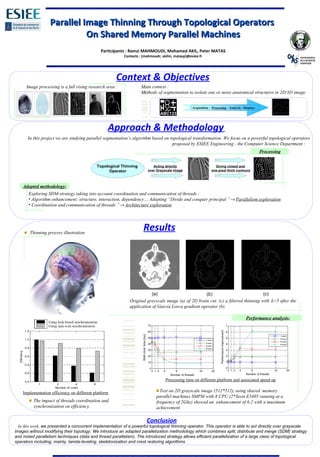
This document discusses parallelizing image thinning algorithms through topological operators on shared memory parallel machines. It presents an approach that combines split-distribute-merge strategy with mixed data and thread parallelism. The methodology was tested on 2D grayscale images using a shared memory machine with 8 CPUs. The results showed a 6.2x speedup with efficient parallel implementation.