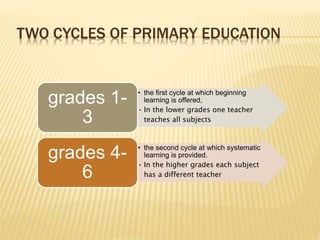
Compulsory education in Poland lasts 12 years, from ages 6 to 18. The educational system has three tiers: primary school, gymnasium, and secondary/higher education. Primary school lasts 6 years and ends with exams in science and arts. Gymnasium lasts 3 years and also ends with exams in science and arts. After completing primary and gymnasium education, students can choose to attend secondary schools providing vocational training or general education to prepare for university or further vocational education.



















![THIS PROJECT HAS BEEN FUNDED WITH SUPPORT FROM THE EUROPEAN
COMMISSION.
THIS PUBLICATION [COMMUNICATION] REFLECTS THE VIEWS ONLY OF THE
AUTHOR, AND THE COMMISSION CANNOT BE HELD RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY USE
WHICH MAY BE MADE OF THE INFORMATION CONTAINED THERE IN.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/educationalsystem-140919133553-phpapp02/85/Educational-system-21-320.jpg)
