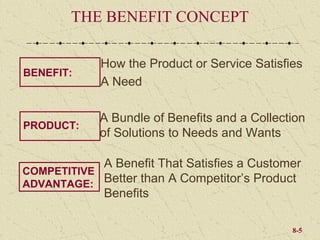
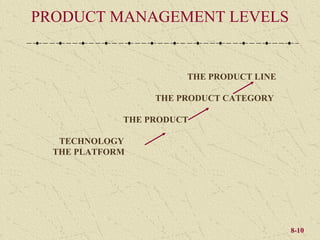
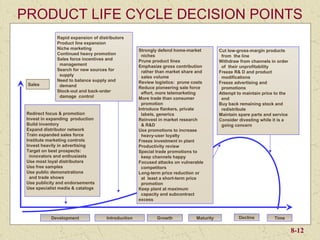
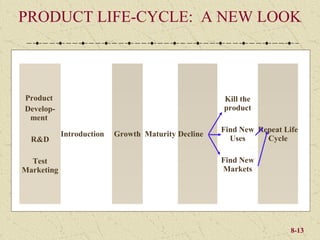
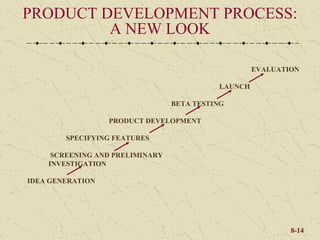
The document discusses product development and management tools used by businesses. It covers product life cycles, portfolio management matrices like the BCG Matrix and GE Matrix, and the product development process. Key decisions for product managers include which products to introduce, keep, promote, and delete or continue at different stages of the product life cycle. Developing products that satisfy customer needs and have a competitive advantage is important for business success.