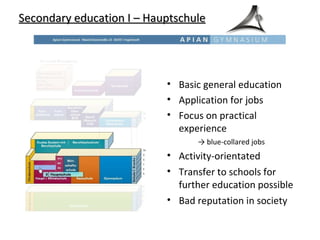
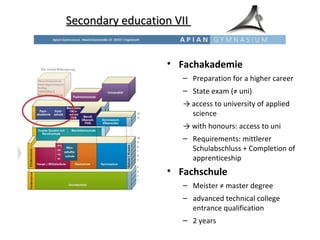
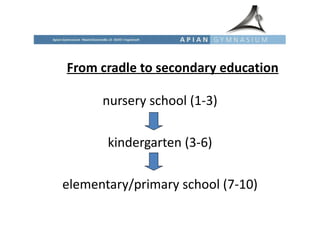
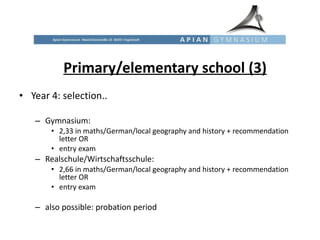
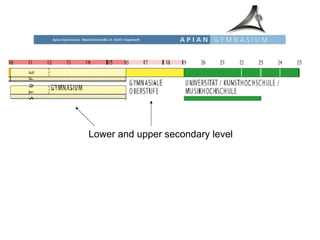
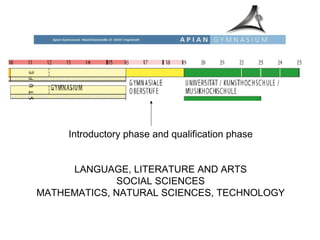
The educational system in Germany is tracked, with students sent to different secondary schools based on academic ability and interests. Primary education is from ages 6-10, after which students are recommended for Hauptschule (vocational), Realschule (intermediate), or Gymnasium (academic) tracks. Gymnasium is the most prestigious and leads to the Abitur exam and university eligibility. There are also vocational schools and dual apprenticeship programs. Tertiary education involves universities and Fachhochschulen (universities of applied sciences).