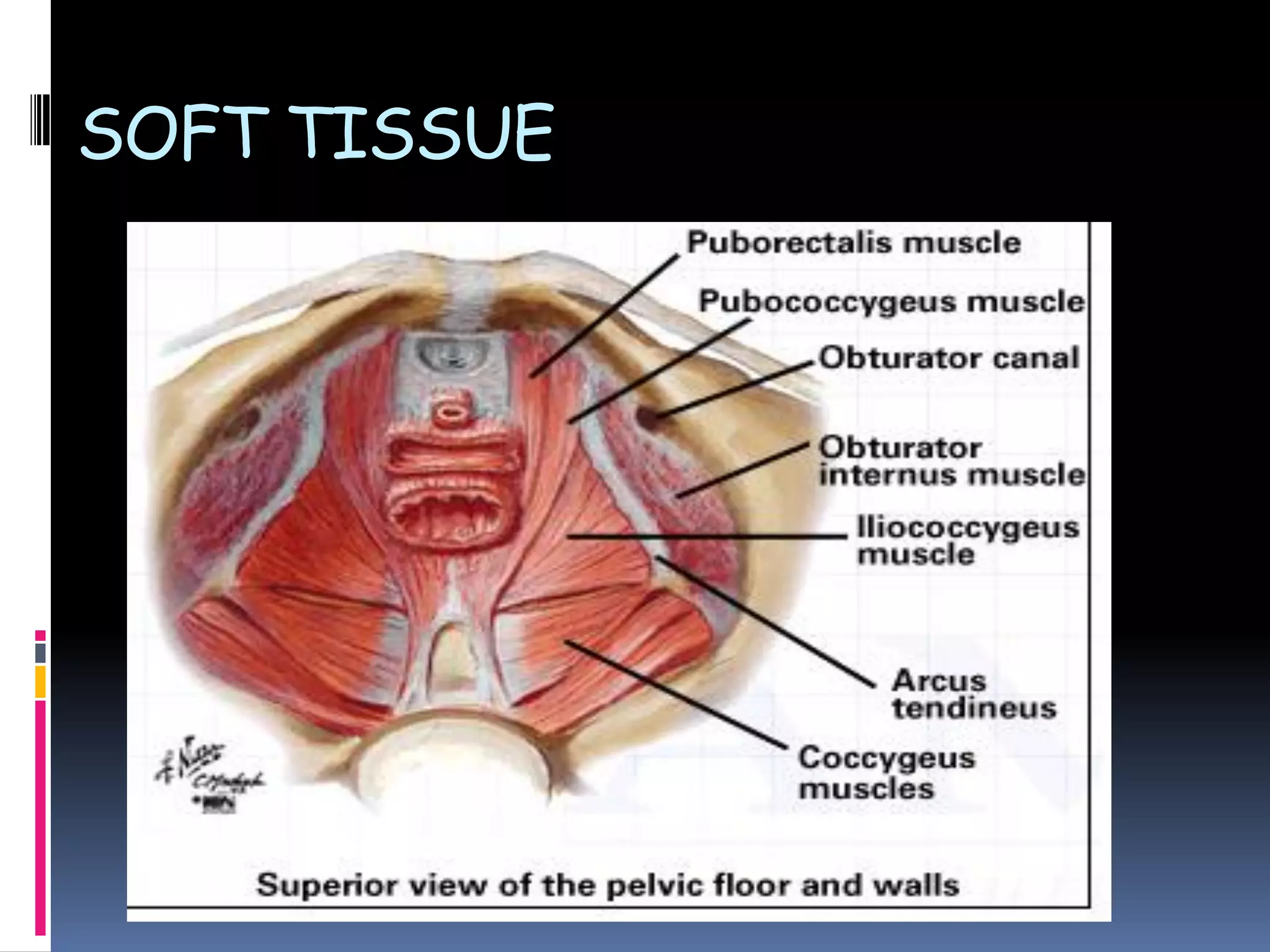
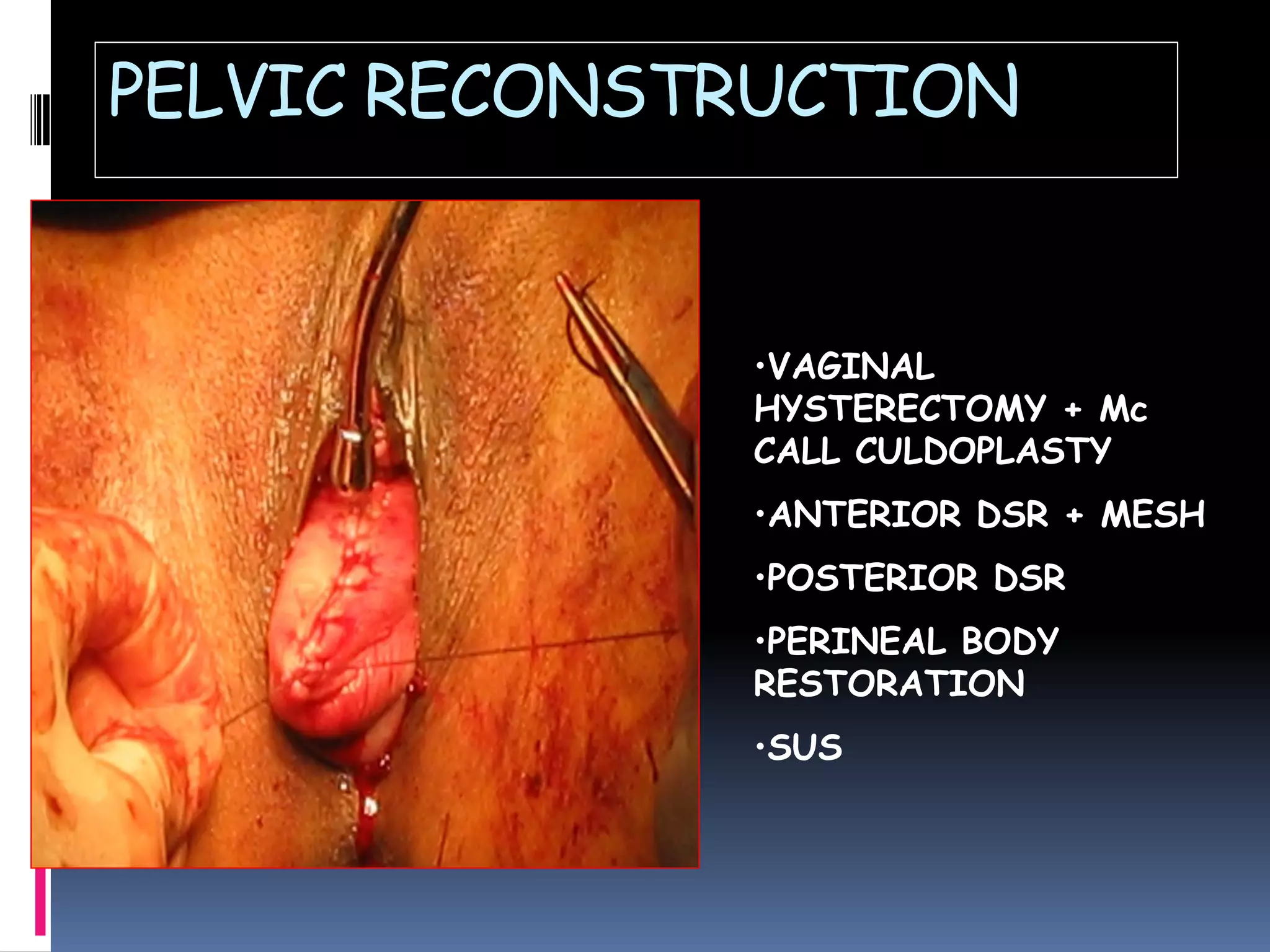
This document discusses various types of gynecological surgeries. It begins with an overview of pelvic anatomy and describes different surgical approaches including open, laparoscopic, vaginal, and robotic. Specific procedures covered include vulva surgeries like Bartholin cyst removal, hymenectomy, and vulvectomy. Vaginal procedures like anterior and posterior prolapse repair and vaginal hysterectomy are also outlined. The document then discusses cervical biopsies, colposcopies, and cerclage. Uterine conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, and cancers are reviewed along with their surgical management. Urinary incontinence procedures such as Burch colposuspension, slings, and inject