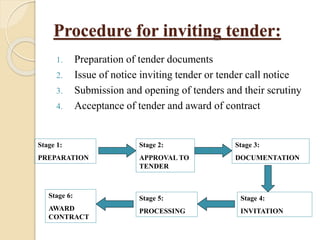
The document outlines the differences between tenders and contracts, defining tenders as formal invitations to execute work and contracts as agreements between parties. It details various classifications of tenders (open, sealed, limited, single, rate contracts) and procedures for inviting tenders, including required information in a tender notice. Additionally, it discusses earnest money deposits, liquidated and unliquidated damages, and classifications of contracts.