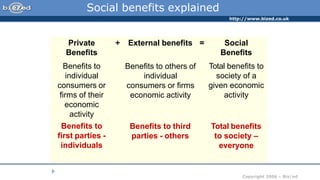
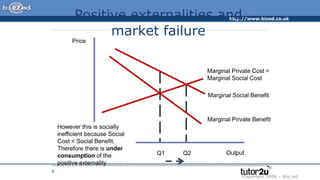
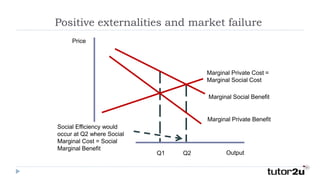
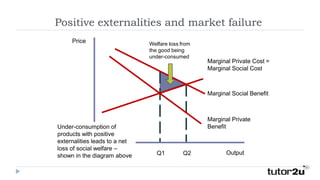
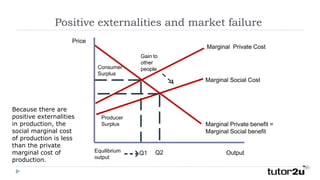
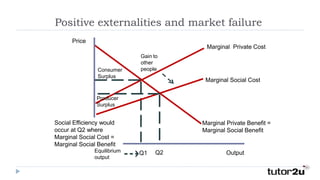
A positive externality occurs when consumption or production of a good provides a benefit to a third party. For example, getting a COVID-19 vaccine provides a private benefit of reduced susceptibility but also a social benefit of preventing community spread. A farmer growing apple trees provides a benefit to beekeepers through increased honey production. Positive externalities can lead to market inefficiency as the social benefit exceeds the private benefit, resulting in underconsumption or underproduction of goods providing external benefits.