The document provides an overview of the history and scope of psychology. It discusses:
1) Psychology's roots in philosophy and biology and Wilhelm Wundt creating the first psychology lab in 1879.
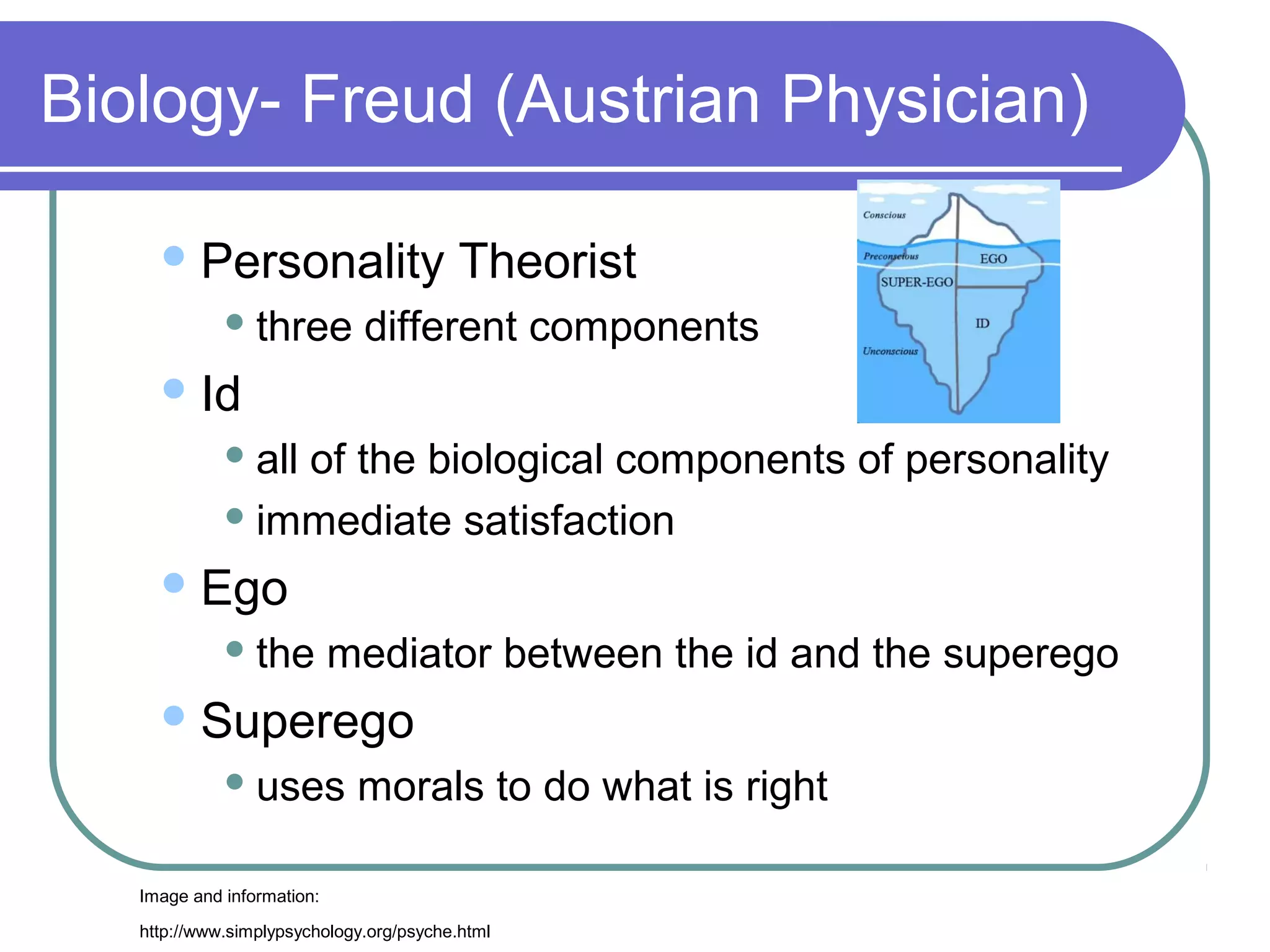
2) Key figures like Pavlov who discovered classical conditioning, Freud and his theories of personality, and Piaget's stages of cognitive development.
3) The four primary perspectives in psychology - behavioral, cognitive, neuroscience, and psychodynamic.
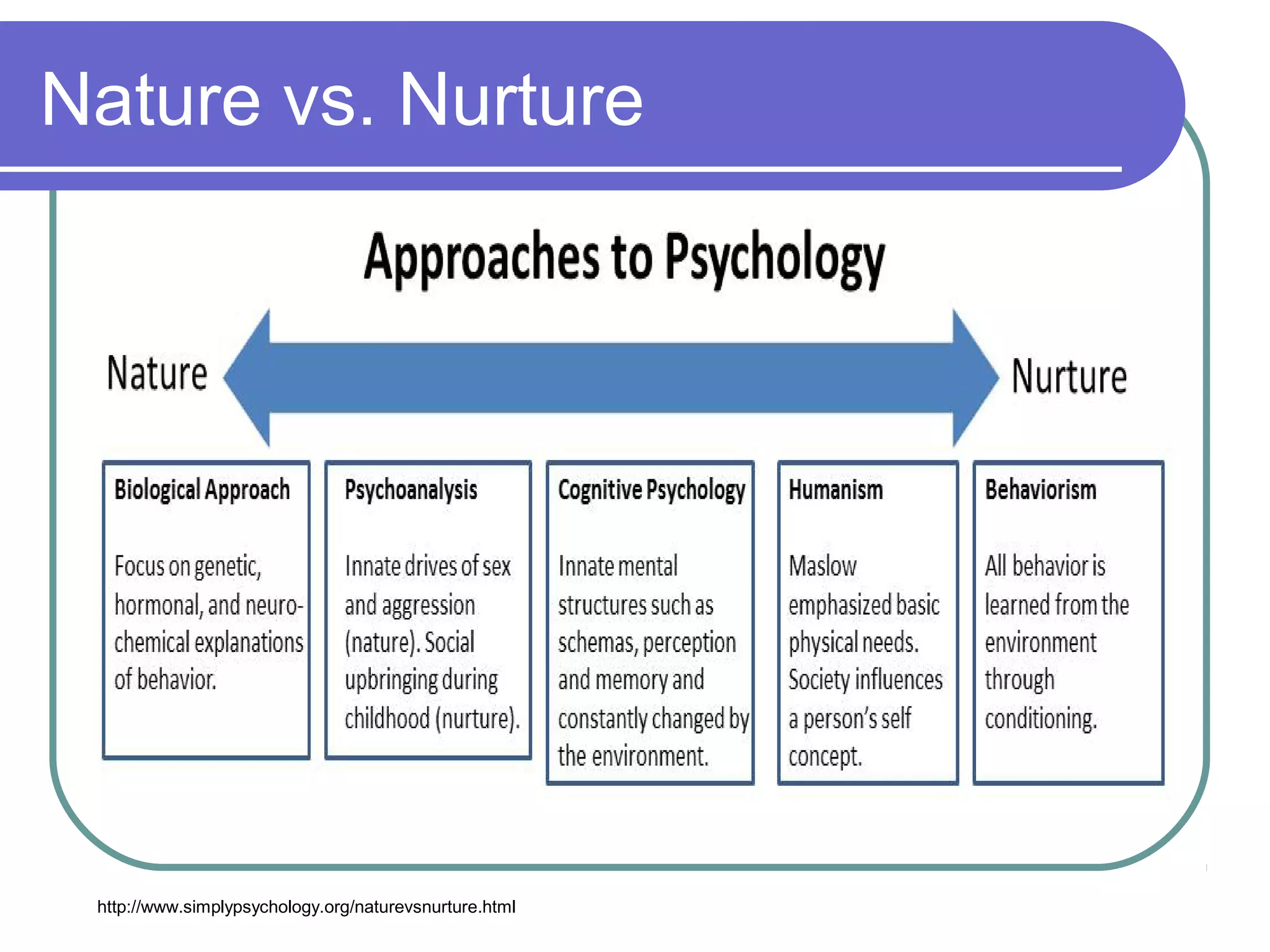
4) The big issue of nature vs nurture and major subfields like developmental, clinical, and industrial/organizational psychology.