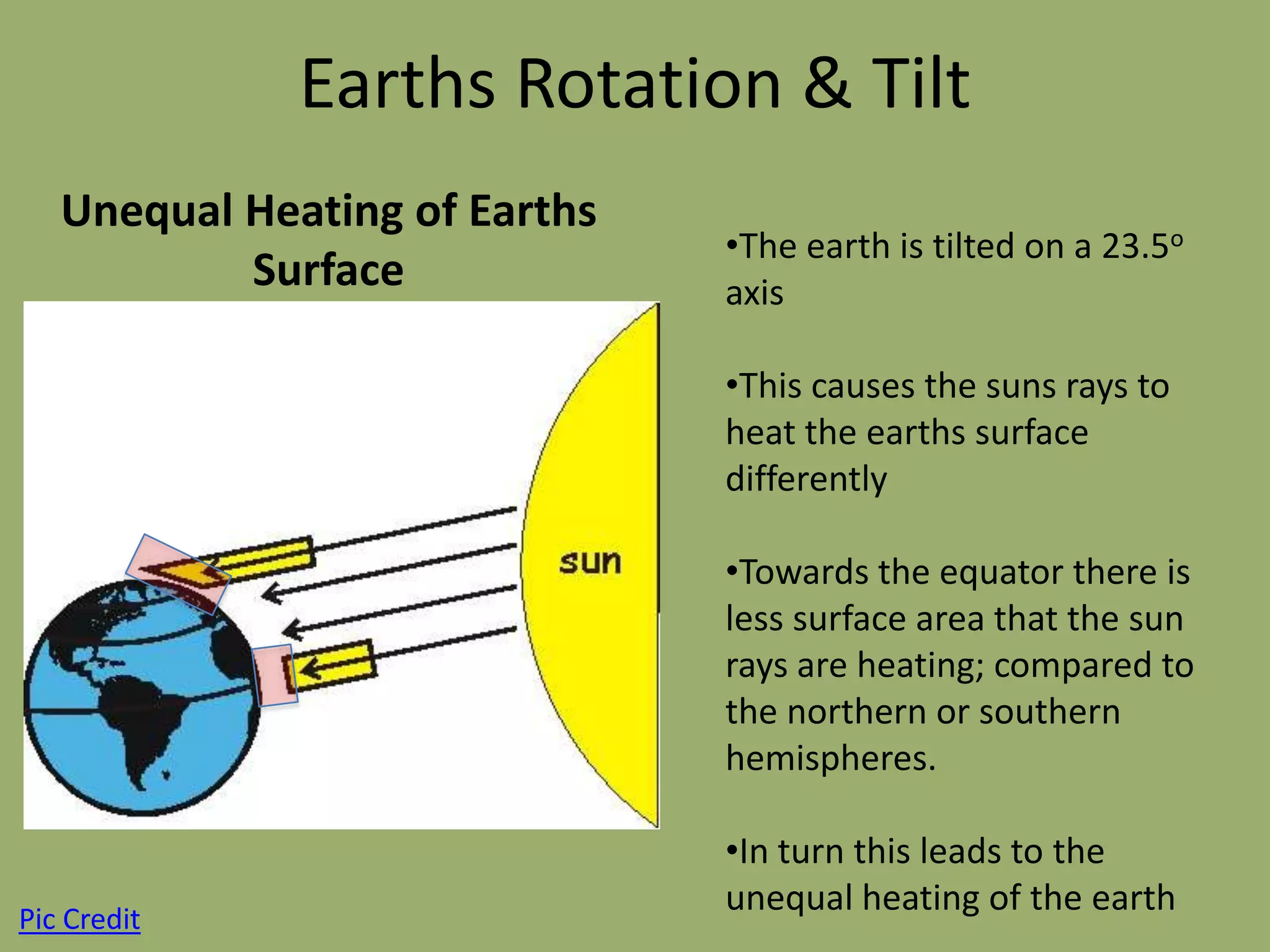
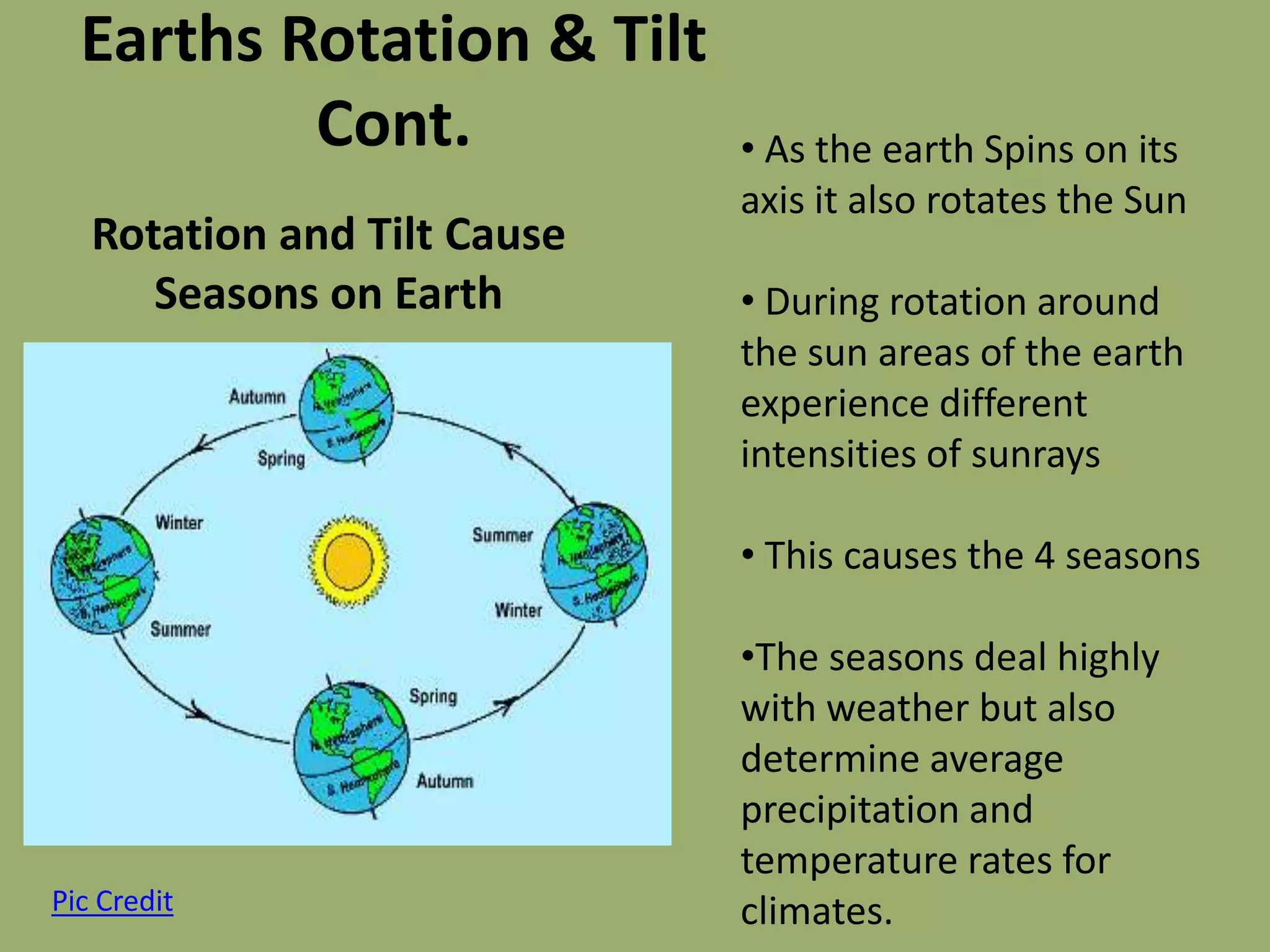
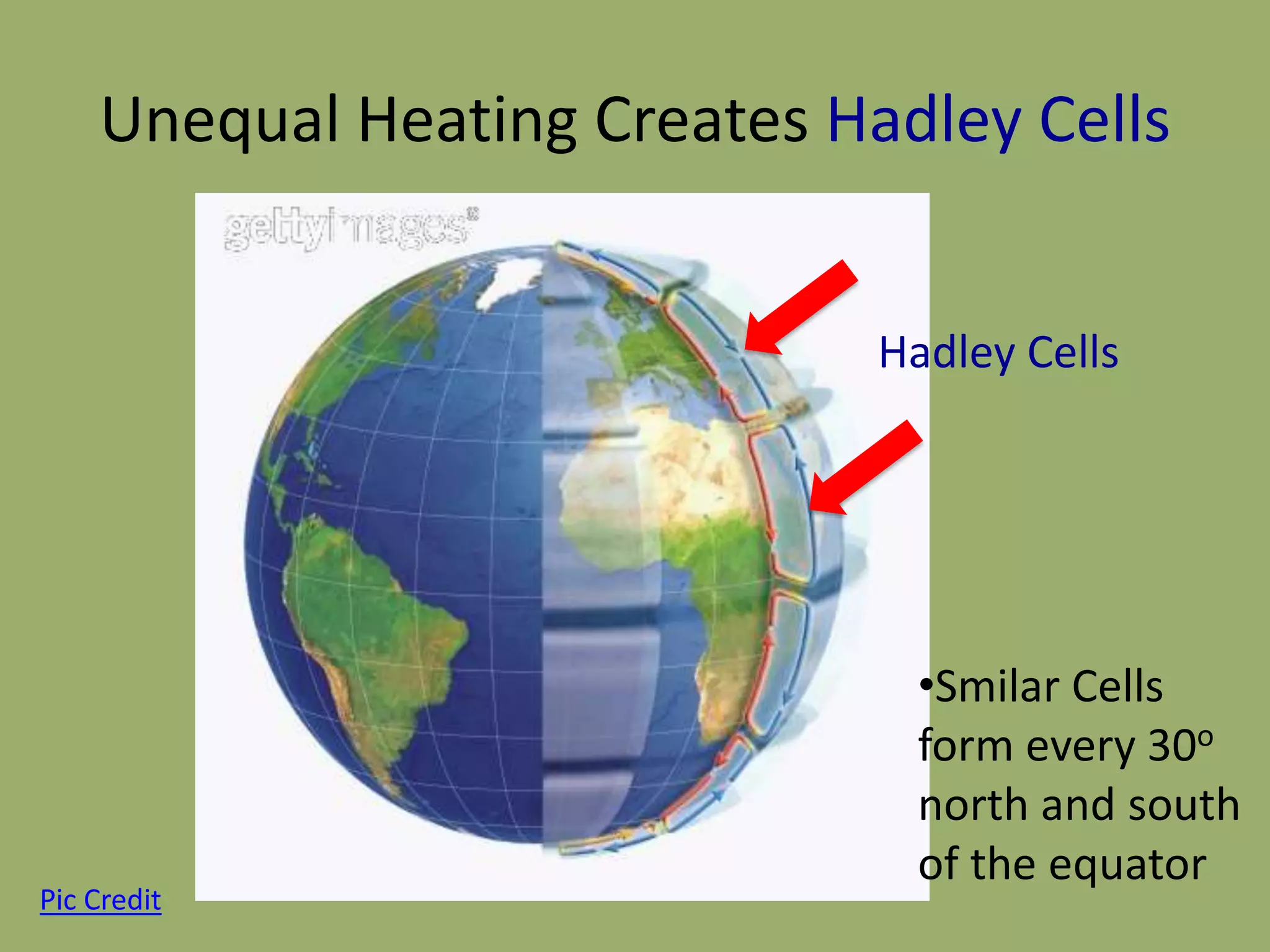
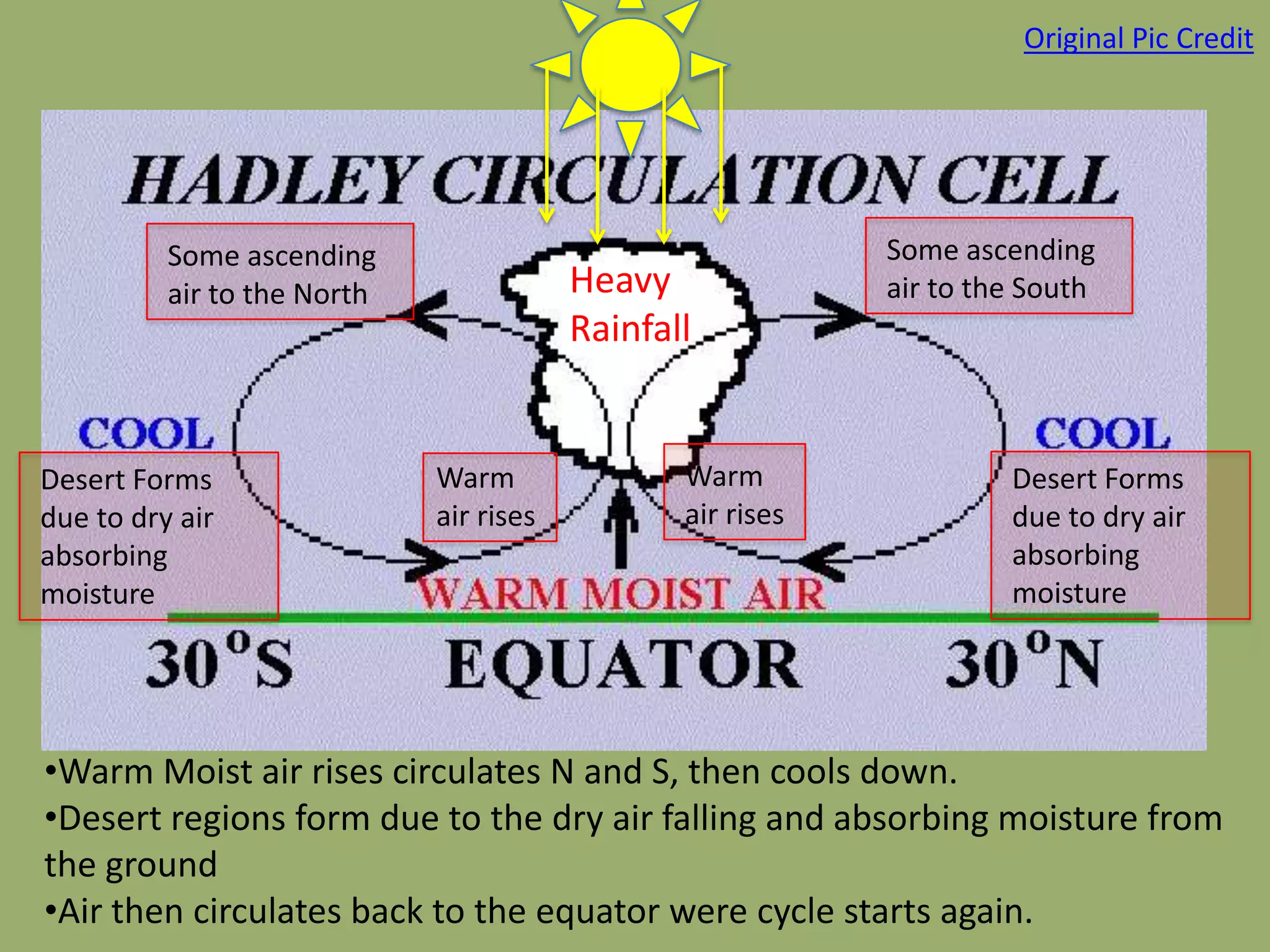
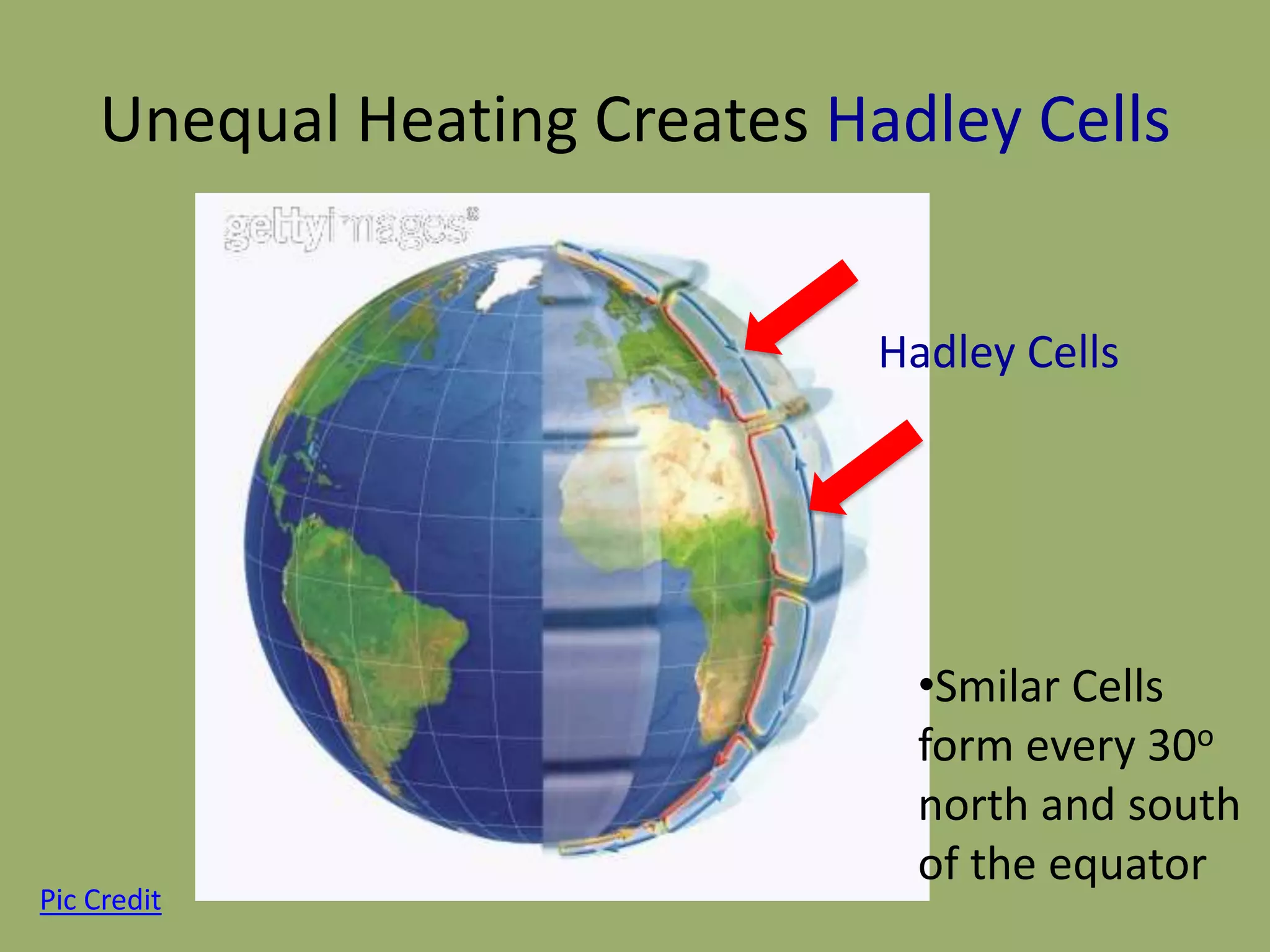
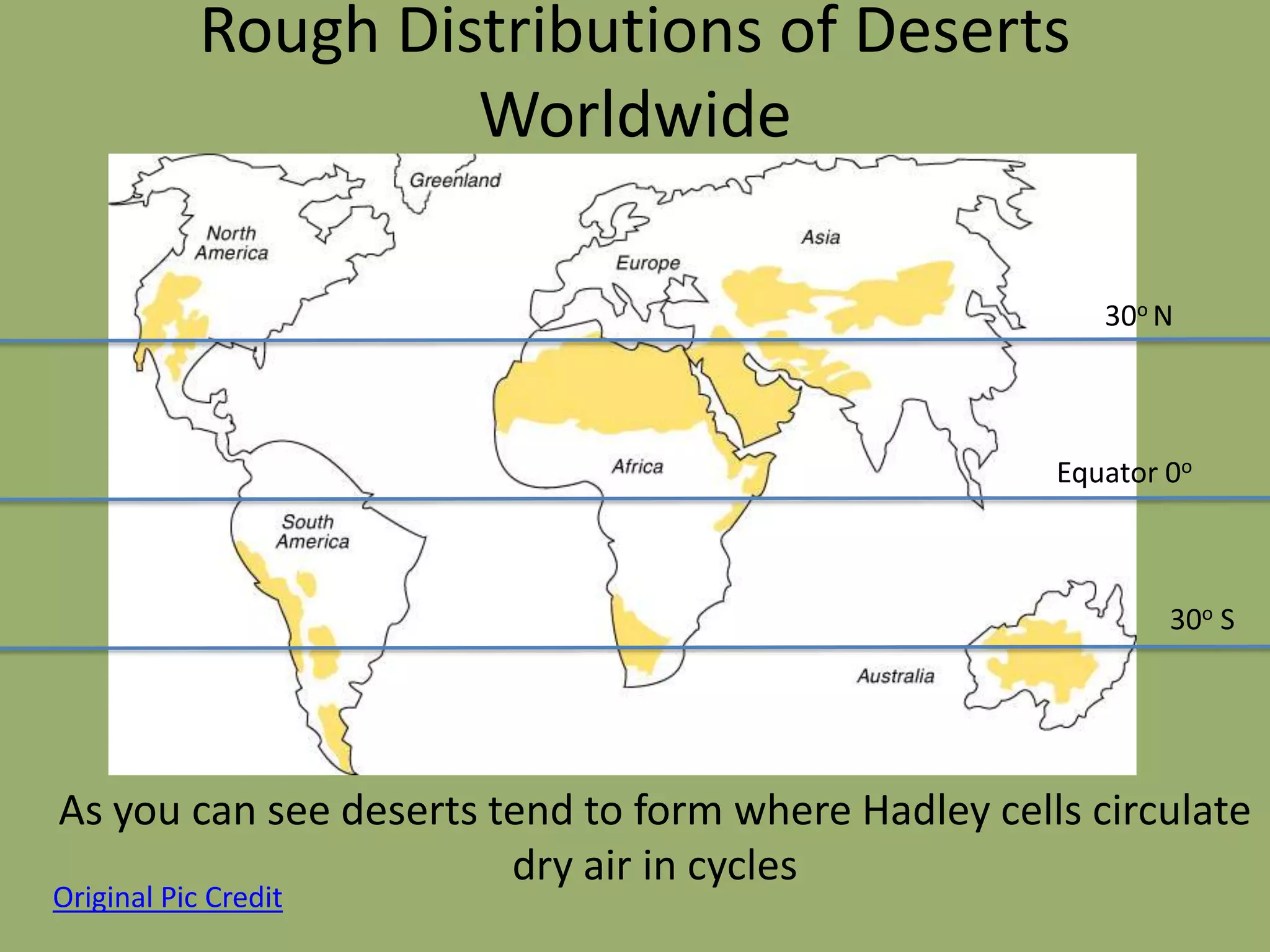
This document discusses the key factors that influence Earth's climates. It explains that climate refers to long-term weather patterns in an area, focusing on temperature and precipitation averages, while weather describes immediate atmospheric conditions. The document then discusses how Earth's rotation and axial tilt cause uneven heating of its surface and seasonal changes. This uneven heating drives atmospheric circulation cells called Hadley cells that help determine global climate zones. Roughly five major climate types - desert, tropical, polar, continental, and marine - form based on these atmospheric processes. Climates then influence the types of biomes that can exist in different regions of the planet.