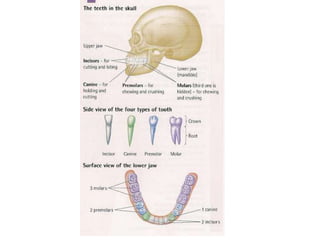
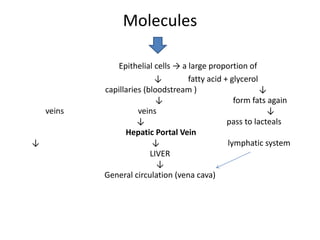
The document summarizes the human digestive system. It describes the stages of ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. Key parts of the digestive system discussed include the mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, and pancreas. The roles of enzymes and absorption through the small intestine walls are also summarized.