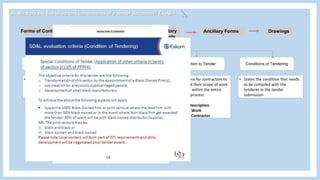
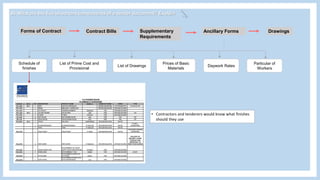
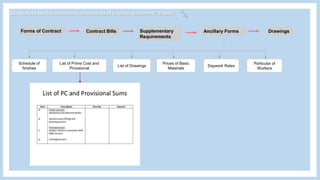
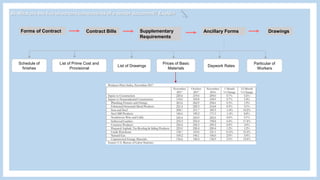
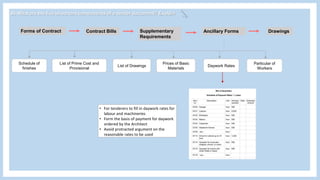
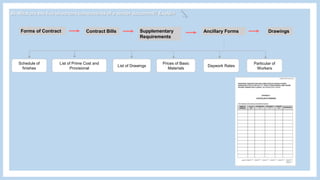
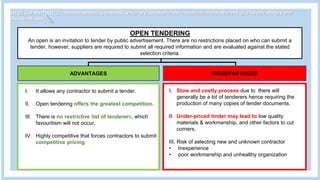
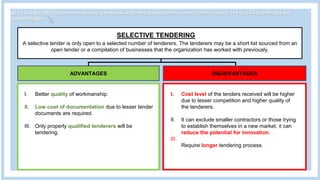
The document provides information about a group project for Professional Practice 1 and includes a tender document discussion. It lists the group members and the course information. It then answers two questions about tender documents. For the first question, it explains what a tender document is, its main purpose, and lists the five important components of a tender document. For the second question, it discusses the factors a construction firm's head of tender department would consider before deciding to participate in a tender for a 20-story condominium project in Kuala Lumpur, including the firm's capability, the project site, profitability, and risks.
![Group Members:
• Tan Kai Xuan (0325066)
• Tan Shen Sin (0324602)
• Tee Wan Nee (0325074)
• Teo Chiang Loong (0323762)
Professional Practice 1
QSB 60103
[ Tender Document / Tender Method/ Factors to consider before entering a tender ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pp1presentation2-180515043613/75/Pp1-presentation-2-1-2048.jpg)