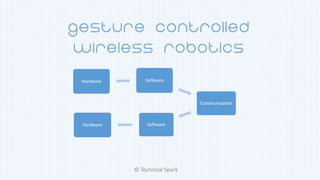
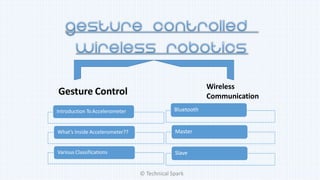
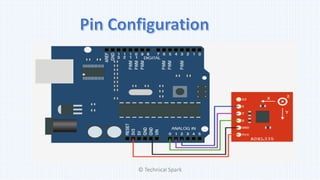
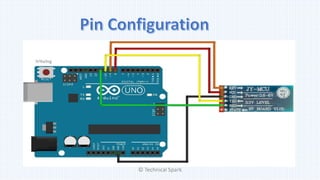
1) The document discusses different types of accelerometers, how they work, and their applications.
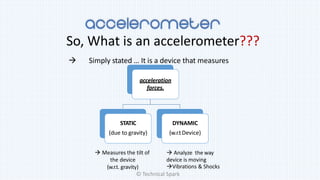
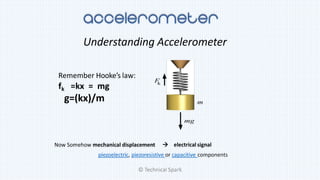
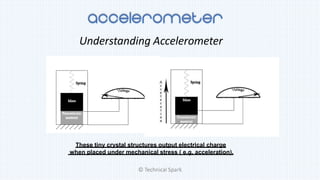
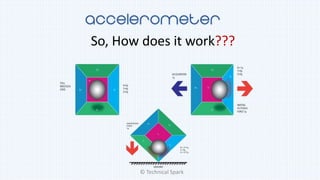
2) It explains that an accelerometer is a device that measures acceleration forces, both static forces due to gravity and dynamic forces with respect to device movement.
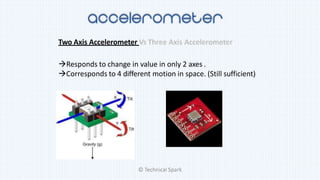
3) The document compares digital and analog accelerometers, as well as 2-axis and 3-axis models, and recommends using a 3-axis analog accelerometer for highest sensitivity and full motion detection.