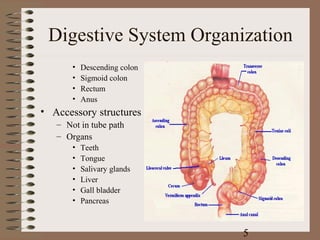
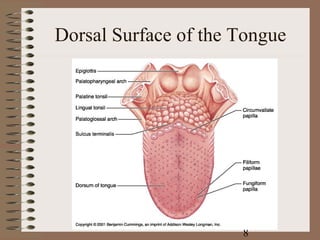
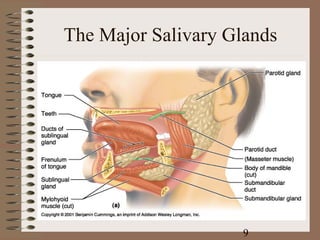
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the digestive system. It describes the mechanical and chemical digestion that occurs, the major organs involved including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, and pancreas. It explains the roles of these organs in ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination of waste. Accessory structures like teeth, salivary glands, and the gallbladder are also outlined.