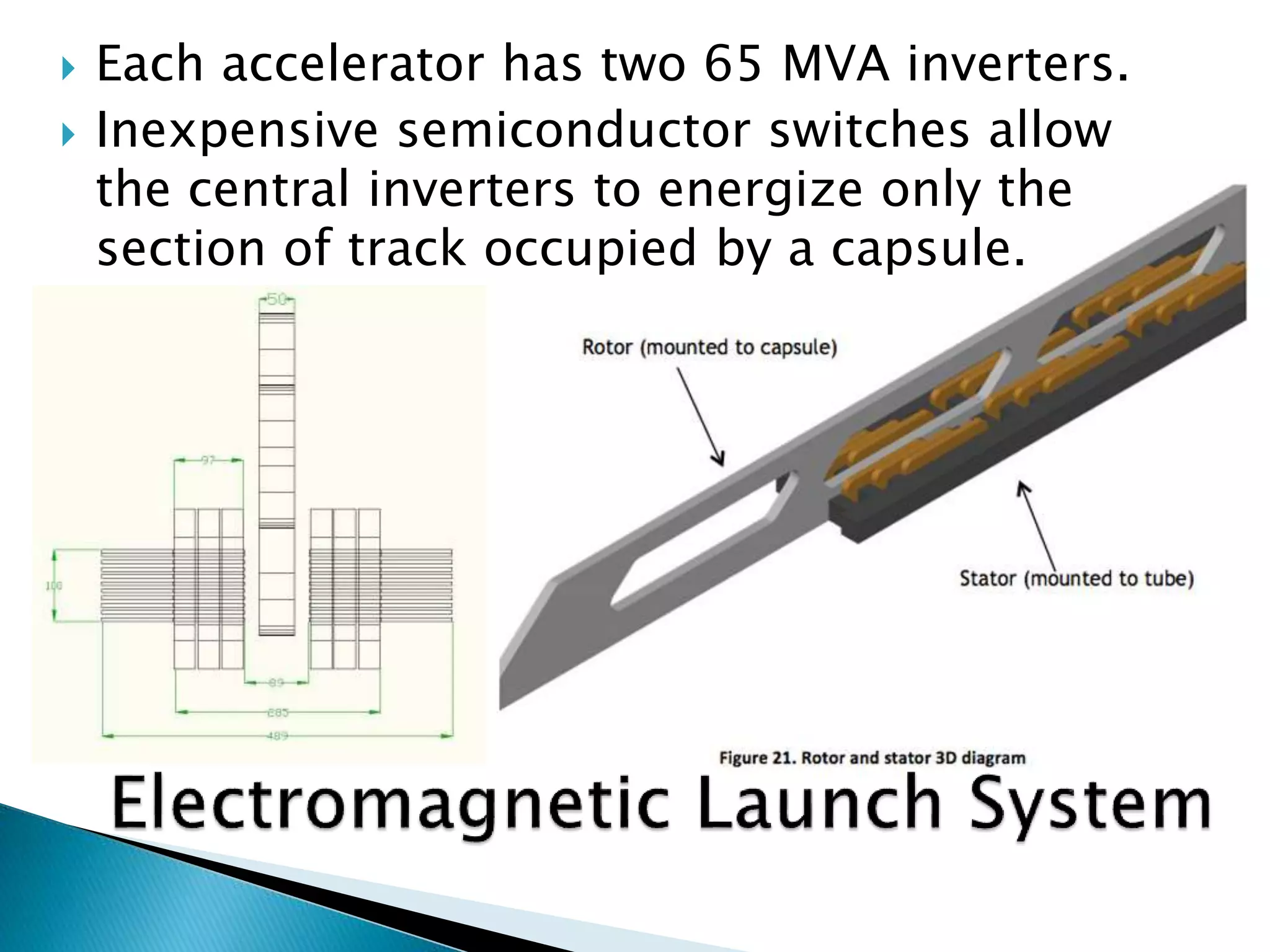
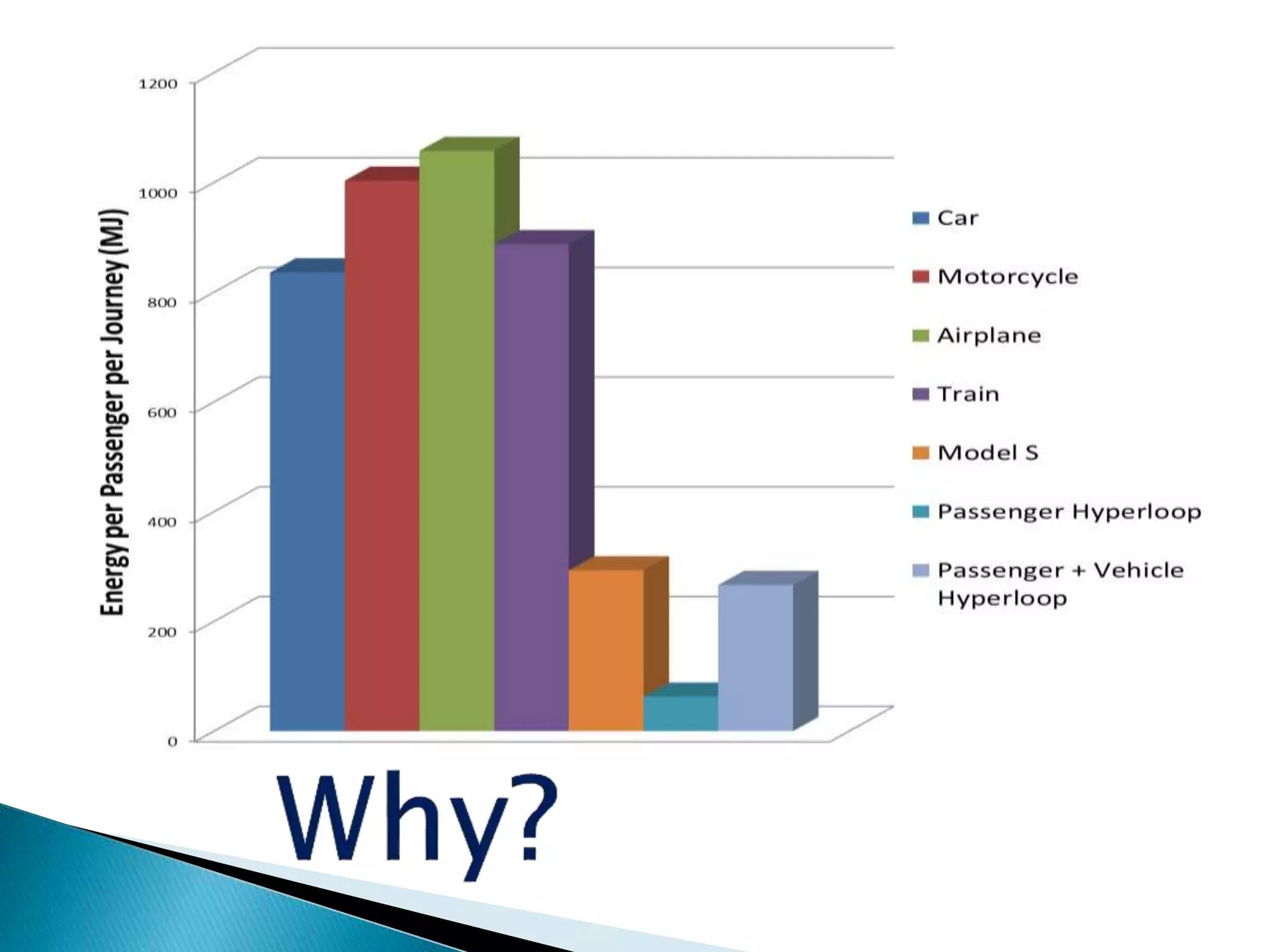
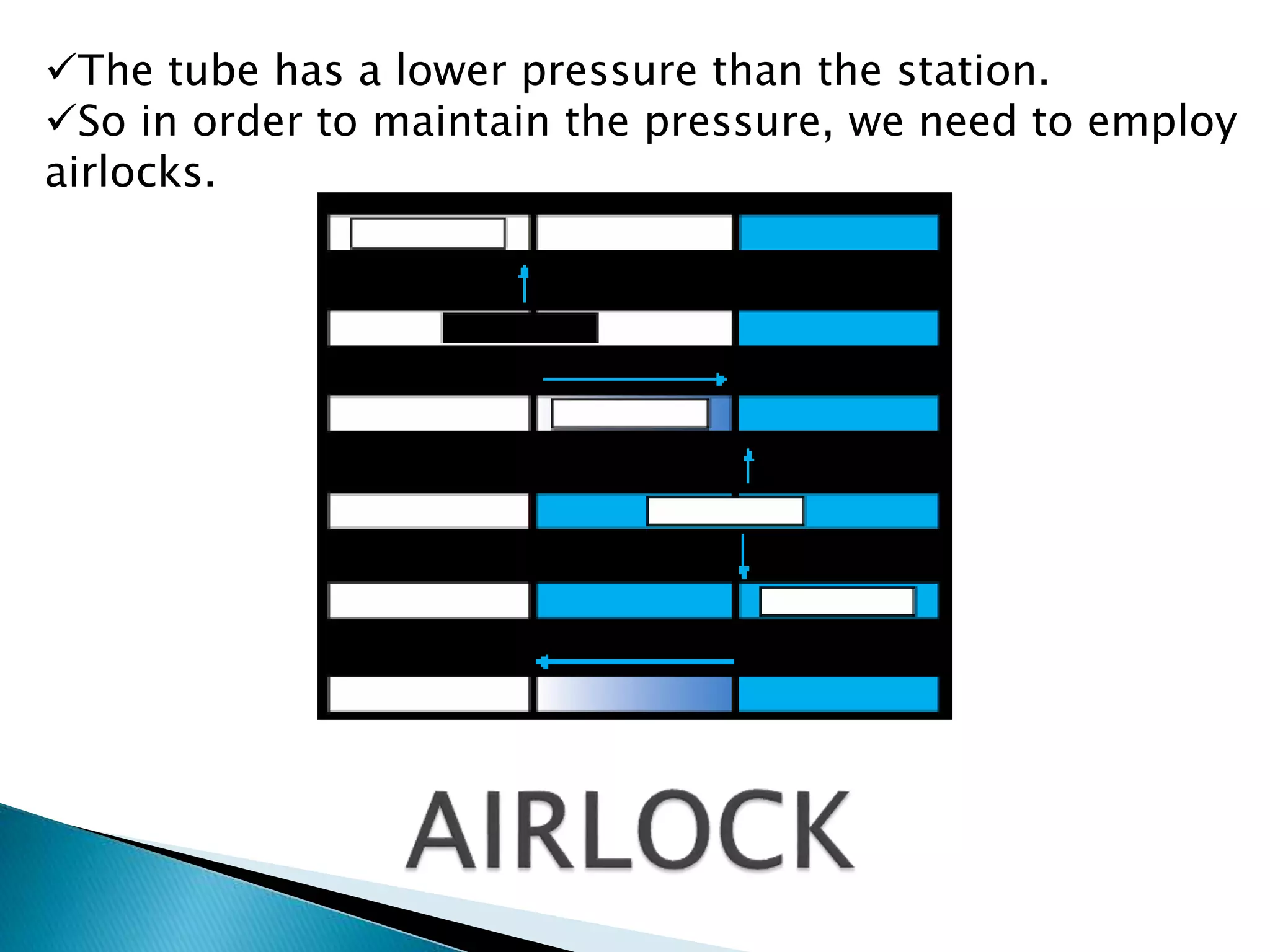
The document presents an overview of the Hyperloop transportation system. It describes Hyperloop as consisting of low pressure tubes that contain capsules transported at low and high speeds. The key components are the low pressure tube, capsule, electromagnetic launch system, axial compressor, and suspension. It discusses the technical aspects like tube pressure, capsule payload, and propulsion. The document concludes that Hyperloop has advantages of being faster, lower cost, and more sustainable than existing transportation while also having technical challenges to overcome.